filmov
tv
Type IV hypersensitivity (mechanism of disease)

Показать описание
This overview of Type IV hypersensitivity covers the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Destruction of pancreatic islets β cells → Type 1 diabetes mellitus →
polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, weight loss, thin appearance, fatigue, poor wound healing, infections, +/- DKA
Destruction of thyroid tissue → Hashimoto thyroiditis →
Early stage: goiter and hasitoxicosis with transient hyperthyroidism (irritability, heat intolerance, diarrhea)
Late stage: Hypothyroidism (cold intolerance, constipation, fatigue); thyroid is normal size or smaller (if fibrotic)
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR):
Drug rxn w eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): anticonvulsants, antimicrobials, HHV-6 → waxing and waning fever, diffuse rash, facial edema, LAD, eosinophilia +/- organ (liver) inflammation
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS): anticonvulsants, antibiotics, allopurinol → painful vesicles and bullae affecting 10% of skin; positive Nikolsky sign with sloughing, oral, genital involvement; conjunctivitis; flu-like symptoms, fever
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): same as SJS, but affecting 30% of skin
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): antibiotics, sulfonamides, quinolones, quinine derivatives, piroxicam (NSAID), diltiazem → hundreds of non-follicular sterile pustules in the intertriginous areas
Risk factors / SDOH
Cell / tissue damage
Vascular / flow physiology
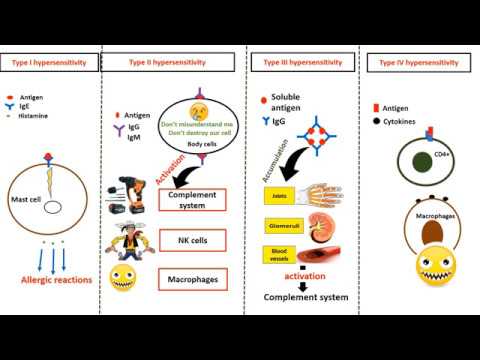
Type IV hypersensitivity
Medicine / iatrogenic
Infectious / microbial
Environment / toxins
Immunology / inflammation
Signs / symptoms
Condition / procedure / results
Diet / nutrition
Genetics / hereditary
Neoplasm / cancer
Pathophysiology
Etiology
Manifestations
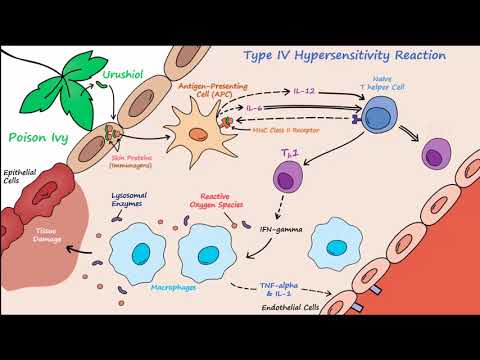
Antigen uptake into Langerhans cells
Migration to
lymph nodes
Formation of sensitized T cells
Repeated contact with antigen
Exposure to antigen
+/- skin penetration
CD4+ (helper) T cells recognize antigens on antigen-presenting cells
Release of inflammatory lymphokines / cytokines (IFNγ, TNFα)
Macrophage activation
Phagocytosis of target cells
CD8+ (killer, cytotoxic) T cells recognize antigens on somatic cells
Cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Direct destruction of target cell
Allergic contact dermatitis: allergens (metals [nickel, cobalt, chromium]. perfumes, soaps, cosmetics, plants containing urushiol [poison ivy, oak, sumac], gloves [latex], solvents, detergents) → pruritic erythematous papular rash appears after 12-48 hours; +/- oozing vesicles; pattern of rash can correspond to exposure
Tuberculin skin test (aka purified protein derivative test, Mantoux test)
Prior exposure to M. tuberculosis → purified protein derivative (PPD) injected intradermally on the forearm creates wheal → T cells stimulated and infiltrate the site of injection → large palpable induration 48-72 hours later
HLA-DRB1*15 allele, lack of HLA-A*02 allele, low vit D, cigarettes, EBV, HHV-6 → inflammation, demyelination, and axonal degeneration in the CNS → Multiple sclerosis → Impaired vision first, then intermittent exacerbations of other neuro deficits (optic gaze, posture, balance, gait, bowel/bladder function, depression, memory, concentration)
Rheumatoid arthritis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Type II hypersensitivity
Type III hypersensitivity
Organ or graft transplantation → Acute cellular rejection or Graft-versus-host disease →
Acute rejection: fever, deterioration of condition, pain over graft, graft edema, graft failure.
