filmov
tv
Brachial Plexus Branches & Nerves - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim

Показать описание
Educational video describing the branches of the brachial plexus.
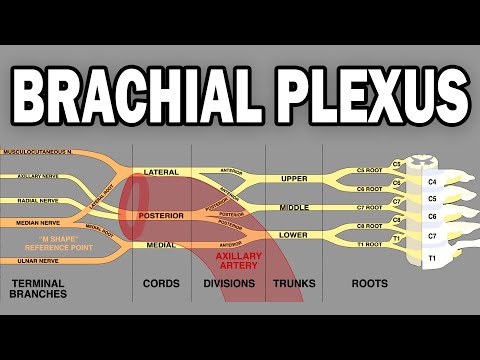
The long thoracic nerve arises from three nerve roots: C5,C6, & C7. Medial winging of the scapula is most commonly caused by deficit in the serratus anterior muscle due to impingement injury of the long thoracic nerve.
The dorsal scapular nerve (nerve to rhomboids) supplies three muscles:
1-Levator scapulae 2-Rhomboid minor 3-Rhomboids major
When an injury occurs to the dorsal scapular nerve, it will cause rhomboids winging of the scapula and loss of shoulder abduction.
The nerve to subclavius is a very small nerve that supplies a very small muscle, the subclavius muscle.
The suprascapular nerve gives branches to the supraspinatus muscle as well as the infraspinatus muscle. Entrapment of the nerve can occur within the suprascapular notch or the spinoglenoid notch.
The lateral pectoral nerve is a muscular nerve that pierces the clavipectoral fascia and ends by supplying the pectoralis major muscle.
The upper subscapular nerve supplies the upper part of the subscapularis muscle.
The thoracodorsal nerve forms at the posterior cord between the lower and upper subscapular nerves, running through the axilla passing obliquely laterally and downwards.
The lower subscapular nerve supplies the lower part of the subscapularis (that which is not supplied by the upper subscapular nerve) and teres major muscles. The upper subscapular nerve supplies only the upper part of the muscle while the lower subscapular nerve supplies the teres major muscle and the remaining lower part of the subscapularis muscle.
The medial pectoral nerve supplies the muscles of the pectoralis major and minor.
Areas of the skin that are supplied by the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm and arm.
The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. It supplies the biceps muscle and the shoulder. It also supplies the coracobrachialis muscle and brachialis muscle on the lateral side of the arm.
The axillary nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The axillary nerve runs anteriorly across the subscapularis muscle. The nerve passes through the quadrangular space. The axillary nerve supplies the muscles of the deltoid and teres minor, giving sensation over the shoulder area.
The radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The radial nerve supplies the extensor muscles allowing for extension of the wrist and the fingers. Injury to the nerve will cause wrist drop.
The ulnar nerve originates from the C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The ulnar nerve does not give branches in the axilla or the upper arm. It starts giving muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. At the elbow, the ulnar passes behind the medial epicondyle. Just past the elbow, the nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus. In the forearm, the ulnar nerve divides into dorsal and palmar cutaneous branches. In the hand, the nerve further divides into superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve divides into palmar digital nerves after it passes under and supplies the palmaris brevis muscle. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles, the medial two lumbricals, the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. The palmar cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve provides sensation to the palm of the hand. The dorsal cutaneous branch gives innervation to the medial dorsal aspect of the hand and the one and a half fingers.
The median nerve originates from the lateral cord and the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The median nerve runs down the arm where it passes on the medial side of arm between the brachialis and the biceps brachii. At the elbow, the median nerve moves into the area of the cubital fossa and then passes medial to the brachial artery, in front of the point of insertion of the brachialis muscle and deep to the biceps. The median nerve branches as its course through the forearm. The anterior interosseous nerve branches out to innervate the muscles of the deep group of the anterior compartment of the forearm. At the wrist, the median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel deep to the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve supplies motor innervation to the 1st and 2nd lumbrical muscles and the majority of muscles in the thenar group. The median nerve innervates the skin on the palmar side of the thumb, the index finger, the middle finger and half of the ring finger.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
The long thoracic nerve arises from three nerve roots: C5,C6, & C7. Medial winging of the scapula is most commonly caused by deficit in the serratus anterior muscle due to impingement injury of the long thoracic nerve.
