filmov
tv
Static Stress, Linear Dynamics, and Heat Transfer Overview - Autodesk Simulation
Показать описание
Autodesk® Simulation software, part of the Autodesk® solution for Digital Prototyping, provides a range of mechanical simulation tools to help designers, engineers, and analysts make decisions earlier in the engineering design process. With these tools, you can predict the real‐world performance of your product, helping to save the time and money required to build multiple physical prototypes.
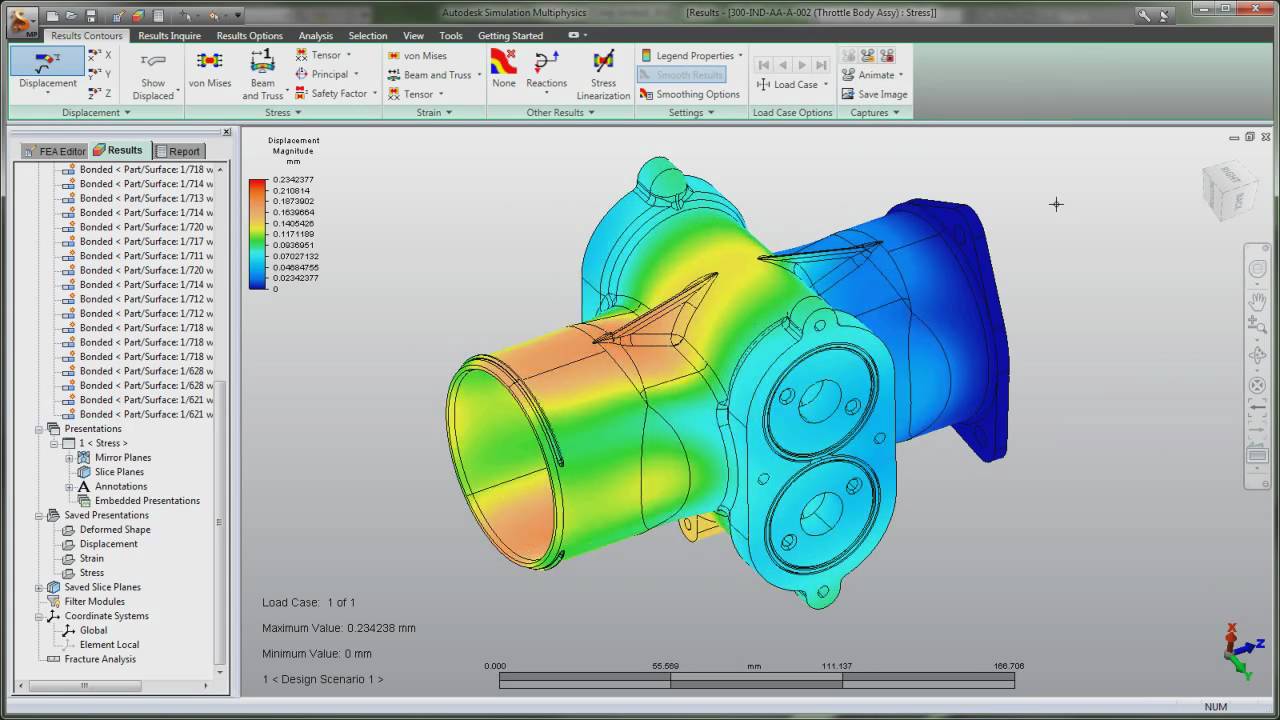
Autodesk® Simulation Mechanical and Autodesk® Simulation Multiphysics software includes tools for static stress and linear dynamic simulations—helping you study stress, strain, displacement, shear, and axial forces resulting from structural loading—including forces, moments, pressures, gravity, and displacements.
Autodesk® Simulation software also helps you determine a part's natural frequencies and mode shapes in order to avoid frequencies that are disruptive or harmful to your design. In addition, it helps you avoid structural failure by determining the amount of load that would cause a structure to buckle—letting you review the predicted buckling shape so you can then add supports and stiffeners to your design.
Autodesk® Simulation software includes support for steady-state and transient heat transfer simulations—helping to predict changes in a product's temperature profile in order to reveal potential failure. Study linear and nonlinear thermal effects by considering conduction, convection, heat flux, heat generation, radiation, and thermal contact.
Support for multi-CAD environments and finite element modeling tools help manufacturers study initial design intent and accurately predict product performance. Autodesk Simulation software supports direct data exchange with most CAD software tools, Autodesk® Moldflow® plastic injection molding simulation tools, and Autodesk® Vault data management software. Autodesk Simulation software allows you to validate and optimize designs before manufacturing—increasing efficiency, minimizing reliance on physical prototypes, reducing costs, and decreasing errors.
 0:02:15
0:02:15
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:01:35
0:01:35
 0:01:58
0:01:58
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:04:14
0:04:14
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:03:55
0:03:55
 0:07:43
0:07:43
 0:06:27
0:06:27
 0:03:06
0:03:06
 0:08:27
0:08:27
 0:14:35
0:14:35
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:07:22
0:07:22
 0:15:15
0:15:15
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:13:35
0:13:35
 0:02:14
0:02:14
 0:51:59
0:51:59
 0:10:29
0:10:29