filmov
tv
Integral of sin^4x

Показать описание
This calculus video tutorial explains how to find the integral of sin^4x using the power reducing formulas and pythagorean identities found in trigonometry.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Integral of sin^4(x)
Integral of sin^4x
Integral of sin(4x)
How to Integrate sin(4x) | Calculus Integrals #shorts
Class 12th – Integral of Sin^4 x dx | Integrals | Tutorials Point
Integral of sin^4x | Calculus 2 Exercises
Integral of ∫ sin(4x) / cos^4(x) dx
Integration of sin^4 x
Integration Super Method for sin 4 power x | sin^4 x Integration | kamaldheeriya
int[sin^4(x)]
What is the Integration of sin4x || Sin4x Integration || How to integrate sin4x
The Integral of sin(2x)/sin(4x)
Integral of sec(cos(4x))sin(4x) Calculus U Substitution Video
How to Integrate sin4x
How to integrate ∫sin^4(x)cos^2(x)dx - even powers
Evaluate the following integrals : ` int sin^(4) x dx `
Maths: Integration of sin4x in Hindi
Integral of sin4x
Find the integral of sin^4x using the power reduction formula
CLASS 12 | Integral sin^4x dx | Integral cos^4x dx |previous year questions | in malayalam |
Trigonometric Integrals
Integral of sin 2x sin 4x dx
integration of sin^4x
integral of sin(4x - 1) / 1 - sin²(4x - 1) dx
Комментарии
 0:06:24
0:06:24
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:02:55
0:02:55
![int[sin^4(x)]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Lwmn-ZTCBMI/hqdefault.jpg) 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:01:23
0:01:23
 0:08:08
0:08:08
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:01:33
0:01:33
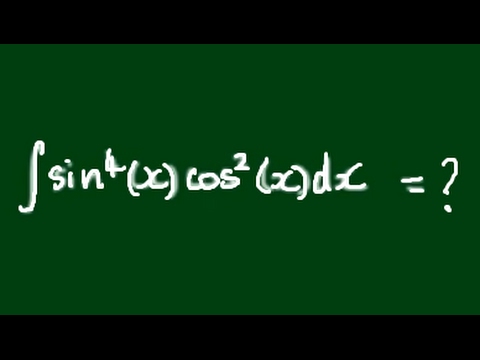 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:04:34
0:04:34
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:05:30
0:05:30
 0:12:04
0:12:04
 0:31:29
0:31:29
 0:01:29
0:01:29
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:03:28
0:03:28