filmov
tv
External ventricular drain

Показать описание
What is an external shunt?
A shunt is a long plastic tube that lets fluid drain from the brain. Doctors use shunts to relieve pressure on the brain. This pressure is usually caused by a condition called hydrocephalus. ... An external shunt, which drains CSF outside the body.
What is an EVD used for?
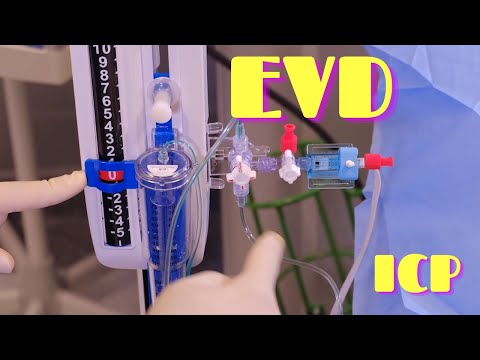
External ventricular drain (EVD): A temporary system that allows drainage of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) from the ventricles to an external closed system. Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring: A temporary device allowing measurement and recording of intracranial pressure.
What is external drainage system?
External drainage and monitoring is the temporary drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the lateral ventricles of the brain, or the lumbar space of the spine, into an external collection bag. An external ventricular drainage (EVD) system drains CSF by using a combination of gravity and intercerebral pressure.
Where should EVD be placed?
EVD placement
The EVD catheter is most frequently placed by way of a twist-drill craniostomy placed at Kocher's point, a location in the frontal bone of the skull, with the goal of placing the catheter tip in the frontal horn of the lateral ventricle or in the third ventricle.
How long does shunt surgery take?
Your VP shunt surgery will take place in the operating room while you're asleep. The surgery will take about 1 hour. Once you're asleep, the doctor will shave off some hair near the area where they'll make the incision (surgical cut) on your head.
What are the side effects of a shunt?
Some of the most common risks of CSF shunts include infection, shunt malfunction, and improper drainage. Infection from a shunt may produce symptoms such as a low-grade fever, soreness of the neck or shoulder muscles, and redness or tenderness along the shunt tract
How much should an EVD drain per hour?
Drainage should not be turned off for longer than needed, as this can cause the catheter to block. Early signs of over-drainage include headaches, and the neurosurgical team should be notified urgently if the rate of drainage exceeds 10ml per hour or a total of more than 30ml drains in one hour
How do you get rid of brain fluid?
The key treatment for hydrocephalus is a shunt. A shunt is a thin tube implanted in the brain to drain away the excess CSF to another part of the body (often the abdominal cavity, the space around the bowel) where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The CSF is controlled by a valve.
What happens if too much CSF is drained?
It is possible that the puncture of the ventricle or the opening of the dura will result in an intracranial hemorrhage. It is possible that if too much CSF is removed from the ventricles, either during a drainage procedure or when the ventricle is first punctured, the ventricle may collapse and occlude the catheter.
What is an EVD infection?
Definition of Infection. We defined EVD-related infection as (1) positive CSF culture result plus clinical symptoms or CNS pleocytosis/cell count increase, or (2) in the case of negative CSF culture, clinical symptoms, and CNS pleocytosis/cell count increase
How long does an EVD stay in?
How long will the EVD last? This varies from child to child, depending on the reason why EVD was needed in the first place. However, it is a temporary method of draining CSF and is rarely used for more than 14 days. Your child will need to stay in hospital until the drainage system is removed.
When should EVD be placed?
EVDs can be placed rapidly at the bedside in emergent situations, or they may be inserted during surgery and left in place after the operation to drain debris and blood products from the ventricles to reduce the risk of shunt dependence.
What is normal ICP?
For the purpose of this article, normal adult ICP is defined as 5 to 15 mm Hg (7.5–20 cm H2O). ICP values of 20 to 30 mm Hg represent mild intracranial hypertension; however, when a temporal mass lesion is present, herniation can occur with ICP values less than 20 mm Hg
How do EVD work?
How does the EVD work? The EVD tube connects to a collection system that lets the CSF drain into a bag hanging on a pole. The surgeon orders the pressure levels to keep the brain fluid pressure correct. Your child's nurse adjusts the EVD zero line so it's level with your child's ear.
How Serious Is shunt surgery?
Unlike most surgical procedures, in which the risks are highest during the operation itself, most of the common problems associated with shunting can and do occur at a later time. The most common complications with shunting are obstruction, infection, and overdrainage of cerebrospinal fluid.
How long are you in the hospital after shunt surgery?
Recovery from a VP shunt placement takes three to four days. Most people can leave the hospital within seven days after the procedure. During your hospitalization, the hospital staff will monitor your heart rate and blood pressure, and your doctor will administer preventive antibiotics.
