filmov
tv
RNA & DNA STURUCTUE | Interesting video | Viral Video | Khan sir DNA & RNA Class

Показать описание
RNA & DNA STURUCTUE | Pushkar Sir Bio Wale | Biology wallah | Interesting video | Viral Video | Khan sir DNA & RNA Class
DNA
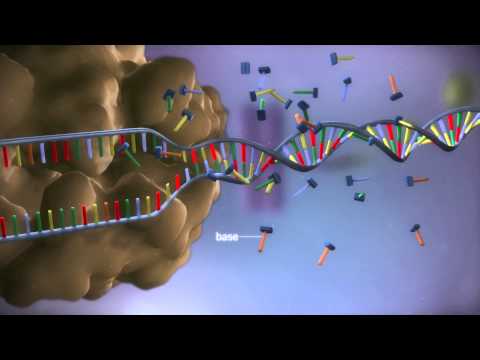
In cells, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid that functions as the original blueprint for the synthesis of proteins. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, phosphates and a unique sequence of the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T).
Brief Insight into the Structure and Composition of DNA
The DNA molecules contain instructions a living entity requires to grow, develop and reproduce. These instructions are present inside each cell and are inherited from the parents to their offspring.
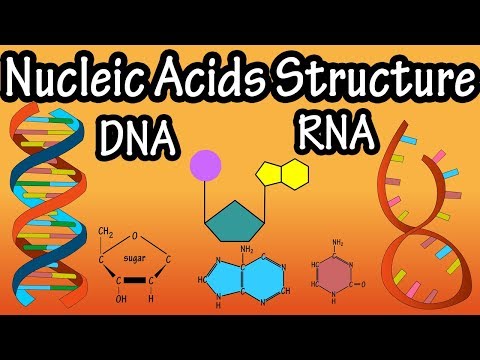
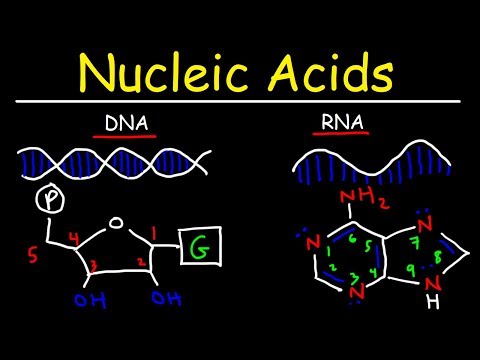
It is made up of nucleotides which contain a nitrogenous group, a phosphate group, and a sugar group. The order of the nitrogenous bases – thymine(T), guanine(G), cytosine(C), and adenine(A), is crucial in determining the genetic code.
Genes are formed by the order of the nitrogenous bases present in the DNA which is crucial for protein synthesis. RNA is another nucleic acid that translates genetic information into proteins from DNA.
The nucleotides are linked together for the formation of two long strands which spiral to produce a structure known as the double-helix which resembles that of a ladder wherein the sugar and phosphate molecules form the sides while the rungs are formed by the bases.
The bases located on one strand pair up with the bases on the other strand, as in – guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with thymine.
The DNA molecules are extremely long and hence without the right packaging, they cannot fit into cells. Thus, DNA is tightly coiled to produce formations referred to as chromosomes. Every chromosome has a single DNA molecule. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes that are present within the nucleus of the cells.
Main article: DNA Structure
Types Of DNA
A-DNA: It is found at a relative humidity of 75%. In an environment where there is a higher salt concentration or ionic concentrations, such as K+, Na+, Cs+ or in a state of dehydration it endures in a form that contains 11 nucleotide pairs with a rise of 2.56Å vertically per base pair. It has the broadest helical diameter amongst all DNA forms – 23Å DNA which is a typical helix that is right-handed with a rotation of 32.70 per base pair.
B-DNA: The most common form, present in most DNA at neutral pH and physiological salt concentrations, is B-form. It has 10 base pairs per turn from the helix axis. There is a distance of 3.4Å with a helical diameter of 20Å. Watson-Crick’s double helix model is defined as a B-form of DNA.
C-DNA: It is observed at a relative humidity of 66% and in the occupancy of a few ions such as Lithium(Li+). It closely has 9.33 base pairs for every turn. The diameter of the helix is about 19Å and the vertical rise for every base pair for the right-handed helix is 3.320.
D-DNA: It is observed rarely as an extreme variant. The 8 base pairs are titled negatively from the helix axis with an axial rise of about 3.03Å
Z-DNA: It is found in an environment with a very high salt concentration. Unlike the A, B, and C types of DNA, it is a left-handed helical structure. The backbone is arranged in a zig-zag pattern formed by the sugar-phosphate linkage wherein the recurrent monomer is the dinucleotide in contrast to the mononucleotide, which is observed in alternate forms.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid which is directly involved in protein synthesis. Ribonucleic acid is an important nucleotide with long chains of nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its main role is to act as a messenger conveying instructions from DNA for controlling protein synthesis.
RNA contains the sugar ribose, phosphates, and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U). DNA and RNA share the nitrogenous bases A, G, and C. Thymine is usually only present in DNA and uracil is usually only present in RNA.
