filmov
tv
Iterative method of Engineering Mathematics |Fixed Point Method| Method of Successive Approximations

Показать описание
Iterative method of Engineering Mathematics |Fixed Point Method| Method of Successive Approximations
The fixed point method is a numerical technique used to find the roots of an equation. The core idea is to transform the equation into the form x = g(x), where a fixed point is a value x such that g(x) = x.
How it works:
Rearrange the equation: Convert the given equation into the form x = g(x).
Choose an initial guess: Select a starting value, x0, as an approximation to the root.
Iterate: Apply the formula x_(n+1) = g(x_n) repeatedly to generate a sequence of approximations.
Convergence: If the sequence converges to a value x, then x is a fixed point and an approximate root of the original equation.
Key points:
Convergence: Not all functions g(x) lead to convergent iterations. The method's convergence depends on the properties of g(x).
Rate of convergence: The speed at which the iterations approach the root can vary. Some functions converge faster than others.
Applications: The fixed point method is used in various fields, including engineering, physics, and economics, to solve equations numerically.
#IterativeMethod
#EngineeringMathematics
#FixedPointMethod
#MethodOfSuccessiveApproximations
#NumericalMethods
#Mathematics
#Engineering
#Science
#Education
#Tutorial
#NumericalAnalysis
#EngineeringMath
#IterativeMethods
#SuccessiveApproximations
#FixedPointIteration
#MathematicalModeling
#ComputationalMathematics
#MathTutorials
#MathHelp
#EngineeringStudents
The fixed point method is a numerical technique used to find the roots of an equation. The core idea is to transform the equation into the form x = g(x), where a fixed point is a value x such that g(x) = x.
How it works:
Rearrange the equation: Convert the given equation into the form x = g(x).
Choose an initial guess: Select a starting value, x0, as an approximation to the root.
Iterate: Apply the formula x_(n+1) = g(x_n) repeatedly to generate a sequence of approximations.
Convergence: If the sequence converges to a value x, then x is a fixed point and an approximate root of the original equation.
Key points:
Convergence: Not all functions g(x) lead to convergent iterations. The method's convergence depends on the properties of g(x).
Rate of convergence: The speed at which the iterations approach the root can vary. Some functions converge faster than others.
Applications: The fixed point method is used in various fields, including engineering, physics, and economics, to solve equations numerically.
#IterativeMethod
#EngineeringMathematics
#FixedPointMethod
#MethodOfSuccessiveApproximations
#NumericalMethods
#Mathematics
#Engineering
#Science
#Education
#Tutorial
#NumericalAnalysis
#EngineeringMath
#IterativeMethods
#SuccessiveApproximations
#FixedPointIteration
#MathematicalModeling
#ComputationalMathematics
#MathTutorials
#MathHelp
#EngineeringStudents
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:18:06
0:18:06
 0:16:07
0:16:07
 0:15:17
0:15:17
 0:16:39
0:16:39
 0:09:35
0:09:35
 0:10:21
0:10:21
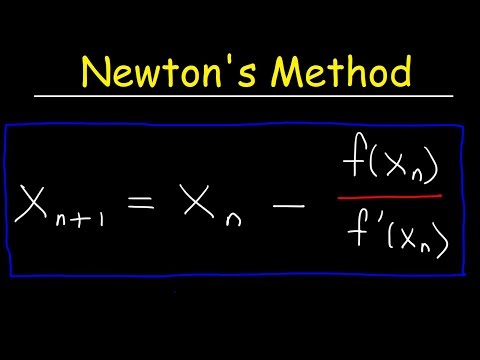 0:10:41
0:10:41
 1:45:00
1:45:00
 0:21:03
0:21:03
 0:36:17
0:36:17
 0:12:06
0:12:06
 0:06:54
0:06:54
 0:16:08
0:16:08
 0:12:33
0:12:33
 0:11:58
0:11:58
 0:17:05
0:17:05
 0:06:06
0:06:06
 0:10:00
0:10:00
 0:12:36
0:12:36
 0:24:45
0:24:45
 0:36:25
0:36:25
 0:12:24
0:12:24
 0:04:35
0:04:35