filmov
tv
Graph a polynomial by finding the x-intercepts

Показать описание
Graph a polynomial by finding the x-intercepts
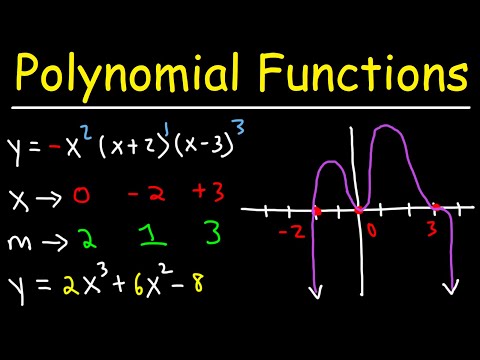
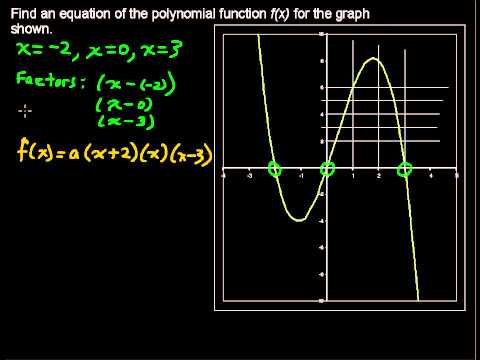
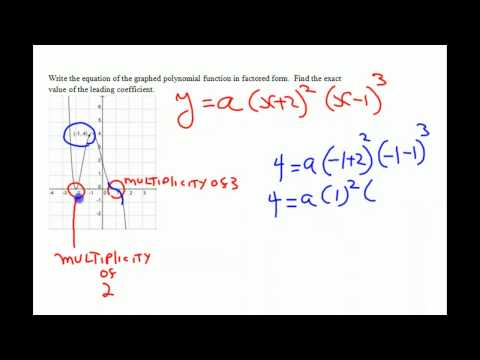
In this lesson you will learn to graph a polynomial by finding the x-intercepts.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.HSF-IF.C.7.c Graph polynomial functions, identifying zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing end behavior.
TEKS.A2.2.A graph the functions 𝑓(𝑥)=√𝑥, 𝑓(𝑥)=1/𝑥, 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑥³, 𝑓(𝑥)= ³√𝑥, 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑏 to the 𝑥 power, 𝑓(𝑥)=|𝑥|, and 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑏 (𝑥) where 𝑏 is 2, 10, and 𝑒, and, when applicable, analyze the key attributes such as domain, range, intercepts, symmetries, asymptotic behavior, and maximum and minimum given an interval;
TEKS.A1.7.A graph quadratic functions on the coordinate plane and use the graph to identify key attributes, if possible, including 𝑥-intercept, 𝑦-intercept, zeros, maximum value, minimum values, vertex, and the equation of the axis of symmetry;
IN.AII.PR.2 Graph relations and functions including polynomial, square root, and piecewise-defined functions (including step functions and absolute value functions) with and without technology. Identify and describe features, such as intercepts, zeros, domain and range, end behavior, and lines of symmetry.
VA.F.AII.6.b use knowledge of transformations to convert between equations and the corresponding graphs of functions.
VA.F.AII.8 The student will investigate and describe the relationships among solutions of an equation, zeros of a function, x-intercepts of a graph, and factors of a polynomial expression.
VA.F.A.7.f connections between and among multiple representations of functions using verbal descriptions, tables, equations, and graphs.
In this lesson you will learn to graph a polynomial by finding the x-intercepts.
ADDITIONAL MATERIALS
STANDARDS
CCSS.HSF-IF.C.7.c Graph polynomial functions, identifying zeros when suitable factorizations are available, and showing end behavior.
TEKS.A2.2.A graph the functions 𝑓(𝑥)=√𝑥, 𝑓(𝑥)=1/𝑥, 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑥³, 𝑓(𝑥)= ³√𝑥, 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑏 to the 𝑥 power, 𝑓(𝑥)=|𝑥|, and 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑏 (𝑥) where 𝑏 is 2, 10, and 𝑒, and, when applicable, analyze the key attributes such as domain, range, intercepts, symmetries, asymptotic behavior, and maximum and minimum given an interval;
TEKS.A1.7.A graph quadratic functions on the coordinate plane and use the graph to identify key attributes, if possible, including 𝑥-intercept, 𝑦-intercept, zeros, maximum value, minimum values, vertex, and the equation of the axis of symmetry;
IN.AII.PR.2 Graph relations and functions including polynomial, square root, and piecewise-defined functions (including step functions and absolute value functions) with and without technology. Identify and describe features, such as intercepts, zeros, domain and range, end behavior, and lines of symmetry.
VA.F.AII.6.b use knowledge of transformations to convert between equations and the corresponding graphs of functions.
VA.F.AII.8 The student will investigate and describe the relationships among solutions of an equation, zeros of a function, x-intercepts of a graph, and factors of a polynomial expression.
VA.F.A.7.f connections between and among multiple representations of functions using verbal descriptions, tables, equations, and graphs.
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:20:28
0:20:28
 0:09:15
0:09:15
 0:04:03
0:04:03
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:19:43
0:19:43
 0:10:34
0:10:34
 0:07:59
0:07:59
 0:04:13
0:04:13
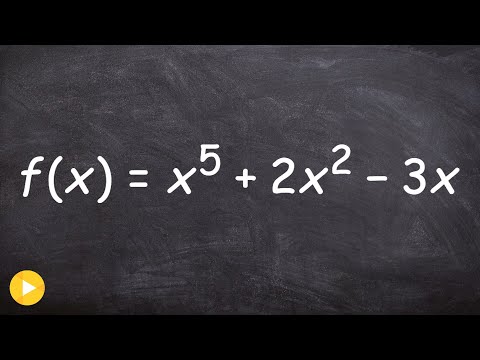 0:04:24
0:04:24
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:04:05
0:04:05
 0:03:32
0:03:32
 0:01:53
0:01:53
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:12:18
0:12:18
 0:12:53
0:12:53
 0:06:18
0:06:18