filmov
tv
For natural number m and n , if (1- y)^m (1+y)^n = 1+ a1y+a2y^2 , then(m,n) is
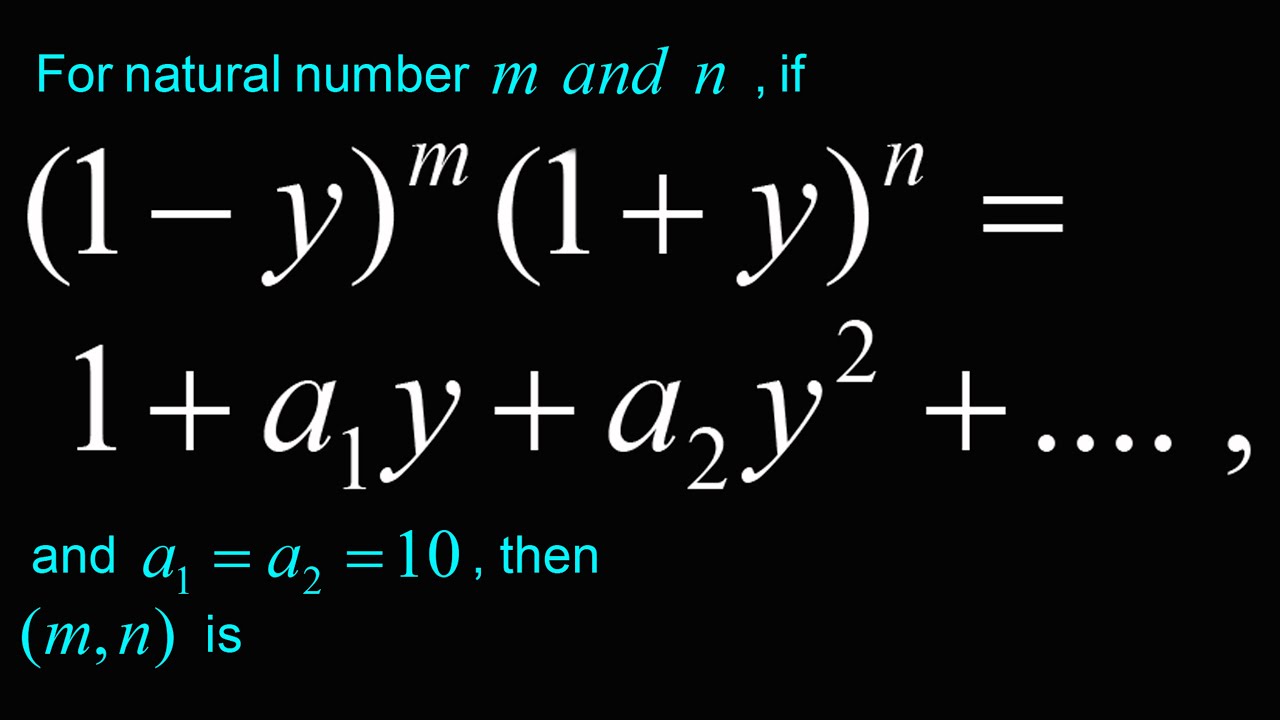
Показать описание
For natural number m and n , if (1- y)^m (1+y)^n = 1+ a1y+a2y^2 , then
(m,n) is + .......
(a) (20,45)
(b) (35,20)
(c) (45,35)
(d) (35,45)
binomial theorem
--
Algebra Playlist:
Permutations & Combinations:
Matrices:
Determinants:
Binomial Theorem:
Progression ( A.P,G.P, H.P & Special Series):
Quadratic equation & Inequations:
--
To buy complete Course please Visit–
join Impetus Gurukul live classes via the official Website:
Our Social links
--
binomial theorem
In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) is describing the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial (x + y)n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc, here exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with b + c = n, and the coefficient a of each term is a specific positive integer depending on n and b. For example (for n = 6),
Binomial theorem for any positive integer n,
(x–y)n = nC0xn – nC1xn – 1 y + nC2xn – 2 y2 + ... + (–1)n nCn yn
Tr+1 = nCr an–rbr.
Binomial Theorem, Binomial Theorem class 11, Binomial Theorem formula, Binomial Theorem jee mains questions, Binomial Theorem expansion, Binomial Theorem for negative index, Binomial Theorem formula pdf, Binomial Theorem in hindi, Binomial Theorem for competitive exams, Binomial Theorem for NIMCET,
(m,n) is + .......
(a) (20,45)
(b) (35,20)
(c) (45,35)
(d) (35,45)
binomial theorem
--
Algebra Playlist:
Permutations & Combinations:
Matrices:
Determinants:
Binomial Theorem:
Progression ( A.P,G.P, H.P & Special Series):
Quadratic equation & Inequations:
--
To buy complete Course please Visit–
join Impetus Gurukul live classes via the official Website:
Our Social links
--
binomial theorem
In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) is describing the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial (x + y)n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc, here exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with b + c = n, and the coefficient a of each term is a specific positive integer depending on n and b. For example (for n = 6),
Binomial theorem for any positive integer n,
(x–y)n = nC0xn – nC1xn – 1 y + nC2xn – 2 y2 + ... + (–1)n nCn yn
Tr+1 = nCr an–rbr.
Binomial Theorem, Binomial Theorem class 11, Binomial Theorem formula, Binomial Theorem jee mains questions, Binomial Theorem expansion, Binomial Theorem for negative index, Binomial Theorem formula pdf, Binomial Theorem in hindi, Binomial Theorem for competitive exams, Binomial Theorem for NIMCET,
 0:03:24
0:03:24
 0:03:01
0:03:01
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:29:47
0:29:47
 0:00:34
0:00:34
 0:01:34
0:01:34
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:04:18
0:04:18
 0:14:01
0:14:01
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:05:29
0:05:29
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:46
0:00:46
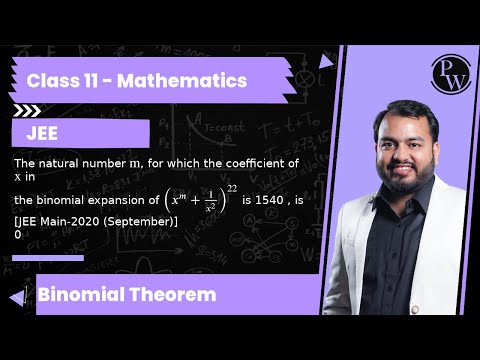 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:05:15
0:05:15
 0:05:48
0:05:48