filmov
tv
Positron | Wikipedia audio article

Показать описание
This is an audio version of the Wikipedia Article:
Positron
00:00:40 1 History
00:00:48 1.1 Theory
00:04:28 1.2 Experimental clues and discovery
00:06:27 2 Natural production
00:09:21 2.1 Observation in cosmic rays
00:11:47 3 Artificial production
00:12:28 4 Applications
00:13:35 5 See also
Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago.
Learning by listening is a great way to:
- increases imagination and understanding
- improves your listening skills
- improves your own spoken accent
- learn while on the move
- reduce eye strain
Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone.
You can find other Wikipedia audio articles too at:
You can upload your own Wikipedia articles through:
"The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing."
- Socrates
SUMMARY
=======
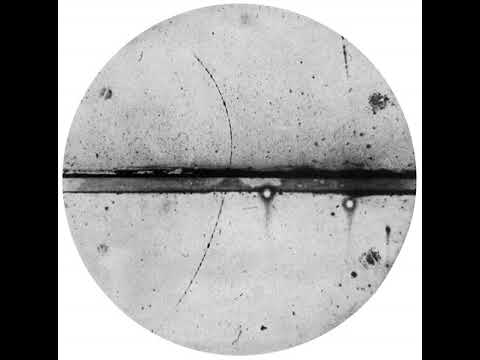
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. The positron has an electric charge of +1 e, a spin of 1/2 (same as electron), and has the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more gamma ray photons (see electron–positron annihilation).
Positrons can be created by positron emission radioactive decay (through weak interactions), or by pair production from a sufficiently energetic photon which is interacting with an atom in a material.
Positron
00:00:40 1 History
00:00:48 1.1 Theory
00:04:28 1.2 Experimental clues and discovery
00:06:27 2 Natural production
00:09:21 2.1 Observation in cosmic rays
00:11:47 3 Artificial production
00:12:28 4 Applications
00:13:35 5 See also
Listening is a more natural way of learning, when compared to reading. Written language only began at around 3200 BC, but spoken language has existed long ago.
Learning by listening is a great way to:
- increases imagination and understanding
- improves your listening skills
- improves your own spoken accent
- learn while on the move
- reduce eye strain
Now learn the vast amount of general knowledge available on Wikipedia through audio (audio article). You could even learn subconsciously by playing the audio while you are sleeping! If you are planning to listen a lot, you could try using a bone conduction headphone, or a standard speaker instead of an earphone.
You can find other Wikipedia audio articles too at:
You can upload your own Wikipedia articles through:
"The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing."
- Socrates
SUMMARY
=======
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. The positron has an electric charge of +1 e, a spin of 1/2 (same as electron), and has the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more gamma ray photons (see electron–positron annihilation).
Positrons can be created by positron emission radioactive decay (through weak interactions), or by pair production from a sufficiently energetic photon which is interacting with an atom in a material.
 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:33:21
0:33:21
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:18:17
0:18:17
 0:29:28
0:29:28
 0:18:17
0:18:17
 0:29:29
0:29:29
 0:09:10
0:09:10
 0:01:49
0:01:49
 0:03:07
0:03:07
 0:00:45
0:00:45
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:07:29
0:07:29
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:05:21
0:05:21
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:03:54
0:03:54
 0:09:09
0:09:09
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:00:47
0:00:47