filmov
tv
The effect of electrowetting
Показать описание
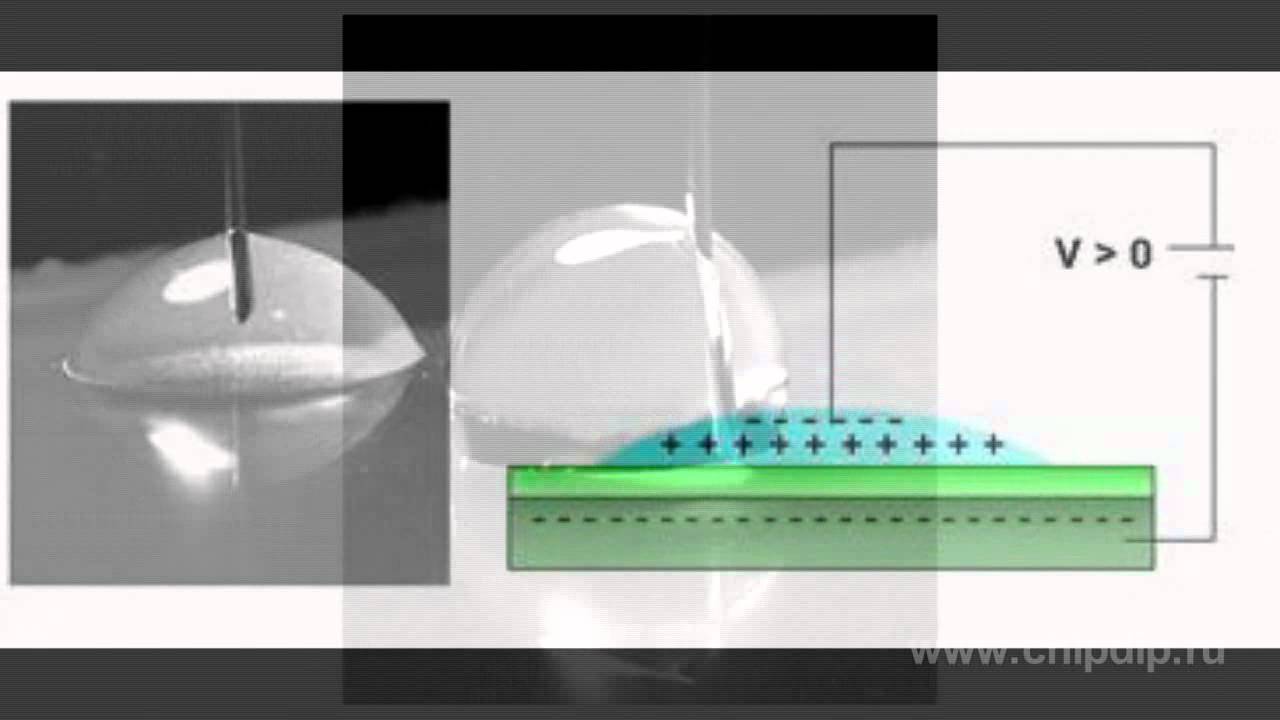
The effect of electrowettingThe electrowetting effect is a variation of the surface wetting coefficient under the influence of an electric field or a current. This effect was discovered in the second half of 19th century by French physicist Gabriel Lippmann.Its essence is as follows: a drop of water is placed on the metal substrate covered with a thin water-repellent layer of dielectric. Due to the forces of surface tension, a liquid drop on the water-repelling surface takes a form close to spherical.If electric potential difference is applied to the electrode inside the droplet and to the electrode under the water-repellent insulator, the surface wettability somewhat dramatically increases, and the drop will be spread. After the removal of the voltage, the drop again will gather into a ball. And so on to infinity. However, this technology has not found a practical application.Further development of this technology was the placement in a closed space of 2 immiscible liquids (water and coated oil) having a different density, and water-repellent dielectric.There is a transparent electrode at the bottom, and water acts as the upper electrode. Under normal conditions, a drop of oil spreads over the entire surface, forming a film on the water under the influence of surface tension. If, however, an electric field of sufficient magnitude is created, the oil will gather in a drop, vacating the major part of the water surface.When there is no voltage, a dark spot forms, because the oil film poorly reflects the incident light. When the voltage is applied, the spot is light, as the oil relieves the most part of the surface. The higher the applied voltage, the more compressed the "ink" drop.Electrowetting technology can operate in the modes of light transmission, transparency, reflection, and translucency and allows to create saturated, full-colour displays with low power consumption.
Комментарии
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:01:12
0:01:12
 0:02:48
0:02:48
 0:00:38
0:00:38
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:10:09
0:10:09
 0:00:07
0:00:07
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:00:40
0:00:40
 0:25:02
0:25:02
 0:01:39
0:01:39
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:10:07
0:10:07
 0:00:55
0:00:55
 0:00:23
0:00:23