filmov
tv
Abstract Algebra, Lec 19B: Factor Group Applications (Cauchy's Theorem), Internal Direct Products

Показать описание
(0:00) Make sure you truly understand what it means for (left) coset multiplication to be well-defined.
(0:58) Outline the rest of the proof that the factor (quotient) group G/H is well-defined.
(4:05) The G/Z Theorem and corollaries (including example where G = D6: it turns out that D6/Z(D6) is isomorphic to D3 (and S3) and the fact that if G is a non-Abelian group of order pq, then Z(G) = {e}).
(11:08) G/Z(G) is isomorphic to Inn(G).
(12:32) Cauchy's Theorem for Abelian groups (a partial converse of Lagrange's Theorem) (a special case of the First Sylow Theorem).
(14:24) The proof uses factor groups and induction (one of the most powerful proof techniques in abstract algebra because G/H will be "smaller" than G if H is not {e}).
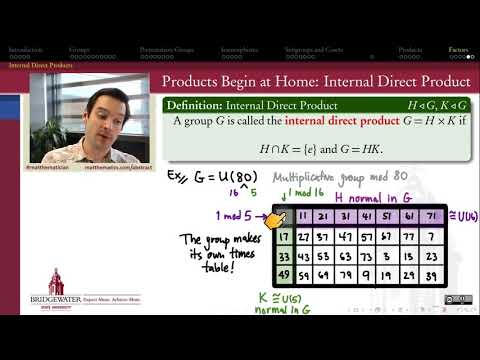
(15:55) Internal direct product (of two subgroups) definition and unique representation consequence (and discuss analog from linear algebra).
(21:22) If G = H x K, then, G is isomorphic to H + K and discuss how the isomorphism would be defined.
(23:55) General philosophy of external versus internal direct products.
(25:05) Another classification fact and corollary (groups of order p^2 are either cyclic or isomorphic to the external direct product of cyclic groups of order p, and are therefore Abelian).
(27:19) Notes about proofs to study.
AMAZON ASSOCIATE
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
 0:28:33
0:28:33
 0:33:02
0:33:02
 0:04:20
0:04:20
 0:31:00
0:31:00
 0:05:16
0:05:16
 0:23:42
0:23:42
 0:11:33
0:11:33
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:29:58
0:29:58
 0:08:15
0:08:15
 0:15:16
0:15:16
 0:13:48
0:13:48
 0:52:21
0:52:21
 0:35:02
0:35:02
 0:18:31
0:18:31
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:45:44
0:45:44
 0:17:19
0:17:19
 0:22:19
0:22:19
 0:41:59
0:41:59
 0:35:29
0:35:29
 0:26:57
0:26:57
 0:13:02
0:13:02
 0:51:07
0:51:07