filmov
tv
Understanding Spectrum Analyzers – Noise Figure

Показать описание
This video provides a brief technical introduction to noise figure measurements using a spectrum analyzer and the Y-factor method.
Timeline:
00:00 Introduction
00:13 About signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
01:05 Ideal device
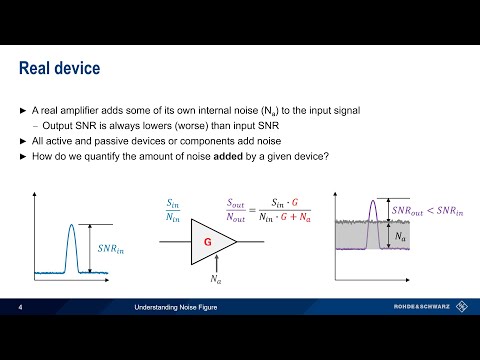
01:43 Real device
02:28 Defining noise figure
03:09 About noise figure (NF)
04:06 Measuring noise figure
05:15 The Y factor method
06:04 Two steps in the Y factor method
06:46 Details of the Y factor method
08:03 Additional NF measurement topics
08:29 About noise sources and ENR
09:56 About preamplifiers and NF measurements
10:54 About noise figure measurement uncertainty
11:58 About cascaded noise figure
13:28 Summary
Timeline:
00:00 Introduction
00:13 About signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
01:05 Ideal device
01:43 Real device
02:28 Defining noise figure
03:09 About noise figure (NF)
04:06 Measuring noise figure
05:15 The Y factor method
06:04 Two steps in the Y factor method
06:46 Details of the Y factor method
08:03 Additional NF measurement topics
08:29 About noise sources and ENR
09:56 About preamplifiers and NF measurements
10:54 About noise figure measurement uncertainty
11:58 About cascaded noise figure
13:28 Summary
Understanding Spectrum Analyzers – Noise Figure
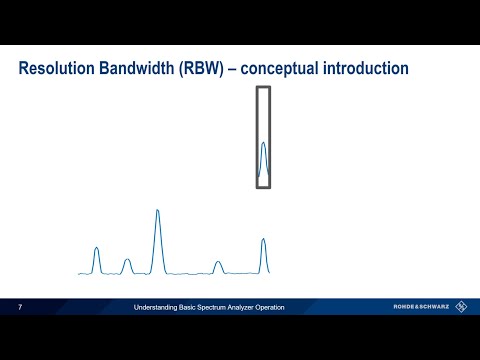
Understanding Basic Spectrum Analyzer Operation
R&S FSW Signal and Spectrum Analyzer, Measuring noise figure and gain
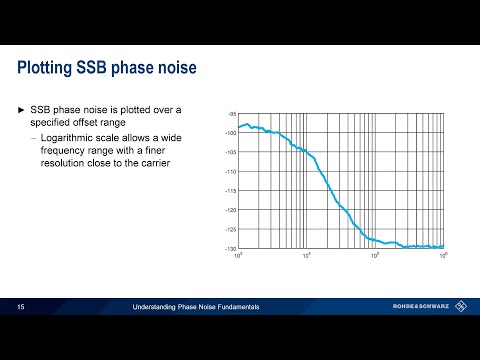
Understanding Phase Noise Fundamentals
Understanding Phase Noise - the Spectrum Analyzer Method
Understanding Spectrum Analyzers – DANL
How to use a Spectrum Analyzer; techniques, controls, test methods, hints & tips
Measuring Noise Figure using a Spectrum Analyzer - The Gain Method
How to Measure a Spectrum Analyzer's Phase Noise
Understanding Spectrum Analyzers - Dynamic Range
Measuring system noise
Don't Make This Mistake When Mixing With Spectrum Analyzers
Measuring Phase Noise with a Spectrum Analyzer
How To Mix With a Spectrum Analyser - SPAN Tutorial
#1542 Measuring Phase Noise
What is signal and what is noise?
Measuring At / Below Signal Analyzer Noise Floor | EXA Signal Analyzer with Multi-touch UI |Keysight
#582b Resolution Bandwidth and Noise Floor in Spectrum Analyzers
Analyzing Phase Noise with FSx-K40
Analyzing Phase Noise with the FSWP
Signal to Noise Explained in plain English. | Ham Radio For Dummies K6UDA Radio
How to Measure the Noise Floor of Your Signal Analyzer
What is a power spectrum?
INTERCEPT ANY RADIO SIGNAL!!!!
Комментарии
 0:14:53
0:14:53
 0:11:31
0:11:31
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:14:19
0:14:19
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:08:59
0:08:59
 0:10:21
0:10:21
 0:12:29
0:12:29
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:09:14
0:09:14
 0:15:55
0:15:55
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:02:57
0:02:57
 0:13:54
0:13:54
 0:16:40
0:16:40
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:07:04
0:07:04
 0:03:12
0:03:12
 0:13:04
0:13:04
 0:13:48
0:13:48
 0:16:11
0:16:11
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:10:04
0:10:04