filmov
tv
Lipids Lecture 3 for Pharm D students 2 Nov 2024

Показать описание
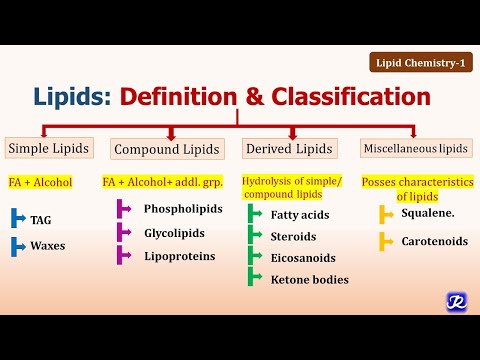
CASTOR OIL
OLIVE OIL
LINSEED OIL
SESAME OIL
CHAULMOOGRA OIL
CASTOR OIL
Synonyms
Oleum ricini, Ricinus oil.
Biological Source
It is a fixed oil which is obtained by cold expression of the seeds of the plant, Ricinus communis (family- Euphorbiaceae).
Location
Brazil, Thailand, United States of America, Romania and India (Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Chennai, West Bengal, Maharashtra and Karnataka). India ranks second in the world in the production of castor oil. In India, Andhra Pradesh produces about 60% of the total Indian production.
Cultivation and Method of Preparation
Plant Description
Castor is a monoecious herb which is cultivated yearly.
It consists of a circular, hollow, erect, reddish-brown stem marked with definite nodes, from where the leaves arise.
Leaves are petiolate, arranged alternately, palmate having 5-11 lobes, with serrate margins.
Inflorescence is present terminally in the bracts.
Fruits or capsules of the plant are covered with spines. Seeds present within the fruits are albuminous in nature and are derived from anatropous ovules. Embryo of seeds contain an oily endosperm.
Castor seeds are graded according to their sizes and are made free from any impurities like organic matter, sand, iron particles etc.
To obtain castor oil of medicinal value, seeds are decorticated i.e., their testa are removed.
This technique helps to improve the colour of the oil and also to control its acid value.
Decortication is achieved by passing the seeds between the rollers.
Seed kernels are then added to an oil-press and are subjected to a pressure of 2 tons/inch² under normal temperature conditions.
By doing so, about 30% of fixed oil present in the seeds can be obtained.
The oil is initially filtered and then exposed to steam at 80°-100°C. Steaming helps to remove the toxic protein termed ricin and the enzyme lipase which can hydrolyze the oil and render it rancid.
After steaming, the oil is filtered again.
The oil so obtained is known as cold drawn oil which is bleached and treated with sodium carbonate to get rid of free fatty acids.
Any impurities in the oil are removed by adsorption with activated charcoal.
Characteristics
Colour - Pale yellow to colourless
Odour - Slight and characteristic
Taste - Initially bland, then acrid and finally nauseating
State - Viscous liquid
Solubility
(a) It is the only fixed oil soluble in alcohol, due to the OH groups of ricinoleic acid.
(b) It is miscible in chloroform, petroleum ether and glacial acetic acid but insoluble in mineral oil,
Standards -
Specific gravity at 20°C: 0.945 to 0.965 g ,Acid value : NMT 2
Acetyl value: NMT 143, Iodine value: 82-90, Hydroxyl value: NLT 150
Saponification value: 176 to 187, Optical rotation : + 3.5 degrees to + 6.0 degrees
Solidifying point: - 10◦C to -18◦C ,Viscosity: 6-8 poise ,Refractive index: 1.4758 to 1.4798.
Chemical Constituents
1.Castor Seed
It consists of 75% kernel and 25% hull.
(b) In kernel, the oil content varies from 36 to 60%.
(c) Hull consists of minerals, alkaloid (ricinine), resin and pigments.
(d) Castor seeds contain enzymes like invertase, lipase and maltase.
2.Castor Oil
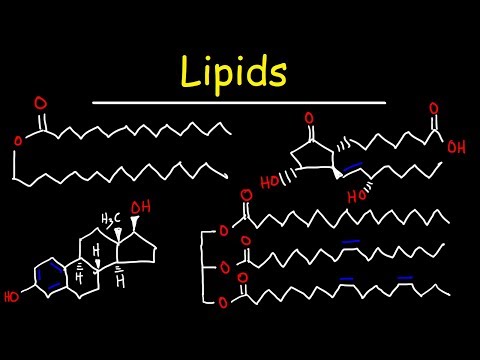
(a) The main active constituent of castor oil is 80% triglycerides of ricinoleic acid (C19H34O3) responsible for viscosity and purgative action of castor oil.
(b) Castor oil also contains other triglycerides of isoricinoleic acid, linoleic acid, stearic acid and isostearic acid
(c) It contains heptanal, undecenoic acid and sebacic acid.
(d) It also contains hair growth vitamin.
Uses
1.It has mild purgative or aperient action as ricinoleic acid irritates the intestinal mucosa and enhances the motility of colon.
2.It is administered in food poisoning.
3.Products obtained from castor oil like undecyenic acid is used as a fungicide.
4.It is used in the manufacture of soaps and detergents. is used in the preparation of varnishes, enamel, grease, polish and printing ink
5.Ricinoleic acid is an important constituent of spermicidal creams and jellies.
6.Ricinoleic acid is used as an abortifacient.
7.It is used as an emollient due to its moisturizing property.
OLIVE OIL
Synonyms
Oleum olivac, Sweet oil, Salad oil.
Biological Source
It is a fixed oil obtained by expressing the pericarp of the ripe fruits of the plant Olea europaea (family-Oleaceae).
Location
Palestine, USA, Australia, Italy, Spain, Greece, Turkey, Tunisia, Morocco and Syria.