The dorsal scapular nerve (nerve to rhomboids) supplies three muscles:
1-Levator scapulae 2-Rhomboid minor 3-Rhomboids major
When an injury occurs to the dorsal scapular nerve, it will cause rhomboids winging of the scapula and loss of shoulder abduction.
The nerve to subclavius is a very small nerve that supplies a very small muscle, the subclavius muscle.
The suprascapular nerve gives branches to the supraspinatus muscle as well as the infraspinatus muscle. Entrapment of the nerve can occur within the suprascapular notch or the spinoglenoid notch.
The lateral pectoral nerve is a muscular nerve that pierces the clavipectoral fascia and ends by supplying the pectoralis major muscle.
The upper subscapular nerve supplies the upper part of the subscapularis muscle.
The thoracodorsal nerve forms at the posterior cord between the lower and upper subscapular nerves, running through the axilla passing obliquely laterally and downwards.
The lower subscapular nerve supplies the lower part of the subscapularis (that which is not supplied by the upper subscapular nerve) and teres major muscles. The upper subscapular nerve supplies only the upper part of the muscle while the lower subscapular nerve supplies the teres major muscle and the remaining lower part of the subscapularis muscle.
The medial pectoral nerve supplies the muscles of the pectoralis major and minor.
Areas of the skin that are supplied by the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm and arm.
The musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus. It supplies the biceps muscle and the shoulder. It also supplies the coracobrachialis muscle and brachialis muscle on the lateral side of the arm.
The axillary nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The axillary nerve runs anteriorly across the subscapularis muscle. The nerve passes through the quadrangular space. The axillary nerve supplies the muscles of the deltoid and teres minor, giving sensation over the shoulder area.
The radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The radial nerve supplies the extensor muscles allowing for extension of the wrist and the fingers. Injury to the nerve will cause wrist drop.
The ulnar nerve originates from the C8-T1 nerve roots which form the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The ulnar nerve does not give branches in the axilla or the upper arm. It starts giving muscular and cutaneous branches in the upper forearm and hand. At the elbow, the ulnar passes behind the medial epicondyle. Just past the elbow, the nerve gives branches to the flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus. In the forearm, the ulnar nerve divides into dorsal and palmar cutaneous branches. In the hand, the nerve further divides into superficial and deep branches. The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve divides into palmar digital nerves after it passes under and supplies the palmaris brevis muscle. The deep branch of the ulnar nerve innervates the three hypothenar muscles, the medial two lumbricals, the adductor pollicis and the deep head of the flexor pollicis brevis. The palmar cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve provides sensation to the palm of the hand. The dorsal cutaneous branch gives innervation to the medial dorsal aspect of the hand and the one and a half fingers.
The median nerve originates from the lateral cord and the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The median nerve runs down the arm where it passes on the medial side of arm between the brachialis and the biceps brachii. At the elbow, the median nerve moves into the area of the cubital fossa and then passes medial to the brachial artery, in front of the point of insertion of the brachialis muscle and deep to the biceps. The median nerve branches as its course through the forearm. The anterior interosseous nerve branches out to innervate the muscles of the deep group of the anterior compartment of the forearm. At the wrist, the median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel deep to the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve supplies motor innervation to the 1st and 2nd lumbrical muscles and the majority of muscles in the thenar group. The median nerve innervates the skin on the palmar side of the thumb, the index finger, the middle finger and half of the ring finger.
Become a friend on facebook:
Follow me on twitter:
Комментарии
 0:10:26
0:10:26
 0:03:39
0:03:39
 0:17:12
0:17:12
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 0:04:22
0:04:22
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:38:07
0:38:07
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:04:12
0:04:12
 0:20:42
0:20:42
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:01:15
0:01:15
 0:20:35
0:20:35
 0:21:38
0:21:38
 0:08:54
0:08:54
 0:13:16
0:13:16
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:16:52
0:16:52
 0:08:37
0:08:37
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:18:09
0:18:09
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:11:20
0:11:20
 0:03:34
0:03:34