A shunt is a long plastic tube that lets fluid drain from the brain. Doctors use shunts to relieve pressure on the brain. This pressure is usually caused by a condition called hydrocephalus. ... An external shunt, which drains CSF outside the body.
What is an EVD used for?
External ventricular drain (EVD): A temporary system that allows drainage of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) from the ventricles to an external closed system. Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring: A temporary device allowing measurement and recording of intracranial pressure.
What is external drainage system?
External drainage and monitoring is the temporary drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the lateral ventricles of the brain, or the lumbar space of the spine, into an external collection bag. An external ventricular drainage (EVD) system drains CSF by using a combination of gravity and intercerebral pressure.
Where should EVD be placed?
EVD placement
The EVD catheter is most frequently placed by way of a twist-drill craniostomy placed at Kocher's point, a location in the frontal bone of the skull, with the goal of placing the catheter tip in the frontal horn of the lateral ventricle or in the third ventricle.
How long does shunt surgery take?
Your VP shunt surgery will take place in the operating room while you're asleep. The surgery will take about 1 hour. Once you're asleep, the doctor will shave off some hair near the area where they'll make the incision (surgical cut) on your head.
What are the side effects of a shunt?
Some of the most common risks of CSF shunts include infection, shunt malfunction, and improper drainage. Infection from a shunt may produce symptoms such as a low-grade fever, soreness of the neck or shoulder muscles, and redness or tenderness along the shunt tract
How much should an EVD drain per hour?
Drainage should not be turned off for longer than needed, as this can cause the catheter to block. Early signs of over-drainage include headaches, and the neurosurgical team should be notified urgently if the rate of drainage exceeds 10ml per hour or a total of more than 30ml drains in one hour
How do you get rid of brain fluid?
The key treatment for hydrocephalus is a shunt. A shunt is a thin tube implanted in the brain to drain away the excess CSF to another part of the body (often the abdominal cavity, the space around the bowel) where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The CSF is controlled by a valve.
What happens if too much CSF is drained?
It is possible that the puncture of the ventricle or the opening of the dura will result in an intracranial hemorrhage. It is possible that if too much CSF is removed from the ventricles, either during a drainage procedure or when the ventricle is first punctured, the ventricle may collapse and occlude the catheter.
What is an EVD infection?
Definition of Infection. We defined EVD-related infection as (1) positive CSF culture result plus clinical symptoms or CNS pleocytosis/cell count increase, or (2) in the case of negative CSF culture, clinical symptoms, and CNS pleocytosis/cell count increase
How long does an EVD stay in?
How long will the EVD last? This varies from child to child, depending on the reason why EVD was needed in the first place. However, it is a temporary method of draining CSF and is rarely used for more than 14 days. Your child will need to stay in hospital until the drainage system is removed.
When should EVD be placed?
EVDs can be placed rapidly at the bedside in emergent situations, or they may be inserted during surgery and left in place after the operation to drain debris and blood products from the ventricles to reduce the risk of shunt dependence.
What is normal ICP?
For the purpose of this article, normal adult ICP is defined as 5 to 15 mm Hg (7.5–20 cm H2O). ICP values of 20 to 30 mm Hg represent mild intracranial hypertension; however, when a temporal mass lesion is present, herniation can occur with ICP values less than 20 mm Hg
How do EVD work?
How does the EVD work? The EVD tube connects to a collection system that lets the CSF drain into a bag hanging on a pole. The surgeon orders the pressure levels to keep the brain fluid pressure correct. Your child's nurse adjusts the EVD zero line so it's level with your child's ear.
How Serious Is shunt surgery?
Unlike most surgical procedures, in which the risks are highest during the operation itself, most of the common problems associated with shunting can and do occur at a later time. The most common complications with shunting are obstruction, infection, and overdrainage of cerebrospinal fluid.
How long are you in the hospital after shunt surgery?
Recovery from a VP shunt placement takes three to four days. Most people can leave the hospital within seven days after the procedure. During your hospitalization, the hospital staff will monitor your heart rate and blood pressure, and your doctor will administer preventive antibiotics.
Комментарии
 0:57:41
0:57:41
 0:10:04
0:10:04
 0:03:04
0:03:04
 0:00:09
0:00:09
 0:03:23
0:03:23
 0:07:34
0:07:34
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:10:14
0:10:14
 0:13:15
0:13:15
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:02:21
0:02:21
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:01:05
0:01:05
 0:21:56
0:21:56
 0:00:58
0:00:58
 0:07:46
0:07:46
 0:01:48
0:01:48
 0:04:06
0:04:06
 0:04:42
0:04:42
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:05:30
0:05:30