filmov
tv
Platelets & Blood Clotting | Biology | FuseSchool

Показать описание
Do you remember tripping over as a kid and cutting your knee? And then like magic the bleeding suddenly stops? Have you ever wondered why this happens?
Our body is very clever and produces substances to seal off the open wound.
In this video we are going to look at how and why blood clots.
Clotting prevents us from bleeding to death, and also protects us from nasty disease-causing organisms, called pathogens, entering our body.
When we injure ourselves, we can damage the blood vessels just below our skin. This can cause blood to either leak into our tissue and form a bruise, or, if the skin is broken to openly bleed.
To prevent these horrible things happening, blood clotting occurs.
So let’s have a look at how this happens.
Starting with platelets. These are tiny cell fragments that float around in our blood.
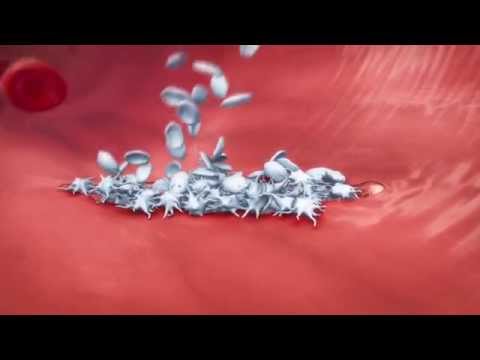
When a blood vessel is damaged, collagen is exposed. This collagen exposure attracts platelets to the injured area. The platelets then stick together to form a plug.
They’ve quickly built a little barrier that stops us from losing too much blood. However, this platelet plug isn’t that strong. So it needs to be made stronger.
A protein called fibrin does exactly that.
In our blood there are soluble fibrinogen proteins. At a wound, these soluble fibrinogen proteins are exposed to outside chemicals that aren’t normally found in blood vessels. Like with the collagen and platelets, this exposure causes the fibrinogen proteins to turn into sticky fibrin fibres.
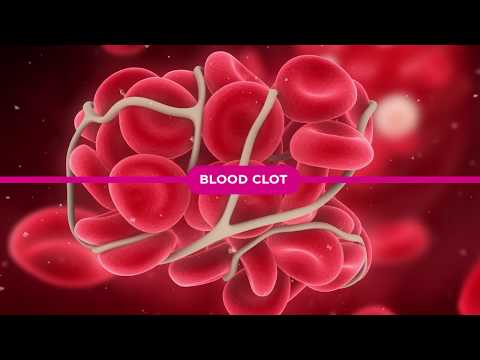
The fibrin fibres form a mesh, holding all the platelets together and making a much stronger clot.
More platelets, red blood cells and other components in our blood, all get stuck in the mesh making it even stronger. This clot stops more blood escaping the body. And also prevents nasty pathogens entering our body from the outside.
The clot develops into a scab, which protects the wound as it heals and new layers of skin form underneath. So really, all a scab is is just platelets trapped in the fibrin mesh!
When the new skin is fully formed, the scab will fall off, revealing the lovely brand new skin underneath.
Remember that I said the exposure to collagen causes the platelets to stick together? And the exposure to outside chemicals causes the fibrinogen to turn into sticky fibrin?
Both the platelets and the fibrin only become sticky AFTER the exposure. This means that in a normal, healthy blood vessel they won’t randomly cause clots.
So from this video, you should understand the magic of blood clotting. Platelets are first to the scene closely followed by fibrin fibres. Our blood clots so that we don’t lose a lot of blood and don’t let lots of nasty pathogens into our body if we cut ourselves.
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here:
Find all of our Biology videos here:
Find all of our Maths videos here:
Our body is very clever and produces substances to seal off the open wound.
In this video we are going to look at how and why blood clots.
Clotting prevents us from bleeding to death, and also protects us from nasty disease-causing organisms, called pathogens, entering our body.
When we injure ourselves, we can damage the blood vessels just below our skin. This can cause blood to either leak into our tissue and form a bruise, or, if the skin is broken to openly bleed.
To prevent these horrible things happening, blood clotting occurs.
So let’s have a look at how this happens.
Starting with platelets. These are tiny cell fragments that float around in our blood.
When a blood vessel is damaged, collagen is exposed. This collagen exposure attracts platelets to the injured area. The platelets then stick together to form a plug.
They’ve quickly built a little barrier that stops us from losing too much blood. However, this platelet plug isn’t that strong. So it needs to be made stronger.
A protein called fibrin does exactly that.
In our blood there are soluble fibrinogen proteins. At a wound, these soluble fibrinogen proteins are exposed to outside chemicals that aren’t normally found in blood vessels. Like with the collagen and platelets, this exposure causes the fibrinogen proteins to turn into sticky fibrin fibres.
The fibrin fibres form a mesh, holding all the platelets together and making a much stronger clot.
More platelets, red blood cells and other components in our blood, all get stuck in the mesh making it even stronger. This clot stops more blood escaping the body. And also prevents nasty pathogens entering our body from the outside.
The clot develops into a scab, which protects the wound as it heals and new layers of skin form underneath. So really, all a scab is is just platelets trapped in the fibrin mesh!
When the new skin is fully formed, the scab will fall off, revealing the lovely brand new skin underneath.
Remember that I said the exposure to collagen causes the platelets to stick together? And the exposure to outside chemicals causes the fibrinogen to turn into sticky fibrin?
Both the platelets and the fibrin only become sticky AFTER the exposure. This means that in a normal, healthy blood vessel they won’t randomly cause clots.
So from this video, you should understand the magic of blood clotting. Platelets are first to the scene closely followed by fibrin fibres. Our blood clots so that we don’t lose a lot of blood and don’t let lots of nasty pathogens into our body if we cut ourselves.
SUBSCRIBE to the FuseSchool YouTube channel for many more educational videos. Our teachers and animators come together to make fun & easy-to-understand videos in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Maths & ICT.
These videos can be used in a flipped classroom model or as a revision aid.
Find all of our Chemistry videos here:
Find all of our Biology videos here:
Find all of our Maths videos here:
Комментарии
 0:03:10
0:03:10
 0:02:08
0:02:08
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:43:13
0:43:13
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:25:10
0:25:10
 0:00:51
0:00:51
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:10:00
0:10:00
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:12:54
0:12:54
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:11:39
0:11:39
 0:21:06
0:21:06
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:21:01
0:21:01
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:16:42
0:16:42
 0:09:43
0:09:43
 0:05:49
0:05:49