filmov
tv
Types of Tissues | The Tissue Level of Organization | Unit 1: Levels of Organization

Показать описание
The human body contains more than 200 types of cells that can all be classified into
four types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues
act as coverings controlling the movement of materials across the surface. Connective
tissue integrates the various parts of the body and provides support and protection to
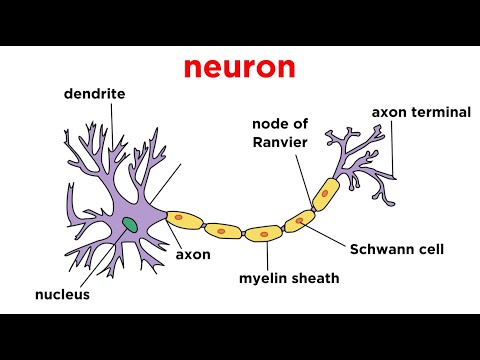
organs. Muscle tissue allows the body to move. Nervous tissues propagate
information.
The study of the shape and arrangement of cells in tissue is called
histology. All cells and tissues in the body derive from three germ layers in the embryo:
the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Different types of tissues form membranes that
enclose organs, provide a friction-free interaction between organs, and keep organs
together. Synovial membranes are connective tissue membranes that protect and line the
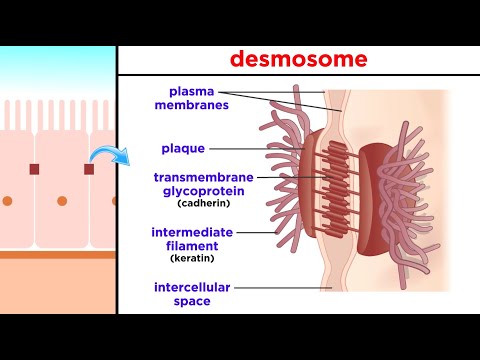
joints. Epithelial membranes are formed from epithelial tissue attached to a layer of
connective tissue. There are three types of epithelial membranes: mucous, which contain
glands; serous, which secrete fluid; and cutaneous which makes up the skin.
00:00 Types of Tissues
01:12 The four types of tissues
02:41 Embryonic origin of tissues
04:04 Tissue membranes
04:36 Connective tissue membranes
05:33 Epithelial membranes
07:57 Chapter review
Attribution: OpenStax, Anatomy & Physiology Book
four types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Epithelial tissues
act as coverings controlling the movement of materials across the surface. Connective
tissue integrates the various parts of the body and provides support and protection to
organs. Muscle tissue allows the body to move. Nervous tissues propagate
information.
The study of the shape and arrangement of cells in tissue is called
histology. All cells and tissues in the body derive from three germ layers in the embryo:
the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Different types of tissues form membranes that
enclose organs, provide a friction-free interaction between organs, and keep organs
together. Synovial membranes are connective tissue membranes that protect and line the
joints. Epithelial membranes are formed from epithelial tissue attached to a layer of
connective tissue. There are three types of epithelial membranes: mucous, which contain
glands; serous, which secrete fluid; and cutaneous which makes up the skin.
00:00 Types of Tissues
01:12 The four types of tissues
02:41 Embryonic origin of tissues
04:04 Tissue membranes
04:36 Connective tissue membranes
05:33 Epithelial membranes
07:57 Chapter review
Attribution: OpenStax, Anatomy & Physiology Book
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:05:12
0:05:12
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:09:24
0:09:24
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:16:00
0:16:00
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:08:29
0:08:29
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:24:38
0:24:38
 0:03:13
0:03:13
 0:37:43
0:37:43
 0:11:03
0:11:03
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:06:49
0:06:49
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:18:45
0:18:45