Types Of RNA
Only some of the genes in cells are expressed into RNA. The following are the types of RNA wherein each type is encoded by its own type of gene:
tRNA– The transfer RNA or the tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes while translation
mRNA – The messenger RNA or the mRNA encodes amino acid sequences of a polypeptide
rRNA – The ribosomal RNA or the rRNA produces ribosomes with the ribosomal proteins that are organelles responsible for the translation of the mRNA.
snRNA – The small nuclear RNA forms the complexes along with proteins which are utilized in RNA processing in the eukaryotes.
#rna #dna #biology #science #biotechnology #genetics #lnp #mrna #molecularbiology #follow #covid #bio #biologymajor #physicswallah #biology #biochemistry #bornfree #cells #biologymemes #biotech #vaccine #microbiology #university #therapeutics #research #pharmaceuticals #laboratory #uracil #pharmaceutical #drugdelivery #fda #vaccines
DNA
In cells, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid that functions as the original blueprint for the synthesis of proteins. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, phosphates and a unique sequence of the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T).
Brief Insight into the Structure and Composition of DNA
The DNA molecules contain instructions a living entity requires to grow, develop and reproduce. These instructions are present inside each cell and are inherited from the parents to their offspring.
It is made up of nucleotides which contain a nitrogenous group, a phosphate group, and a sugar group. The order of the nitrogenous bases – thymine(T), guanine(G), cytosine(C), and adenine(A), is crucial in determining the genetic code.
Genes are formed by the order of the nitrogenous bases present in the DNA which is crucial for protein synthesis. RNA is another nucleic acid that translates genetic information into proteins from DNA.
The nucleotides are linked together for the formation of two long strands which spiral to produce a structure known as the double-helix which resembles that of a ladder wherein the sugar and phosphate molecules form the sides while the rungs are formed by the bases.
The bases located on one strand pair up with the bases on the other strand, as in – guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with thymine.
The DNA molecules are extremely long and hence without the right packaging, they cannot fit into cells. Thus, DNA is tightly coiled to produce formations referred to as chromosomes. Every chromosome has a single DNA molecule. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes that are present within the nucleus of the cells.
Main article: DNA Structure
Types Of DNA
A-DNA: It is found at a relative humidity of 75%. In an environment where there is a higher salt concentration or ionic concentrations, such as K+, Na+, Cs+ or in a state of dehydration it endures in a form that contains 11 nucleotide pairs with a rise of 2.56Å vertically per base pair. It has the broadest helical diameter amongst all DNA forms – 23Å DNA which is a typical helix that is right-handed with a rotation of 32.70 per base pair.
B-DNA: The most common form, present in most DNA at neutral pH and physiological salt concentrations, is B-form. It has 10 base pairs per turn from the helix axis. There is a distance of 3.4Å with a helical diameter of 20Å. Watson-Crick’s double helix model is defined as a B-form of DNA.
C-DNA: It is observed at a relative humidity of 66% and in the occupancy of a few ions such as Lithium(Li+). It closely has 9.33 base pairs for every turn. The diameter of the helix is about 19Å and the vertical rise for every base pair for the right-handed helix is 3.320.
D-DNA: It is observed rarely as an extreme variant. The 8 base pairs are titled negatively from the helix axis with an axial rise of about 3.03Å
Z-DNA: It is found in an environment with a very high salt concentration. Unlike the A, B, and C types of DNA, it is a left-handed helical structure. The backbone is arranged in a zig-zag pattern formed by the sugar-phosphate linkage wherein the recurrent monomer is the dinucleotide in contrast to the mononucleotide, which is observed in alternate forms.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a nucleic acid which is directly involved in protein synthesis. Ribonucleic acid is an important nucleotide with long chains of nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its main role is to act as a messenger conveying instructions from DNA for controlling protein synthesis.
RNA contains the sugar ribose, phosphates, and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U). DNA and RNA share the nitrogenous bases A, G, and C. Thymine is usually only present in DNA and uracil is usually only present in RNA.
Types Of RNA
Only some of the genes in cells are expressed into RNA. The following are the types of RNA wherein each type is encoded by its own type of gene:
tRNA– The transfer RNA or the tRNA carries amino acids to ribosomes while translation
mRNA – The messenger RNA or the mRNA encodes amino acid sequences of a polypeptide
rRNA – The ribosomal RNA or the rRNA produces ribosomes with the ribosomal proteins that are organelles responsible for the translation of the mRNA.
snRNA – The small nuclear RNA forms the complexes along with proteins which are utilized in RNA processing in the eukaryotes.
#rna #dna #biology #science #biotechnology #genetics #lnp #mrna #molecularbiology #follow #covid #bio #biologymajor #physicswallah #biology #biochemistry #bornfree #cells #biologymemes #biotech #vaccine #microbiology #university #therapeutics #research #pharmaceuticals #laboratory #uracil #pharmaceutical #drugdelivery #fda #vaccines
Комментарии
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:12:59
0:12:59
 0:46:23
0:46:23
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:11:16
0:11:16
 0:18:38
0:18:38
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:07:05
0:07:05
 0:13:01
0:13:01
 0:08:45
0:08:45
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:02:28
0:02:28
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:33:25
0:33:25
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:02:33
0:02:33
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:18:38
0:18:38
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:04:22
0:04:22