filmov
tv
Muslim Countries GDP Nominal 1960 to 2028

Показать описание
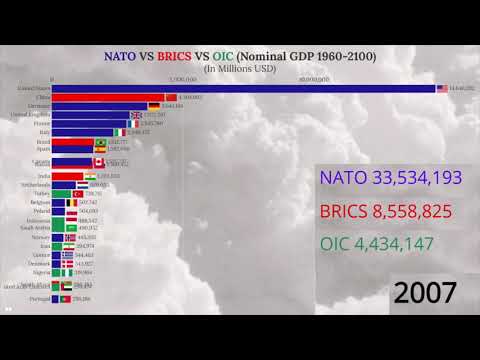
This List based on OIC members (The Organization of Islamic Cooperation). The Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is an international organization founded in 1969, currently comprising 57 member states, all of which have a significant Muslim population. These member economies span across four continents, including countries in the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and Europe. One of the key indicators used to gauge the economic strength and development of these member states is their Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which measures the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders over a specified period, typically annually. Examining the GDP of OIC member economies provides valuable insights into their economic performance, challenges, and opportunities.
The GDP of OIC member economies varies significantly, reflecting the diverse economic landscapes and levels of development across these countries. At one end of the spectrum are oil-rich nations like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Kuwait, whose economies are heavily dependent on petroleum exports. These countries typically boast substantial GDP figures due to their vast oil reserves and high levels of production. For instance, Saudi Arabia, the largest economy in the OIC, has consistently maintained a significant GDP primarily driven by its oil exports and robust government spending on infrastructure and development projects.
On the other hand, several OIC member economies face challenges related to economic diversification, infrastructure development, and political instability, which impact their GDP growth rates. Countries like Afghanistan, Somalia, and Yemen struggle with conflict, political instability, and humanitarian crises, severely hindering their economic growth and development. As a result, their GDP figures are comparatively low, reflecting the adverse impact of prolonged conflicts and instability on their economies. Despite international aid efforts and occasional spurts of growth, these nations continue to face significant economic hurdles.
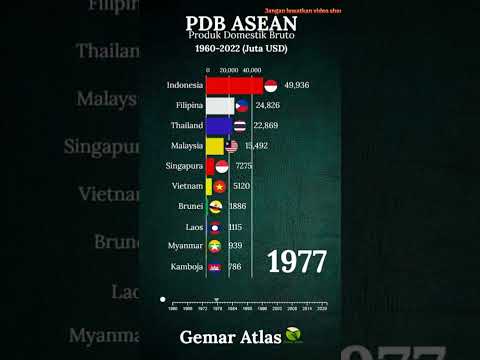
Beyond oil-rich nations and conflict-affected states, there exists a diverse array of OIC member economies with varying levels of GDP and economic development. Malaysia and Indonesia, for example, are notable emerging economies within the OIC, characterized by vibrant manufacturing sectors, natural resource wealth, and increasingly diversified economies. Both countries have experienced robust GDP growth rates in recent years, supported by prudent economic policies, investment in infrastructure, and efforts to attract foreign investment. Malaysia, in particular, has successfully transitioned into a knowledge-based economy, leveraging technology and innovation to drive growth and productivity.
In addition to individual country dynamics, OIC member economies also face common challenges that impact their collective economic performance. These challenges include demographic pressures, youth unemployment, income inequality, and the need for economic diversification away from oil dependency. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts at both the national and regional levels, with a focus on enhancing education and skills development, promoting entrepreneurship and innovation, and fostering inclusive economic growth. Moreover, strengthening economic cooperation and integration among OIC member states can unlock synergies, facilitate trade and investment flows, and stimulate economic development across the Islamic world.
Bar Chart Race:
A bar chart race is a dynamic visualization technique used to display changes in data over time in a visually engaging manner. Unlike static bar charts, which only show a snapshot of data at a single point in time, a bar chart race animates the bars representing different categories or variables as they evolve over a specified time period. This animation creates a compelling narrative that allows viewers to observe trends, patterns, and fluctuations in the data as they unfold chronologically.
The primary components of a bar chart race typically include a horizontal or vertical axis representing the categories or variables being measured, such as countries, companies, products, or demographic groups. The length or height of each bar corresponds to the magnitude or value of the data point for that category at a given time. As the animation progresses, the bars move, grow, or shrink to reflect changes in the data, providing a dynamic representation of how the rankings or values of the categories shift over time.
#economy #barchartrace #muslim
The GDP of OIC member economies varies significantly, reflecting the diverse economic landscapes and levels of development across these countries. At one end of the spectrum are oil-rich nations like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Kuwait, whose economies are heavily dependent on petroleum exports. These countries typically boast substantial GDP figures due to their vast oil reserves and high levels of production. For instance, Saudi Arabia, the largest economy in the OIC, has consistently maintained a significant GDP primarily driven by its oil exports and robust government spending on infrastructure and development projects.
On the other hand, several OIC member economies face challenges related to economic diversification, infrastructure development, and political instability, which impact their GDP growth rates. Countries like Afghanistan, Somalia, and Yemen struggle with conflict, political instability, and humanitarian crises, severely hindering their economic growth and development. As a result, their GDP figures are comparatively low, reflecting the adverse impact of prolonged conflicts and instability on their economies. Despite international aid efforts and occasional spurts of growth, these nations continue to face significant economic hurdles.
Beyond oil-rich nations and conflict-affected states, there exists a diverse array of OIC member economies with varying levels of GDP and economic development. Malaysia and Indonesia, for example, are notable emerging economies within the OIC, characterized by vibrant manufacturing sectors, natural resource wealth, and increasingly diversified economies. Both countries have experienced robust GDP growth rates in recent years, supported by prudent economic policies, investment in infrastructure, and efforts to attract foreign investment. Malaysia, in particular, has successfully transitioned into a knowledge-based economy, leveraging technology and innovation to drive growth and productivity.
In addition to individual country dynamics, OIC member economies also face common challenges that impact their collective economic performance. These challenges include demographic pressures, youth unemployment, income inequality, and the need for economic diversification away from oil dependency. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts at both the national and regional levels, with a focus on enhancing education and skills development, promoting entrepreneurship and innovation, and fostering inclusive economic growth. Moreover, strengthening economic cooperation and integration among OIC member states can unlock synergies, facilitate trade and investment flows, and stimulate economic development across the Islamic world.
Bar Chart Race:
A bar chart race is a dynamic visualization technique used to display changes in data over time in a visually engaging manner. Unlike static bar charts, which only show a snapshot of data at a single point in time, a bar chart race animates the bars representing different categories or variables as they evolve over a specified time period. This animation creates a compelling narrative that allows viewers to observe trends, patterns, and fluctuations in the data as they unfold chronologically.
The primary components of a bar chart race typically include a horizontal or vertical axis representing the categories or variables being measured, such as countries, companies, products, or demographic groups. The length or height of each bar corresponds to the magnitude or value of the data point for that category at a given time. As the animation progresses, the bars move, grow, or shrink to reflect changes in the data, providing a dynamic representation of how the rankings or values of the categories shift over time.
#economy #barchartrace #muslim
Комментарии
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:20:01
0:20:01
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:07:19
0:07:19
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:00:18
0:00:18