filmov
tv
20.3 E/Z isomerism (HL)

Показать описание
Understandings:
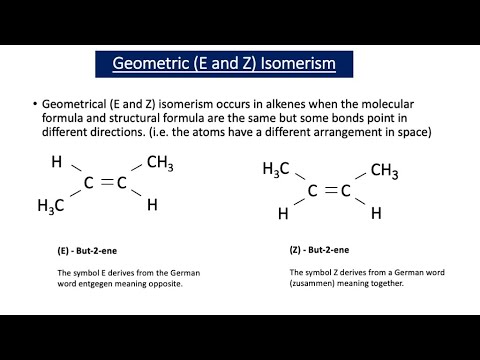
According to IUPAC, E/Z isomers refer to alkenes of the form R1R2C=CR3R4 (R1 ≠ R2, R3 ≠ R4) where neither R1 nor R2 need be different from R3 or R4.
According to IUPAC, E/Z isomers refer to alkenes of the form R1R2C=CR3R4 (R1 ≠ R2, R3 ≠ R4) where neither R1 nor R2 need be different from R3 or R4.
IB Organic Chemistry Isomers Topic 10 HL 20.3 Stereoisomers cis trans EZ optical isomers
IB Chemistry Topic 20.3 (HL): Stereoisomerism - Part 1
20.3 cis-trans isomerism (HL)
Alkene Nomenclature (part 3): E/Z System
IB Chemistry Topic 20.3 (HL): Stereoisomerism - Part 2
Geometric (E and Z) Isomers (AS and A2 Chemistry)
3.3.4 - Alkenes - Lesson 1 of 3 - Bonding and Isomerism
IB Chemistry Paper 1 MCQ (Topic 20-HL)
IB FRQ #20 Organic Chemistry
Aromatic Substitution and Cis Trans Isomerism with Magnetic Models - Updated
Isomers (IB Chemistry S3.2)
23.4.5 Geometric Isomers
Topic 20.3 - Enantiomers
Optical Isomerism Introduction - drawing enantiomers
Cis-trans isomerism Meaning
A-level chemistry transition metals
IB Paper 2 practice #5 organic chemistry
Isomerism in alkanes, Optical Isomerism
Organic Chemistry - Ch 1: Basic Concepts (23 of 97) Alkenes: A Geometric Isomer Example
The name of the compound is : (a) (2Z, 4Z)-2,4-Hexadiene (b) (2 Z, 4 E)-2,4-Hexadiene (c) (2 E, 4...
Stereoisomers || Stereochemistry || Conformational and Configurational isomerism
Optical Isomerism - A-level Chemistry
Mass Spectrometry
Farnesene
Комментарии
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:05:45
0:05:45
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:02:46
0:02:46
 0:05:58
0:05:58
 0:25:42
0:25:42
 0:14:24
0:14:24
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:12:20
0:12:20
 0:01:07
0:01:07
 0:23:36
0:23:36
 0:08:18
0:08:18
 0:10:19
0:10:19
 0:06:58
0:06:58
 0:00:33
0:00:33
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:15:32
0:15:32
 0:02:35
0:02:35
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:01:50
0:01:50