filmov
tv
Using additive inverses to solve simple algebraic equations

Показать описание
Using additive inverses to solve simple algebraic equations
In this lesson you will learn to solve equations by using additive inverses.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.HSA-REI.A.1 Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method.
TEKS.7.11.A model and solve one-variable, two-step equations and inequalities;
TEKS.A1.5.A solve linear equations in one variable, including those for which the application of the distributive property is necessary and for which variables are included on both sides;
IN.AI.L.1 Understand that the steps taken when solving linear equations create new equations that have the same solution as the original. Solve fluently linear equations and inequalities in one variable with integers, fractions, and decimals as coefficients. Explain and justify each step in solving an equation, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Justify the choice of a solution method.
VA.EI.A.4.a multistep linear equations in one variable algebraically;
VA.PFA.8.17 The student will solve multistep linear equations in one variable with the variable on one or both sides of the equation, including practical problems that require the solution of a multistep linear equation in one variable.
FL.MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1 Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method.
In this lesson you will learn to solve equations by using additive inverses.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.HSA-REI.A.1 Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method.
TEKS.7.11.A model and solve one-variable, two-step equations and inequalities;
TEKS.A1.5.A solve linear equations in one variable, including those for which the application of the distributive property is necessary and for which variables are included on both sides;
IN.AI.L.1 Understand that the steps taken when solving linear equations create new equations that have the same solution as the original. Solve fluently linear equations and inequalities in one variable with integers, fractions, and decimals as coefficients. Explain and justify each step in solving an equation, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Justify the choice of a solution method.
VA.EI.A.4.a multistep linear equations in one variable algebraically;
VA.PFA.8.17 The student will solve multistep linear equations in one variable with the variable on one or both sides of the equation, including practical problems that require the solution of a multistep linear equation in one variable.
FL.MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1 Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method.
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:07:15
0:07:15
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:08:35
0:08:35
 0:07:15
0:07:15
 0:08:49
0:08:49
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:27
0:00:27
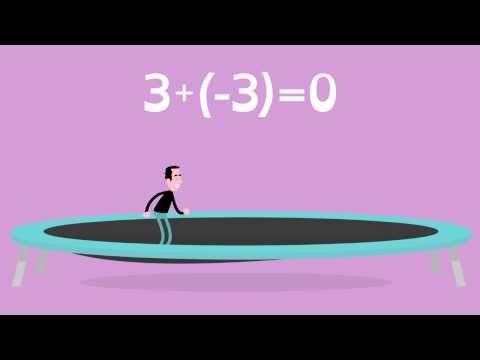 0:01:36
0:01:36
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:03:38
0:03:38
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:04:12
0:04:12