filmov
tv
C sort an array 💱

Показать описание
C sort an array program tutorial example explained
#C #sort #array
#C #sort #array
C sort an array 💱
Using qsort() To Sort An Array | C Programming Example
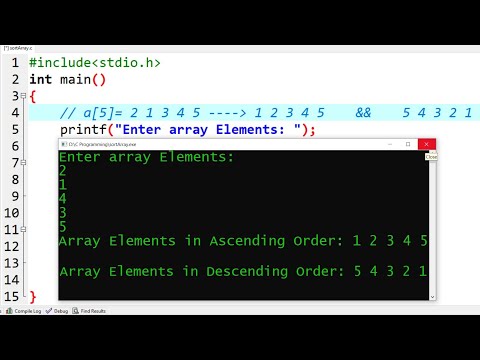
C Program to Sort Array Elements in Ascending & Descending Order | Learn Coding
C. Sort the array
C Program To Short Array In Ascending Order And Decending Order | We Are Engineers
Sorting An Array Of Strings | C Programming Example
c program to sort elements of an array in ascending order #cprogramming #codingguru #youtubeshort 😎...
C40 - Program to arrange numbers in ascending order | sort values in array
Generic Function Example (Q Sort) in C Part-9 | Dynamic Memory Allocation in C Programming
Check If An Array Is Sorted | C Programming Example
123 - Sorting Array of Structure | Structure in C Programming
Sorting with Array of Structures
Bubble Sort Program in C
Sort an Array which contain 1 to N values in O(N) Time Complexity !
C Program to Sort an array of names or strings | GeeksforGeeks
912. Sort an Array | sorting | Leetcode Daily Challenge | DSA | Hindi
Array Sorting Using Pointer in C
Selection Sort Program in C
Array of objects Algorithms - Search, Sort, Reverse, Max, Min, Custom methods
Sorting in Array Data Structure- How to Sort an Array in C++ - Ascending Order - Descending Order
Sorting of Array elements in Ascending order / cprogramming /malayalam
Merge Sorted Array | Live Coding with Explanation | Leetcode - 88
Java Program #17 - Sort an Array of Integers in ascending order
Sort Array in C Programming | Sort Algorithm with easy Explanation
Комментарии
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:09:46
0:09:46
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:08:43
0:08:43
 0:08:46
0:08:46
 0:00:49
0:00:49
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:23:11
0:23:11
 0:09:39
0:09:39
 0:17:40
0:17:40
 0:02:51
0:02:51
 0:22:43
0:22:43
 0:10:22
0:10:22
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:17:51
0:17:51
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:15:27
0:15:27
 0:22:46
0:22:46
 0:15:58
0:15:58
 0:08:32
0:08:32
 0:04:50
0:04:50
 0:07:31
0:07:31
 0:13:04
0:13:04