GvHD: Painful or itchy rash, n/v/d, abdominal pain, jaundice, HSM
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Destruction of pancreatic islets β cells → Type 1 diabetes mellitus →
polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, weight loss, thin appearance, fatigue, poor wound healing, infections, +/- DKA
Destruction of thyroid tissue → Hashimoto thyroiditis →
Early stage: goiter and hasitoxicosis with transient hyperthyroidism (irritability, heat intolerance, diarrhea)
Late stage: Hypothyroidism (cold intolerance, constipation, fatigue); thyroid is normal size or smaller (if fibrotic)
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR):
Drug rxn w eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): anticonvulsants, antimicrobials, HHV-6 → waxing and waning fever, diffuse rash, facial edema, LAD, eosinophilia +/- organ (liver) inflammation
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS): anticonvulsants, antibiotics, allopurinol → painful vesicles and bullae affecting 10% of skin; positive Nikolsky sign with sloughing, oral, genital involvement; conjunctivitis; flu-like symptoms, fever
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): same as SJS, but affecting 30% of skin
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): antibiotics, sulfonamides, quinolones, quinine derivatives, piroxicam (NSAID), diltiazem → hundreds of non-follicular sterile pustules in the intertriginous areas
Risk factors / SDOH
Cell / tissue damage
Vascular / flow physiology
Type IV hypersensitivity
Medicine / iatrogenic
Infectious / microbial
Environment / toxins
Immunology / inflammation
Signs / symptoms
Condition / procedure / results
Diet / nutrition
Genetics / hereditary
Neoplasm / cancer
Pathophysiology
Etiology
Manifestations
Antigen uptake into Langerhans cells
Migration to
lymph nodes
Formation of sensitized T cells
Repeated contact with antigen
Exposure to antigen
+/- skin penetration
CD4+ (helper) T cells recognize antigens on antigen-presenting cells
Release of inflammatory lymphokines / cytokines (IFNγ, TNFα)
Macrophage activation
Phagocytosis of target cells
CD8+ (killer, cytotoxic) T cells recognize antigens on somatic cells
Cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Direct destruction of target cell
Allergic contact dermatitis: allergens (metals [nickel, cobalt, chromium]. perfumes, soaps, cosmetics, plants containing urushiol [poison ivy, oak, sumac], gloves [latex], solvents, detergents) → pruritic erythematous papular rash appears after 12-48 hours; +/- oozing vesicles; pattern of rash can correspond to exposure
Tuberculin skin test (aka purified protein derivative test, Mantoux test)
Prior exposure to M. tuberculosis → purified protein derivative (PPD) injected intradermally on the forearm creates wheal → T cells stimulated and infiltrate the site of injection → large palpable induration 48-72 hours later
HLA-DRB1*15 allele, lack of HLA-A*02 allele, low vit D, cigarettes, EBV, HHV-6 → inflammation, demyelination, and axonal degeneration in the CNS → Multiple sclerosis → Impaired vision first, then intermittent exacerbations of other neuro deficits (optic gaze, posture, balance, gait, bowel/bladder function, depression, memory, concentration)
Rheumatoid arthritis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Type II hypersensitivity
Type III hypersensitivity
Organ or graft transplantation → Acute cellular rejection or Graft-versus-host disease →
Acute rejection: fever, deterioration of condition, pain over graft, graft edema, graft failure.
GvHD: Painful or itchy rash, n/v/d, abdominal pain, jaundice, HSM
Комментарии
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:12:47
0:12:47
 0:05:41
0:05:41
 0:02:58
0:02:58
 0:16:06
0:16:06
 0:14:10
0:14:10
 0:02:10
0:02:10
 0:06:08
0:06:08
 0:10:13
0:10:13
 0:09:01
0:09:01
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:22:03
0:22:03
 0:07:55
0:07:55
 0:03:08
0:03:08
 0:05:37
0:05:37
 0:03:26
0:03:26
 0:11:15
0:11:15
 0:23:11
0:23:11
 0:22:41
0:22:41
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:06:48
0:06:48
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:15:02
0:15:02