filmov
tv
Z - DNA: comparison with A-DNA and B-DNA

Показать описание
The most common form of DNA that occurs in living organisms is B-form or Watson and Crick's model of DNA. Under certain conditions, this form changes its configuration.
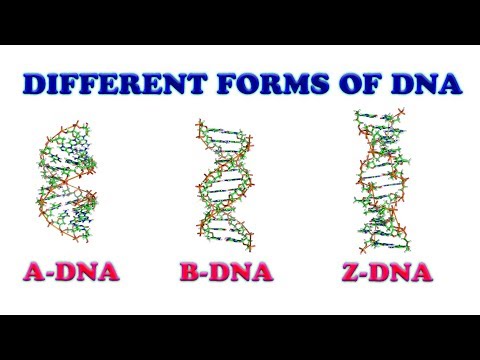
There are 6 different morphological forms of DNA: A, B, C, D, E and Z. Three biologically active forms of DNA are A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.
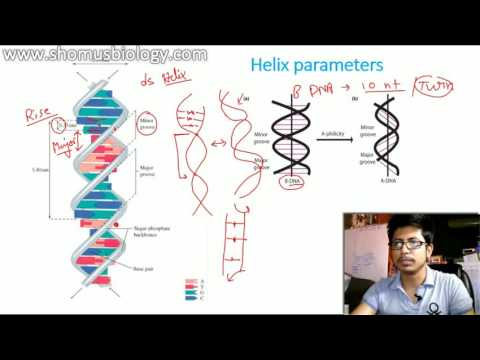
A-DNA: this form is double-stranded, right-handed helical DNA. It is a dehydrated form that occurs in an environment richer in Na+ and less water. It shows 11 base pairs per turn of the helix and a diameter of 23 A. The height of the pitch is 28 A and axial rise is 2.56 A. The sugar-phosphate backbone is regular. The repeating units are mononucleotides. It shows the presence of 2 deep groves and 2 shallow groves.
B-DNA: occurs at low salt concentration and a high degree of hydration (i.e. normal conditions).
Z-DNA: Rich et al. working at MIT, USA studied the molecular structure of DNA fragments at atomic resolution. They proposed a Z-form of DNA along with B-DNA.
The Z-DNA shows the following characteristics:
It is stabilized by high salt concentration.
It is left-handed DNA.
It is a double-helical structure with a zig-zag sugar-phosphate backbone.
In Z-DNA, the repeating unit is a dinucleotide and the sugar residues have an alternating orientation of dinucleotide.
In Z-DNA, 12 base pairs are present per turn.
The height of the pitch is 45 A.
The diameter of the helix is 18 A
For additional information about DNA and Nucleic acids, you can also refer to
There are 6 different morphological forms of DNA: A, B, C, D, E and Z. Three biologically active forms of DNA are A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.
A-DNA: this form is double-stranded, right-handed helical DNA. It is a dehydrated form that occurs in an environment richer in Na+ and less water. It shows 11 base pairs per turn of the helix and a diameter of 23 A. The height of the pitch is 28 A and axial rise is 2.56 A. The sugar-phosphate backbone is regular. The repeating units are mononucleotides. It shows the presence of 2 deep groves and 2 shallow groves.
B-DNA: occurs at low salt concentration and a high degree of hydration (i.e. normal conditions).
Z-DNA: Rich et al. working at MIT, USA studied the molecular structure of DNA fragments at atomic resolution. They proposed a Z-form of DNA along with B-DNA.
The Z-DNA shows the following characteristics:
It is stabilized by high salt concentration.
It is left-handed DNA.
It is a double-helical structure with a zig-zag sugar-phosphate backbone.
In Z-DNA, the repeating unit is a dinucleotide and the sugar residues have an alternating orientation of dinucleotide.
In Z-DNA, 12 base pairs are present per turn.
The height of the pitch is 45 A.
The diameter of the helix is 18 A
For additional information about DNA and Nucleic acids, you can also refer to
Комментарии
 0:07:27
0:07:27
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:04:04
0:04:04
 0:20:03
0:20:03
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:01:20
0:01:20
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:01:03
0:01:03
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:09:36
0:09:36
 0:23:06
0:23:06
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:19:32
0:19:32
 0:17:16
0:17:16
 0:11:36
0:11:36
 0:08:02
0:08:02
 0:06:41
0:06:41
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:48
0:00:48