filmov
tv
Modal Decoupling - Explained with Example

Показать описание
Modal decoupling, normal equations, and mode superposition are concepts commonly used in structural dynamics and vibration analysis. Let's explore each of them in more detail:
Modal Decoupling:
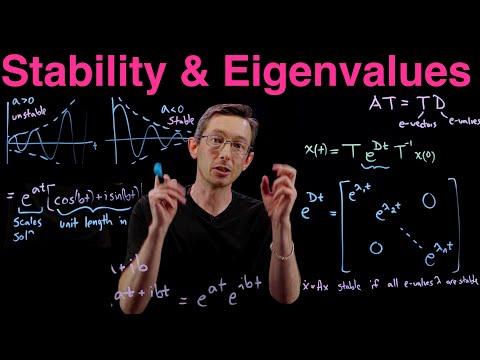
Modal decoupling is a technique used to separate the response of a complex dynamic system into individual modes or natural frequencies. In structural dynamics, a structure's response to external forces can be represented as a sum of responses of its individual modes. By decoupling these modes, engineers can analyze and understand the behavior of a structure more easily.
Modal decoupling is often achieved by transforming the equations of motion of a system into a coordinate system associated with its modes. This transformation diagonalizes the mass and stiffness matrices, resulting in decoupled equations of motion for each mode. It allows engineers to analyze the behavior of each mode independently, including its natural frequency, damping, and mode shape. Modal decoupling is particularly useful when dealing with large and complex structures where the interaction between different modes complicates the analysis.
Normal Equations:
In the context of linear regression or parameter estimation, the normal equations are a set of equations that are used to find the least squares solution to an over-determined system of linear equations. The goal is to find the best-fit parameters that minimize the sum of squared errors between the observed data and the predicted values.
The normal equations can be derived by setting the derivative of the sum of squared errors with respect to the unknown parameters to zero. Solving these equations gives the optimal values for the parameters. The normal equations provide a closed-form solution for linear regression problems, and they can be efficiently solved using various numerical methods, such as matrix factorization or iterative solvers.
Mode Superposition:
Mode superposition is a method used to calculate the dynamic response of a structure subjected to time-varying loads. It assumes that the response of the structure can be approximated as a linear combination of the responses of its individual modes.
In mode superposition, the dynamic response is calculated by combining the modal properties (natural frequencies, damping ratios, and mode shapes) of the structure with the modal participation factors and the time history of the applied loads. The modal participation factors represent the contribution of each mode to the overall response.
The mode superposition method simplifies the analysis of complex dynamic systems by reducing the number of degrees of freedom to consider. It allows engineers to estimate the response of a structure without explicitly considering the interactions between all the degrees of freedom, which can be computationally expensive for large systems.
Overall, modal decoupling, normal equations, and mode superposition are important concepts in structural dynamics and vibration analysis. They provide engineers with tools to analyze and understand the behavior of complex structures, estimate parameter values, and calculate dynamic responses efficiently.
Modal Decoupling:
Modal decoupling is a technique used to separate the response of a complex dynamic system into individual modes or natural frequencies. In structural dynamics, a structure's response to external forces can be represented as a sum of responses of its individual modes. By decoupling these modes, engineers can analyze and understand the behavior of a structure more easily.
Modal decoupling is often achieved by transforming the equations of motion of a system into a coordinate system associated with its modes. This transformation diagonalizes the mass and stiffness matrices, resulting in decoupled equations of motion for each mode. It allows engineers to analyze the behavior of each mode independently, including its natural frequency, damping, and mode shape. Modal decoupling is particularly useful when dealing with large and complex structures where the interaction between different modes complicates the analysis.
Normal Equations:
In the context of linear regression or parameter estimation, the normal equations are a set of equations that are used to find the least squares solution to an over-determined system of linear equations. The goal is to find the best-fit parameters that minimize the sum of squared errors between the observed data and the predicted values.
The normal equations can be derived by setting the derivative of the sum of squared errors with respect to the unknown parameters to zero. Solving these equations gives the optimal values for the parameters. The normal equations provide a closed-form solution for linear regression problems, and they can be efficiently solved using various numerical methods, such as matrix factorization or iterative solvers.
Mode Superposition:
Mode superposition is a method used to calculate the dynamic response of a structure subjected to time-varying loads. It assumes that the response of the structure can be approximated as a linear combination of the responses of its individual modes.
In mode superposition, the dynamic response is calculated by combining the modal properties (natural frequencies, damping ratios, and mode shapes) of the structure with the modal participation factors and the time history of the applied loads. The modal participation factors represent the contribution of each mode to the overall response.
The mode superposition method simplifies the analysis of complex dynamic systems by reducing the number of degrees of freedom to consider. It allows engineers to estimate the response of a structure without explicitly considering the interactions between all the degrees of freedom, which can be computationally expensive for large systems.
Overall, modal decoupling, normal equations, and mode superposition are important concepts in structural dynamics and vibration analysis. They provide engineers with tools to analyze and understand the behavior of complex structures, estimate parameter values, and calculate dynamic responses efficiently.
Комментарии
 0:08:31
0:08:31
 0:09:30
0:09:30
 0:25:11
0:25:11
 0:26:46
0:26:46
 1:21:52
1:21:52
 0:25:57
0:25:57
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:16:39
0:16:39
 0:27:20
0:27:20
 1:21:59
1:21:59
 1:23:02
1:23:02
 0:09:22
0:09:22
 0:10:10
0:10:10
 0:05:50
0:05:50
 0:14:53
0:14:53
 0:18:26
0:18:26
 0:53:38
0:53:38
 0:16:01
0:16:01
 0:32:53
0:32:53
 0:02:18
0:02:18
 1:11:34
1:11:34
 0:59:16
0:59:16
 0:13:08
0:13:08
 0:30:34
0:30:34