Method of Preparation
Olives are collected during the months of December to April, a time when the fruits change from green to purple and the volatile oil begins to accumulate in the mesocarp.
Fruits are collected either by shaking and beating the trees or by means of a ladder.
The entire fruit consist of 20-30% olive oil, while the mesocarp (fruit pulp) alone consists of 60-80% of oil.
OLIVE OIL
LINSEED OIL
SESAME OIL
CHAULMOOGRA OIL
CASTOR OIL
Synonyms
Oleum ricini, Ricinus oil.
Biological Source
It is a fixed oil which is obtained by cold expression of the seeds of the plant, Ricinus communis (family- Euphorbiaceae).
Location
Brazil, Thailand, United States of America, Romania and India (Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Chennai, West Bengal, Maharashtra and Karnataka). India ranks second in the world in the production of castor oil. In India, Andhra Pradesh produces about 60% of the total Indian production.
Cultivation and Method of Preparation
Plant Description
Castor is a monoecious herb which is cultivated yearly.
It consists of a circular, hollow, erect, reddish-brown stem marked with definite nodes, from where the leaves arise.
Leaves are petiolate, arranged alternately, palmate having 5-11 lobes, with serrate margins.
Inflorescence is present terminally in the bracts.
Fruits or capsules of the plant are covered with spines. Seeds present within the fruits are albuminous in nature and are derived from anatropous ovules. Embryo of seeds contain an oily endosperm.
Castor seeds are graded according to their sizes and are made free from any impurities like organic matter, sand, iron particles etc.
To obtain castor oil of medicinal value, seeds are decorticated i.e., their testa are removed.
This technique helps to improve the colour of the oil and also to control its acid value.
Decortication is achieved by passing the seeds between the rollers.
Seed kernels are then added to an oil-press and are subjected to a pressure of 2 tons/inch² under normal temperature conditions.
By doing so, about 30% of fixed oil present in the seeds can be obtained.
The oil is initially filtered and then exposed to steam at 80°-100°C. Steaming helps to remove the toxic protein termed ricin and the enzyme lipase which can hydrolyze the oil and render it rancid.
After steaming, the oil is filtered again.
The oil so obtained is known as cold drawn oil which is bleached and treated with sodium carbonate to get rid of free fatty acids.
Any impurities in the oil are removed by adsorption with activated charcoal.
Characteristics
Colour - Pale yellow to colourless
Odour - Slight and characteristic
Taste - Initially bland, then acrid and finally nauseating
State - Viscous liquid
Solubility
(a) It is the only fixed oil soluble in alcohol, due to the OH groups of ricinoleic acid.
(b) It is miscible in chloroform, petroleum ether and glacial acetic acid but insoluble in mineral oil,
Standards -
Specific gravity at 20°C: 0.945 to 0.965 g ,Acid value : NMT 2
Acetyl value: NMT 143, Iodine value: 82-90, Hydroxyl value: NLT 150
Saponification value: 176 to 187, Optical rotation : + 3.5 degrees to + 6.0 degrees
Solidifying point: - 10◦C to -18◦C ,Viscosity: 6-8 poise ,Refractive index: 1.4758 to 1.4798.
Chemical Constituents
1.Castor Seed
It consists of 75% kernel and 25% hull.
(b) In kernel, the oil content varies from 36 to 60%.
(c) Hull consists of minerals, alkaloid (ricinine), resin and pigments.
(d) Castor seeds contain enzymes like invertase, lipase and maltase.
2.Castor Oil
(a) The main active constituent of castor oil is 80% triglycerides of ricinoleic acid (C19H34O3) responsible for viscosity and purgative action of castor oil.
(b) Castor oil also contains other triglycerides of isoricinoleic acid, linoleic acid, stearic acid and isostearic acid
(c) It contains heptanal, undecenoic acid and sebacic acid.
(d) It also contains hair growth vitamin.
Uses
1.It has mild purgative or aperient action as ricinoleic acid irritates the intestinal mucosa and enhances the motility of colon.
2.It is administered in food poisoning.
3.Products obtained from castor oil like undecyenic acid is used as a fungicide.
4.It is used in the manufacture of soaps and detergents. is used in the preparation of varnishes, enamel, grease, polish and printing ink
5.Ricinoleic acid is an important constituent of spermicidal creams and jellies.
6.Ricinoleic acid is used as an abortifacient.
7.It is used as an emollient due to its moisturizing property.
OLIVE OIL
Synonyms
Oleum olivac, Sweet oil, Salad oil.
Biological Source
It is a fixed oil obtained by expressing the pericarp of the ripe fruits of the plant Olea europaea (family-Oleaceae).
Location
Palestine, USA, Australia, Italy, Spain, Greece, Turkey, Tunisia, Morocco and Syria.
Method of Preparation
Olives are collected during the months of December to April, a time when the fruits change from green to purple and the volatile oil begins to accumulate in the mesocarp.
Fruits are collected either by shaking and beating the trees or by means of a ladder.
The entire fruit consist of 20-30% olive oil, while the mesocarp (fruit pulp) alone consists of 60-80% of oil.
 0:14:26
0:14:26
 0:06:10
0:06:10
 0:33:39
0:33:39
 0:17:04
0:17:04
 0:22:48
0:22:48
 0:17:36
0:17:36
 0:31:04
0:31:04
 0:06:19
0:06:19
 0:22:05
0:22:05
 0:47:06
0:47:06
 0:41:03
0:41:03
 1:22:54
1:22:54
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:38:21
0:38:21
 0:41:52
0:41:52
 0:29:09
0:29:09
 0:26:53
0:26:53
 0:54:14
0:54:14
 0:10:06
0:10:06
 0:10:17
0:10:17
 0:16:51
0:16:51
 0:12:07
0:12:07
 0:17:20
0:17:20
 0:38:36
0:38:36