filmov
tv
cytoskeleton|#microtubules #microfilaments #actin #filaments #intermediate #filaments #Intermediate

Показать описание
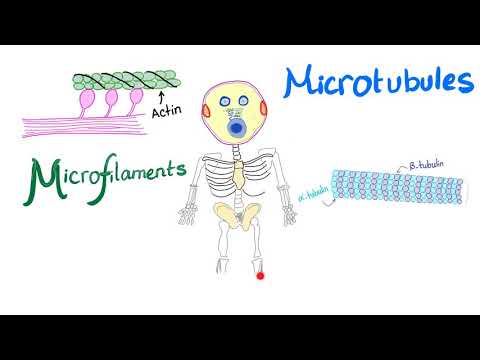
The #cytoskeleton is a #complex network of protein #filaments that provides structural #support and enables various cellular functions in eukaryotic cells. It is composed of three main types of filaments: #microtubules, #microfilaments (#actin f#ilaments), and #intermediate filaments.
1. Microtubules: #Microtubules are hollow, tubular structures composed of a protein called #tubulin. They have a dynamic structure and play crucial roles in several cellular processes, including:
- #Cell #Shape and Support: Microtubules maintain cell shape and provide mechanical support to the cell.
- Intracellular T#ransport: They serve as tracks for the transport of organelles, vesicles, and other cellular components.
- #Cell #Division: #Microtubules form the mitotic spindle during cell division, facilitating the separation of chromosomes.
- Cilia and Flagella: Microtubules form the core structure of cilia and flagella, which are involved in cell motility and sensory functions.
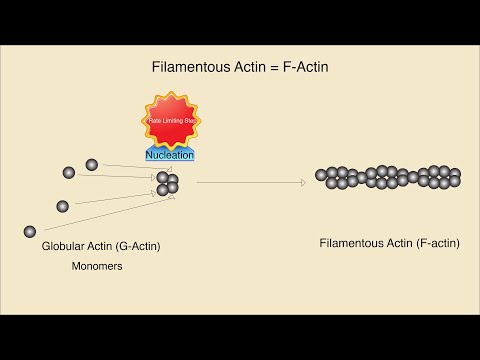
2. Microfilaments (#Actin Filaments): #Microfilaments are thin, flexible filaments composed of actin protein #subunits. They participate in various #cellular #processes, including:
- Cell #Motility: Microfilaments enable cell crawling, contraction, and amoeboid movement.
- #Cell #Shape and #Structure: Actin #filaments help maintain cell shape and provide mechanical support.
- Cell Division: They play a role in #cytokinesis, the process of cell division, by forming the contractile ring.
- Intracellular Transport: Microfilaments are involved in the movement of vesicles within the cell.
3. #Intermediate @Filaments# Intermediate filaments are fibrous proteins that provide mechanical strength to cells. They are more stable than microtubules and microfilaments. The specific functions of intermediate filaments include:
- Cell #Structure and Integrity: Intermediate #filaments help maintain cell shape and provide structural support.
- #Tissue #Integrity: They contribute to the structural integrity of tissues, such as the epidermis and the muscles.
- #Nuclear #Anchorage: Intermediate filaments anchor the #nucleus within the cell.
Overall, the cytoskeleton is crucial for maintaining cell shape, providing mechanical support, #facilitating cellular movement, and organizing intracellular components. The dynamic #nature of the #cytoskeleton allows cells to respond to various stimuli, adapt to changes, and perform #essential functions necessary for cell survival and proper #functioning.
1. Microtubules: #Microtubules are hollow, tubular structures composed of a protein called #tubulin. They have a dynamic structure and play crucial roles in several cellular processes, including:
- #Cell #Shape and Support: Microtubules maintain cell shape and provide mechanical support to the cell.
- Intracellular T#ransport: They serve as tracks for the transport of organelles, vesicles, and other cellular components.
- #Cell #Division: #Microtubules form the mitotic spindle during cell division, facilitating the separation of chromosomes.
- Cilia and Flagella: Microtubules form the core structure of cilia and flagella, which are involved in cell motility and sensory functions.
2. Microfilaments (#Actin Filaments): #Microfilaments are thin, flexible filaments composed of actin protein #subunits. They participate in various #cellular #processes, including:
- Cell #Motility: Microfilaments enable cell crawling, contraction, and amoeboid movement.
- #Cell #Shape and #Structure: Actin #filaments help maintain cell shape and provide mechanical support.
- Cell Division: They play a role in #cytokinesis, the process of cell division, by forming the contractile ring.
- Intracellular Transport: Microfilaments are involved in the movement of vesicles within the cell.
3. #Intermediate @Filaments# Intermediate filaments are fibrous proteins that provide mechanical strength to cells. They are more stable than microtubules and microfilaments. The specific functions of intermediate filaments include:
- Cell #Structure and Integrity: Intermediate #filaments help maintain cell shape and provide structural support.
- #Tissue #Integrity: They contribute to the structural integrity of tissues, such as the epidermis and the muscles.
- #Nuclear #Anchorage: Intermediate filaments anchor the #nucleus within the cell.
Overall, the cytoskeleton is crucial for maintaining cell shape, providing mechanical support, #facilitating cellular movement, and organizing intracellular components. The dynamic #nature of the #cytoskeleton allows cells to respond to various stimuli, adapt to changes, and perform #essential functions necessary for cell survival and proper #functioning.
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:43:29
0:43:29
 0:08:52
0:08:52
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:10:20
0:10:20
 0:05:19
0:05:19
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:11:39
0:11:39
 0:12:14
0:12:14
 0:01:14
0:01:14
 0:20:35
0:20:35
 0:08:41
0:08:41
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:06:52
0:06:52