filmov
tv
Authentication - 6 : User Authentication
Показать описание
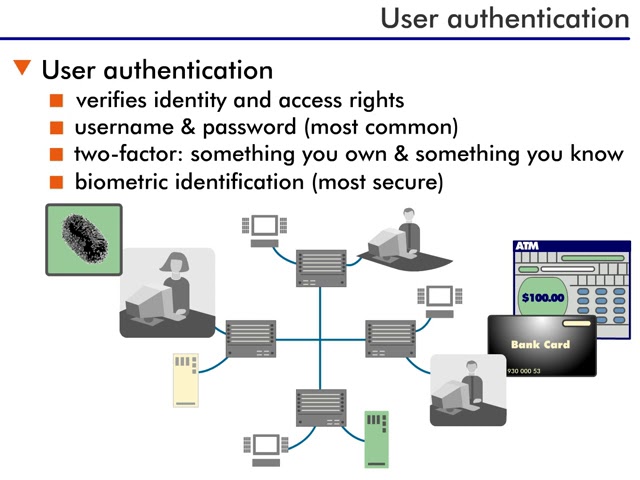
Let's take a look at the different ways that networks use authentication. The first method is user authentication. This takes place when a user logs on to the network. Authentication ensures that specific people have specific permissions once they are on the network. For example, on a school's network, students are not able to access the portion of the network that stores everyone's grades, though they can reach other areas of the network. And a visitor to the school cannot access the network at all.
There are different forms of user authentication, but the most common is a username coupled with a password. In this case, the network administrator assigns you a username and password to get on the network. You may be able to change your password to something that only you know.
A more complex method of authentication is called two-factor identification. To logon using this method, you need to supply two things: something you own and something you know. The thing that you own can be a key, a card, or some other physical object, and the thing you know is a password. An example of this type of authentication in the real world is bank ATM cards. To log into your account and withdraw money at an ATM machine, you must use both your card and your PIN or password.
Finally, the most complex and most secure form of authentication is biometric identification. You may have seen this type of identification in futuristic movies, but it's becoming more prevalent in highly secure environments today. Biometrics involves identifying some part of your body, whether it is your fingerprint, hand print, retina, or the sound of your voice.
You can probably see why this is the most secure form of authentication - it is possible to guess someone's password, but not so easy to fake someone's retinal scan or fingerprint.
There are different forms of user authentication, but the most common is a username coupled with a password. In this case, the network administrator assigns you a username and password to get on the network. You may be able to change your password to something that only you know.
A more complex method of authentication is called two-factor identification. To logon using this method, you need to supply two things: something you own and something you know. The thing that you own can be a key, a card, or some other physical object, and the thing you know is a password. An example of this type of authentication in the real world is bank ATM cards. To log into your account and withdraw money at an ATM machine, you must use both your card and your PIN or password.
Finally, the most complex and most secure form of authentication is biometric identification. You may have seen this type of identification in futuristic movies, but it's becoming more prevalent in highly secure environments today. Biometrics involves identifying some part of your body, whether it is your fingerprint, hand print, retina, or the sound of your voice.
You can probably see why this is the most secure form of authentication - it is possible to guess someone's password, but not so easy to fake someone's retinal scan or fingerprint.
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:07:30
0:07:30
 0:10:17
0:10:17
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 0:14:59
0:14:59
 0:47:15
0:47:15
 0:01:59
0:01:59
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:20:28
0:20:28
 0:22:50
0:22:50
 0:11:03
0:11:03
 0:11:10
0:11:10
 2:05:52
2:05:52
 0:05:49
0:05:49
 0:17:27
0:17:27
 0:55:49
0:55:49
 0:15:18
0:15:18
 0:51:48
0:51:48
 0:39:01
0:39:01
 0:50:56
0:50:56
 0:22:14
0:22:14
 0:02:12
0:02:12
 1:44:37
1:44:37
 0:16:11
0:16:11