filmov
tv
💯 Probability with Replacement | Examples of Choosing Coins and Regular Deck of 52 Cards

Показать описание
💯 Receive Comprehensive Mathematics Practice Papers Weekly for FREE
Timeline:
0:00 Intro
0:58 Question 15 Probability of Coins
3:58 Question 16 Regular Deck of 52 Cards
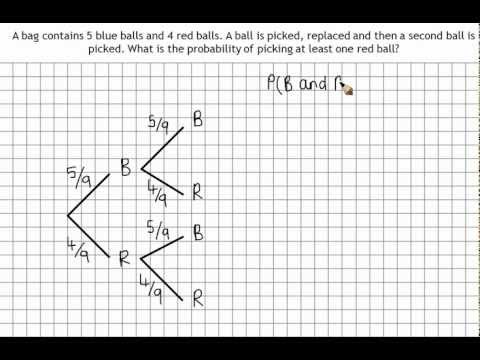
Probability with replacement refers to the probability of selecting items from a set, where the items can be replaced after each selection. This means that the same item can be selected multiple times.
When calculating the probability with replacement, each individual selection is independent of the previous selections, so the probability of each selection is simply the ratio of the number of favourable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes.
Example 1: Choosing Coins
Suppose you have a set of 2 coins: a fair coin and a coin that always lands heads up. If you choose a coin randomly and flip it, the probability of getting heads is 3/4. If you flip the coin again, the probability of getting heads is still 3/4, regardless of whether you got heads or tails on the first flip.
Example 2: Regular Deck of 52 Cards
Suppose you have a standard deck of 52 cards. If you draw a card randomly and replace it, the probability of drawing a specific card (e.g. the Ace of Spades) is 1/52 on each draw. If you draw 2 cards, the probability of drawing the Ace of Spades twice is (1/52) x (1/52) = 1/2704. Note that the probability of each draw is independent, so the probability of a specific sequence of selections is simply the product of the probabilities of each individual draw.
Timeline:
0:00 Intro
0:58 Question 15 Probability of Coins
3:58 Question 16 Regular Deck of 52 Cards
Probability with replacement refers to the probability of selecting items from a set, where the items can be replaced after each selection. This means that the same item can be selected multiple times.
When calculating the probability with replacement, each individual selection is independent of the previous selections, so the probability of each selection is simply the ratio of the number of favourable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes.
Example 1: Choosing Coins
Suppose you have a set of 2 coins: a fair coin and a coin that always lands heads up. If you choose a coin randomly and flip it, the probability of getting heads is 3/4. If you flip the coin again, the probability of getting heads is still 3/4, regardless of whether you got heads or tails on the first flip.
Example 2: Regular Deck of 52 Cards
Suppose you have a standard deck of 52 cards. If you draw a card randomly and replace it, the probability of drawing a specific card (e.g. the Ace of Spades) is 1/52 on each draw. If you draw 2 cards, the probability of drawing the Ace of Spades twice is (1/52) x (1/52) = 1/2704. Note that the probability of each draw is independent, so the probability of a specific sequence of selections is simply the product of the probabilities of each individual draw.
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:18:04
0:18:04
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:07:38
0:07:38
 0:10:18
0:10:18
 0:32:52
0:32:52
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:08:03
0:08:03
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:09:54
0:09:54
 0:05:27
0:05:27