filmov
tv
Thermal conductivity humidity sensors
Показать описание
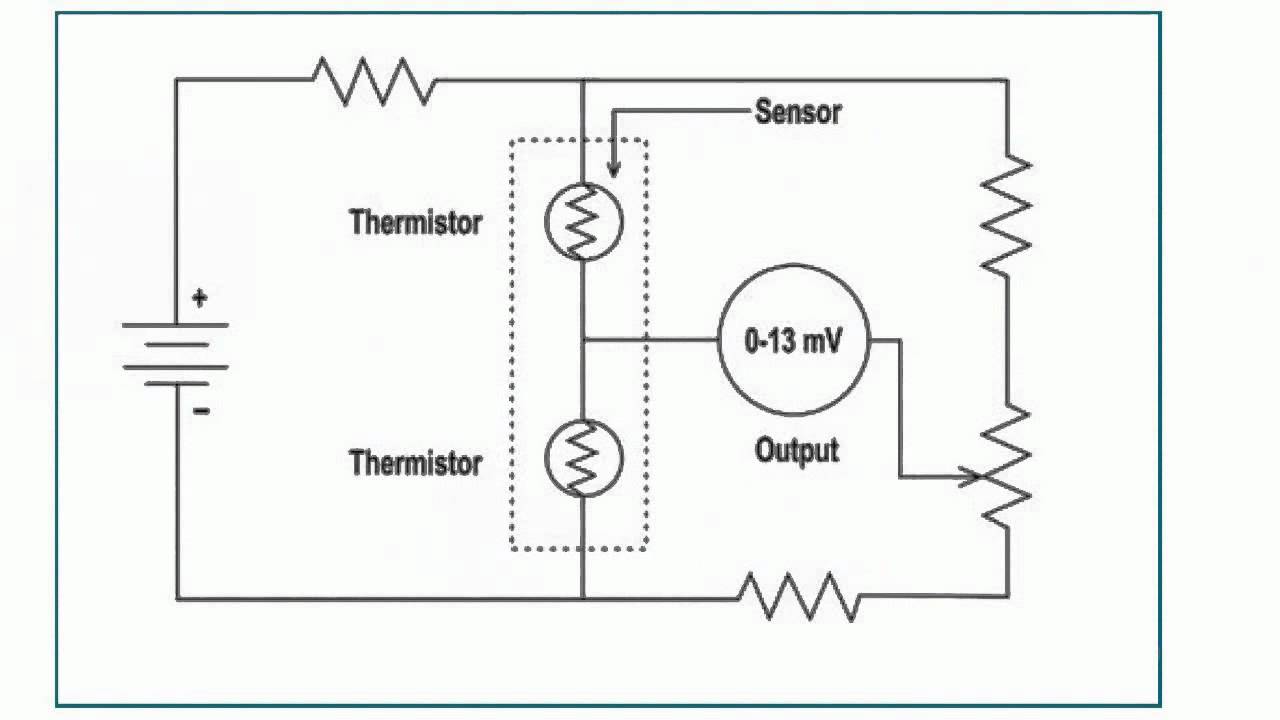
Thermal conductivity humidity sensors Thermal conductivity humidity sensors measure the absolute humidity by calculating the difference between the thermal conductivity of dry air and the air, containing moisture. When the air is dry, it has larger heat capacity, in other words, the ability to absorb heat.For example, in the desert where the air is dry, the nights are quite cold, because dry air absorbs heat. At the same time, in a humid climate the difference between day and night temperatures is negligible, as the heat is stored by the atmospheric moisture.Thermal humidity sensors consist of two thermistors with a negative temperature coefficient, which are included in the bridge circuit. At the same time, one of them is in a sealed glass casing, inside of which there is nitrogen. The second sensor is open for the effects of the ambient conditions. When a current passes through the thermistors, their temperature reaches 200 degrees.There will be more heat dissipated by a closed thermistor than by an open one, because of the difference in thermal conductivity of water vapour compared to dry nitrogen. Therefore, the operating temperatures of both thermistors will be different, which leads to the difference in their resistances and results in the bridge unbalance.Thermal humidity sensors can operate at the temperatures up to 300 degrees. They are insensitive to chemical vapours, because they are covered with inert materials. It should also be noted that the accuracy of thermal humidity sensors depends on the ambient temperature. The calibration of thermal sensors is made by placing an open thermistor in dry air or nitrogen, or by balancing the bridge.
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:11:37
0:11:37
 0:21:44
0:21:44
 0:09:32
0:09:32
 0:05:01
0:05:01
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:11:42
0:11:42
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:21:11
0:21:11
 0:41:30
0:41:30
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:09:17
0:09:17
 0:18:58
0:18:58
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:00:46
0:00:46
 0:02:55
0:02:55
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:00:41
0:00:41
 0:29:04
0:29:04
 0:00:35
0:00:35
 0:03:40
0:03:40