filmov
tv
IB Chemistry Topic 3 Periodicity 3.1 Periodic Table

Показать описание
IB Chemistry Topic 3 Periodicity 3.1 Periodic Table
A full explanation of anatomy of the Periodic Table. The names of the important groups Group 1 alkali metals, transistion metals, halogens, semimetals (metaloids) and noble gases. The main groupings of metals and non-metals. How and why we have anions and cations. A short introduction into some properties and trends.
0:08 Periodic table, atomic number and orbitals
0:49 Groups, periods, and types of elements
1:44 Anion and cation formation from the Periodic Table
3:50 Properties of metals and non-metals
4:58 Metals and non-metals in the Periodic Table
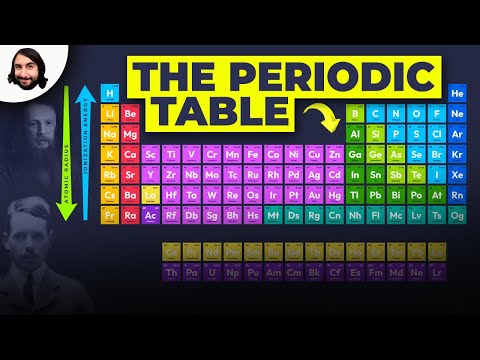
3.1 Periodic table
• The periodic table is arranged into four blocks associated with the four sub-levels—s, p, d, and f.
• The periodic table consists of groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows).
• The period number (n) is the outer energy level that is occupied by electrons.
• The number of the principal energy level and the number of the valence electrons in an atom can be deduced from its position on the periodic table.
• The periodic table shows the positions of metals, non-metals and metalloids.
• Deduction of the electron configuration of an atom from the element’s position
Connect with me:
A full explanation of anatomy of the Periodic Table. The names of the important groups Group 1 alkali metals, transistion metals, halogens, semimetals (metaloids) and noble gases. The main groupings of metals and non-metals. How and why we have anions and cations. A short introduction into some properties and trends.
0:08 Periodic table, atomic number and orbitals
0:49 Groups, periods, and types of elements
1:44 Anion and cation formation from the Periodic Table
3:50 Properties of metals and non-metals
4:58 Metals and non-metals in the Periodic Table
3.1 Periodic table
• The periodic table is arranged into four blocks associated with the four sub-levels—s, p, d, and f.
• The periodic table consists of groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows).
• The period number (n) is the outer energy level that is occupied by electrons.
• The number of the principal energy level and the number of the valence electrons in an atom can be deduced from its position on the periodic table.
• The periodic table shows the positions of metals, non-metals and metalloids.
• Deduction of the electron configuration of an atom from the element’s position
Connect with me:
Комментарии
 0:20:14
0:20:14
 0:05:25
0:05:25
 0:12:30
0:12:30
 0:16:44
0:16:44
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 0:13:43
0:13:43
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:29:25
0:29:25
 0:35:08
0:35:08
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:23:42
0:23:42
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:14:52
0:14:52
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:36:04
0:36:04
 0:07:57
0:07:57
 0:29:03
0:29:03
 0:08:47
0:08:47
 0:42:38
0:42:38
 0:18:06
0:18:06
 0:10:32
0:10:32
 0:15:21
0:15:21