filmov
tv
Krebs Cycle - animated

Показать описание
What is the citric acid, tricarboxylic acid (TCA), or Krebs cycle?
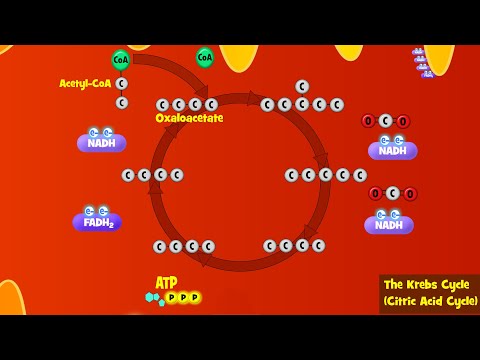
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs or citric acid cycle, is the main source of energy for cells and an important part of aerobic respiration. The cycle harnesses the available chemical energy of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) into the reducing power of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).
The TCA cycle is part of the larger glucose metabolism whereby glucose is oxidized to form pyruvate, which is then oxidized and enters the TCA cycle as acetyl-CoA.
Half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important compounds such as fatty acids, amino acids, or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted, the integrity of the cycle is broken and the cycle no longer functions. Production of essential energy can only be resumed if the diverted intermediate or a subsequent intermediate that leads to oxaloacetate can be replenished by anaplerotic (refilling) reactions.
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs or citric acid cycle, is the main source of energy for cells and an important part of aerobic respiration. The cycle harnesses the available chemical energy of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA) into the reducing power of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).
The TCA cycle is part of the larger glucose metabolism whereby glucose is oxidized to form pyruvate, which is then oxidized and enters the TCA cycle as acetyl-CoA.
Half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important compounds such as fatty acids, amino acids, or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted, the integrity of the cycle is broken and the cycle no longer functions. Production of essential energy can only be resumed if the diverted intermediate or a subsequent intermediate that leads to oxaloacetate can be replenished by anaplerotic (refilling) reactions.
Krebs Cycle - animated
Krebs cycle 3D medical animation
The Krebs Cycle Explained (Aerobic Respiration)
Citric Acid Cycle | HHMI BioInteractive Video
The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs Cycle Animation
KREBS CYCLE MADE SIMPLE - TCA Cycle Carbohydrate Metabolism Made Easy
Overview of the citric acid cycle
Utilization of Krebs cycle | Steps of krebs cycle | Importance of cellular respiration
Citric Acid Cycle (2020) by Drew Berry wehi.tv – #TCA #Krebs
Krebs Cycle ! Explained with Animation
Kreb Cycle | Easy Trick | Mnemonics | 11th | mdcat | Neet | #11th #mdcat #neet #fsc #biology #krebs
Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Electron Transport [3D Animation]
Citric Acid Cycle Animation || Krebs Cycle || TCA Cycle || 8 Steps in details
Cellular Respiration Overview | Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle & Electron Transport Chain
Learn the TCA Cycle! (Full Lesson) | Sketchy MCAT | Biochemistry
Citric Acid Cycle Animation
KREBS CYCLE MADE EASY - Krebs cycle Simple Animation. Carbohydrate Metabolism Lesson
Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
Why do we have to learn about the Krebs cycle?
Doctor remembers Krebs Cycle!
Easy way to learn krebs cycle #animation #medicalanimation #facts #science
How Mitochondria Produce Energy
Learn Krebs Cycle like Never Before 🎵🔥#pwenglish #krebscycle
Комментарии
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:00:24
0:00:24
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:06:11
0:06:11
 0:00:44
0:00:44
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:07:40
0:07:40
 0:06:11
0:06:11
 0:01:56
0:01:56
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:22:39
0:22:39
 0:03:00
0:03:00
 0:22:56
0:22:56
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:13:52
0:13:52
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:02:51
0:02:51