filmov
tv
Blood cell production in the bone marrow| hematopoiesis animation.

Показать описание
________________________________
Watch the detailed updated video on the same topic here,
________________________________
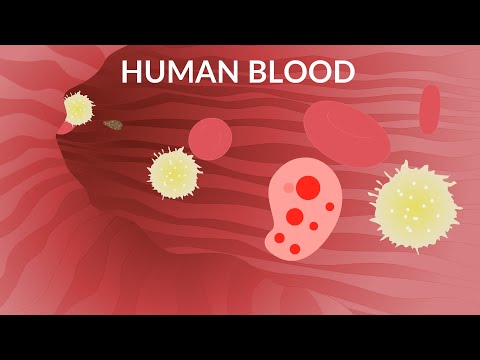
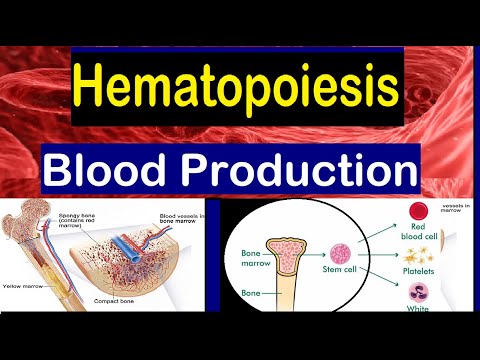
Haematopoiesis also hematopoiesis also h(a)emopoiesis) is the process of formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately 10¹¹–10¹² new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.
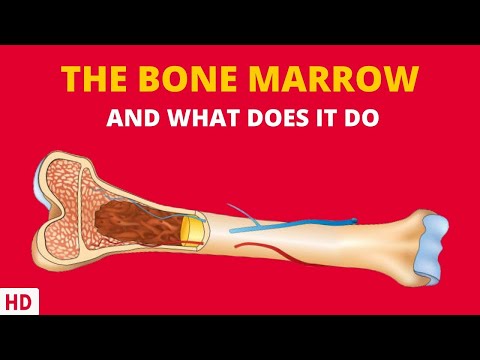
Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs, so the pool of stem cells is not depleted.This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs (myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other differentiation pathways that lead to the production of one or more specific types of blood cell, but cannot renew themselves. The pool of progenitors is heterogeneous and can be divided into two groups; long-term self-renewing HSC and only transiently self-renewing HSC, also called short-terms. This is one of the main vital processes in the body.
Cell types
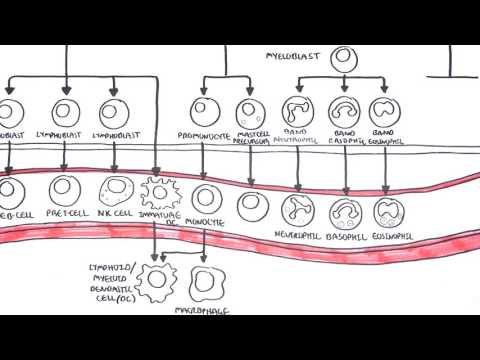
All blood cells are divided into three lineages.
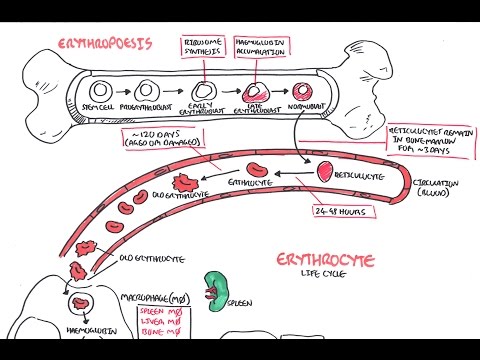
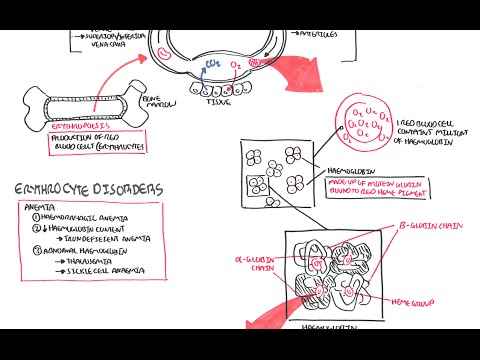
Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes, are the oxygen-carrying cells. Erythrocytes are functional and are released into the blood. The number of reticulocytes, immature red blood cells, gives an estimate of the rate of erythropoiesis.
Lymphocytes are the cornerstone of the adaptive immune system. They are derived from common lymphoid progenitors. The lymphoid lineage is composed of T-cells, B-cells and natural killer cells. This is lymphopoiesis.
Cells of the myeloid lineage, which include granulocytes, megakaryocytes and macrophages, are derived from common myeloid progenitors, and are involved in such diverse roles as innate immunity and blood clotting. This is myelopoiesis.
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is haematopoiesis of granulocytes, except of mast cells which are granulocytes but with an extramedullar maturation.
Megakaryocytopoiesis is haematopoiesis of megakaryocytes.
More detailed and comprehensive diagram
#hemopoiesis #haematopoiesis #hematopoesis
Watch the detailed updated video on the same topic here,
________________________________
Haematopoiesis also hematopoiesis also h(a)emopoiesis) is the process of formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult person, approximately 10¹¹–10¹² new blood cells are produced daily in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.
Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs, so the pool of stem cells is not depleted.This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs (myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other differentiation pathways that lead to the production of one or more specific types of blood cell, but cannot renew themselves. The pool of progenitors is heterogeneous and can be divided into two groups; long-term self-renewing HSC and only transiently self-renewing HSC, also called short-terms. This is one of the main vital processes in the body.
Cell types
All blood cells are divided into three lineages.
Red blood cells, also called erythrocytes, are the oxygen-carrying cells. Erythrocytes are functional and are released into the blood. The number of reticulocytes, immature red blood cells, gives an estimate of the rate of erythropoiesis.
Lymphocytes are the cornerstone of the adaptive immune system. They are derived from common lymphoid progenitors. The lymphoid lineage is composed of T-cells, B-cells and natural killer cells. This is lymphopoiesis.
Cells of the myeloid lineage, which include granulocytes, megakaryocytes and macrophages, are derived from common myeloid progenitors, and are involved in such diverse roles as innate immunity and blood clotting. This is myelopoiesis.
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is haematopoiesis of granulocytes, except of mast cells which are granulocytes but with an extramedullar maturation.
Megakaryocytopoiesis is haematopoiesis of megakaryocytes.
More detailed and comprehensive diagram
#hemopoiesis #haematopoiesis #hematopoesis
Комментарии
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:06:14
0:06:14
 0:29:51
0:29:51
 0:09:23
0:09:23
 0:03:25
0:03:25
 0:04:16
0:04:16
 0:06:04
0:06:04
 0:00:52
0:00:52
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:10:29
0:10:29
 0:35:58
0:35:58
 0:08:58
0:08:58
 0:15:35
0:15:35
 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:08:19
0:08:19
 0:08:26
0:08:26
 0:09:33
0:09:33
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:10:51
0:10:51
 0:16:44
0:16:44
 0:09:29
0:09:29
 0:20:15
0:20:15