filmov
tv
Transport of Water and Salts in Plants - Science
Показать описание
Transport of Water and Salts in Plants
The cells present in the soil dissolve in the water resulting in a salt solution when the soil is watered.
The amount of water provided to the soil is quite large; the solution will be dilute salt solution.
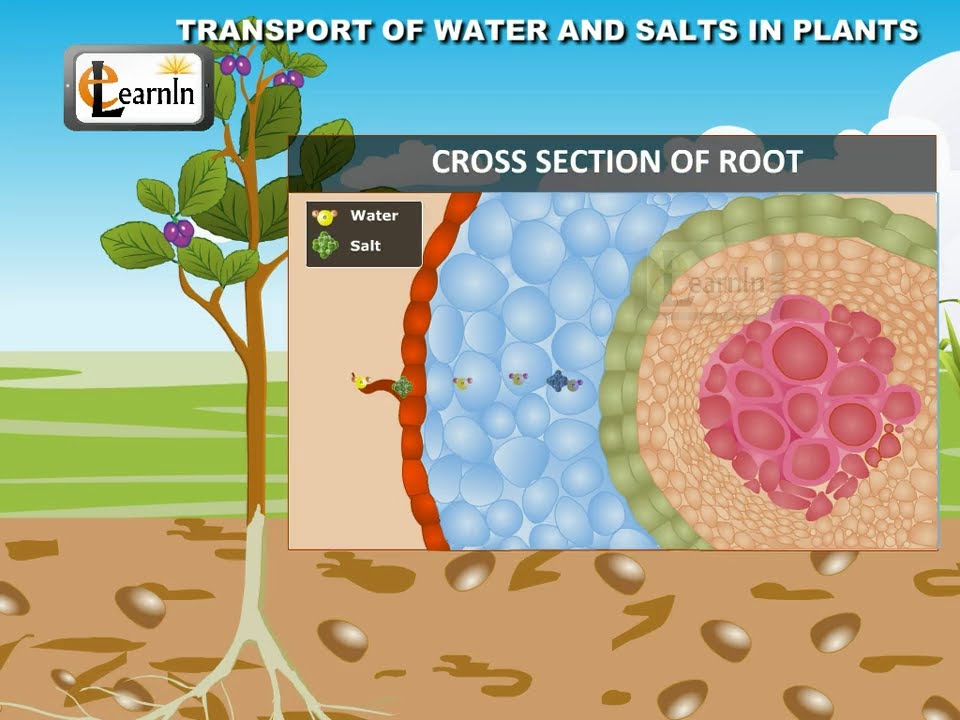
Roots of plants have some hair like structures called Root hairs originating from cells of single layer epidermis. Dissolved salts are present in the cytoplasm of these cells, also called as CellSap. Cell sap is much concentrated than the salt solution present in the soil. Cell sap is also a salt solution. However it is much concentrated than the salt solution present in the soil.
Cell membrane of the root hair is a semi permeable membrane and it separates the cell sap which is the concentrated salt solution from the salt solution in the soil which is the dilute salt solution.
Water flows along with solutes from the soil into the cell sap in the root hairs. Thus roots absorb water and salts from the process of osmosis. The absorbed water and the salts move to the next cell once again by Osmosis. The movement of the water from roots to the parts of the plant above the ground is called ASCENT OF SAP.
Water is transported from the roots to the leaves through Xylem vessels.
Water and salts from the root hairs pass into the epidermal cells then to the cortical cells then to Endodermis cells and finally into Xylem.
The transport of water from roots to the leaves is aided by the physical and chemical properties of water and the composition of the walls of the Xylem vessels.
These vessels are made of lignin and cellulose which have strong, attraction for water molecules.
A thin continuous layer of water Is formed in the walls of xylem vessels. This is because of strong attraction (or) adhesive force between water molecules.
Between water molecules there is a strong attraction (or) cohesive force due to formation of hydrogen bond between water molecules.
Because of this thousands and thousands of water molecules attach to the water molecules present on the walls. Thus forming a continues column of water molecules.
The water molecules already present in the water column either get displaced or moved by the newly entering water molecules, ultimately pushing water towards the leaves.
Root Pressure is the pressure exerted by the water molecules absorbed by the root hairs.
The cells present in the soil dissolve in the water resulting in a salt solution when the soil is watered.
The amount of water provided to the soil is quite large; the solution will be dilute salt solution.
Roots of plants have some hair like structures called Root hairs originating from cells of single layer epidermis. Dissolved salts are present in the cytoplasm of these cells, also called as CellSap. Cell sap is much concentrated than the salt solution present in the soil. Cell sap is also a salt solution. However it is much concentrated than the salt solution present in the soil.
Cell membrane of the root hair is a semi permeable membrane and it separates the cell sap which is the concentrated salt solution from the salt solution in the soil which is the dilute salt solution.
Water flows along with solutes from the soil into the cell sap in the root hairs. Thus roots absorb water and salts from the process of osmosis. The absorbed water and the salts move to the next cell once again by Osmosis. The movement of the water from roots to the parts of the plant above the ground is called ASCENT OF SAP.
Water is transported from the roots to the leaves through Xylem vessels.
Water and salts from the root hairs pass into the epidermal cells then to the cortical cells then to Endodermis cells and finally into Xylem.
The transport of water from roots to the leaves is aided by the physical and chemical properties of water and the composition of the walls of the Xylem vessels.
These vessels are made of lignin and cellulose which have strong, attraction for water molecules.
A thin continuous layer of water Is formed in the walls of xylem vessels. This is because of strong attraction (or) adhesive force between water molecules.
Between water molecules there is a strong attraction (or) cohesive force due to formation of hydrogen bond between water molecules.
Because of this thousands and thousands of water molecules attach to the water molecules present on the walls. Thus forming a continues column of water molecules.
The water molecules already present in the water column either get displaced or moved by the newly entering water molecules, ultimately pushing water towards the leaves.
Root Pressure is the pressure exerted by the water molecules absorbed by the root hairs.
Комментарии
 0:03:52
0:03:52
 0:03:49
0:03:49
 0:04:52
0:04:52
 0:03:09
0:03:09
 0:02:01
0:02:01
 0:04:13
0:04:13
 0:58:14
0:58:14
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:11:17
0:11:17
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:09:50
0:09:50
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:01:51
0:01:51
 0:02:42
0:02:42
 0:08:24
0:08:24
 0:05:20
0:05:20
 0:00:28
0:00:28
 0:18:09
0:18:09
 0:11:13
0:11:13
 0:03:03
0:03:03
 0:17:17
0:17:17
 0:08:14
0:08:14