filmov
tv
Horizontal Range in Projectile Motion: Are You Defining it Correctly?

Показать описание
Projectile motion is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the study of kinematics. Understanding the horizontal range in projectile motion is crucial when analyzing the motion of objects in free fall. In this article, we will delve deeper into the topic of horizontal range in projectile motion, exploring its definition, formula, and practical examples.
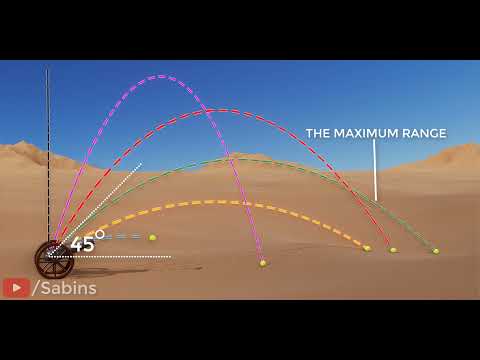
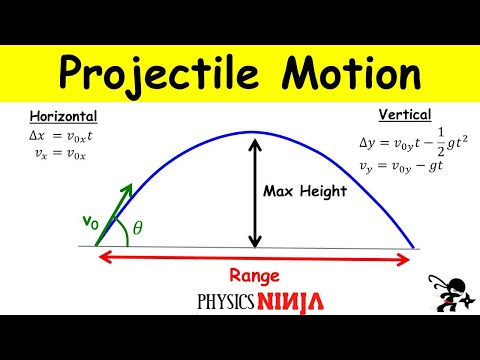
To begin with, the horizontal range refers to the horizontal distance covered by a projectile, from the point of projection to the point where it returns to the same initial height. Imagine launching a projectile, such as a ball, from an initial position of y = 0. When the ball reaches the height of y = 0 again, the distance covered horizontally is known as the horizontal range. It is important to note that the vertical motion does not affect the horizontal range, as the motion in the vertical direction is independent of the motion in the horizontal direction.
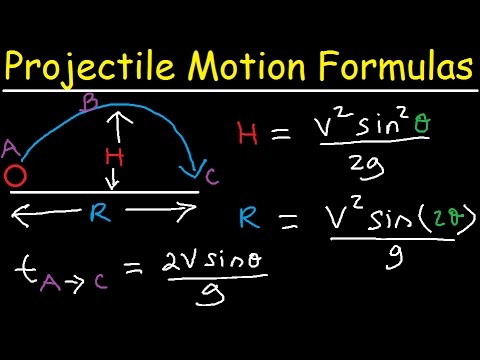
When analyzing projectile motion, it is beneficial to have a formula that relates the various parameters involved. In the case of horizontal range, the formula can be derived using the principles of kinematics. Considering that the only force acting on the projectile in the horizontal direction is the initial velocity, and there is no acceleration horizontally, the formula for horizontal range can be expressed as follows:
Horizontal Range = (Initial Velocity * Time of Flight)
The time of flight represents the total time taken by the projectile to complete its trajectory, from the moment of projection until it returns to the same initial height. By multiplying this time by the initial velocity, we obtain the horizontal range.
Let's consider a practical example to illustrate the concept of horizontal range in projectile motion. Suppose we have a cannon that fires a cannonball with an initial velocity of 50 meters per second. The cannonball reaches the same initial height after 10 seconds of flight. To calculate the horizontal range, we can apply the formula mentioned earlier:
Horizontal Range = (50 m/s * 10 s) = 500 meters
Hence, the horizontal range of the cannonball fired from the cannon is 500 meters.
Projectile motion is a fascinating topic to explore, as it offers insights into the behavior of objects moving under the influence of gravity. Understanding the horizontal range enables us to make predictions about the distance a projectile can cover horizontally, regardless of its vertical motion. It has various applications in fields such as sports, engineering, and physics.
In conclusion, the horizontal range in projectile motion refers to the horizontal distance covered by a projectile from the point of projection to the point where it returns to the same initial height. It can be calculated using the formula Horizontal Range = (Initial Velocity * Time of Flight). By comprehending the concept of horizontal range, we can analyze the motion of projectiles and make predictions about their trajectory. Whether you are studying kinematics in a class 11 physics course or exploring real-world examples of projectile motion, understanding the horizontal range is essential for a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating phenomenon.
To begin with, the horizontal range refers to the horizontal distance covered by a projectile, from the point of projection to the point where it returns to the same initial height. Imagine launching a projectile, such as a ball, from an initial position of y = 0. When the ball reaches the height of y = 0 again, the distance covered horizontally is known as the horizontal range. It is important to note that the vertical motion does not affect the horizontal range, as the motion in the vertical direction is independent of the motion in the horizontal direction.
When analyzing projectile motion, it is beneficial to have a formula that relates the various parameters involved. In the case of horizontal range, the formula can be derived using the principles of kinematics. Considering that the only force acting on the projectile in the horizontal direction is the initial velocity, and there is no acceleration horizontally, the formula for horizontal range can be expressed as follows:
Horizontal Range = (Initial Velocity * Time of Flight)
The time of flight represents the total time taken by the projectile to complete its trajectory, from the moment of projection until it returns to the same initial height. By multiplying this time by the initial velocity, we obtain the horizontal range.
Let's consider a practical example to illustrate the concept of horizontal range in projectile motion. Suppose we have a cannon that fires a cannonball with an initial velocity of 50 meters per second. The cannonball reaches the same initial height after 10 seconds of flight. To calculate the horizontal range, we can apply the formula mentioned earlier:
Horizontal Range = (50 m/s * 10 s) = 500 meters
Hence, the horizontal range of the cannonball fired from the cannon is 500 meters.
Projectile motion is a fascinating topic to explore, as it offers insights into the behavior of objects moving under the influence of gravity. Understanding the horizontal range enables us to make predictions about the distance a projectile can cover horizontally, regardless of its vertical motion. It has various applications in fields such as sports, engineering, and physics.
In conclusion, the horizontal range in projectile motion refers to the horizontal distance covered by a projectile from the point of projection to the point where it returns to the same initial height. It can be calculated using the formula Horizontal Range = (Initial Velocity * Time of Flight). By comprehending the concept of horizontal range, we can analyze the motion of projectiles and make predictions about their trajectory. Whether you are studying kinematics in a class 11 physics course or exploring real-world examples of projectile motion, understanding the horizontal range is essential for a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating phenomenon.
 0:05:27
0:05:27
 0:12:27
0:12:27
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:05:09
0:05:09
 0:02:40
0:02:40
 0:28:11
0:28:11
 0:21:09
0:21:09
 0:07:06
0:07:06
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:05:00
0:05:00
 0:28:19
0:28:19
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:08:53
0:08:53
 0:06:22
0:06:22
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:15:16
0:15:16
 0:01:42
0:01:42
 0:07:33
0:07:33
 0:15:37
0:15:37
 0:23:33
0:23:33
 0:08:16
0:08:16
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:03:29
0:03:29
 0:00:46
0:00:46