filmov
tv
Epithelial Tissue and its Types || Animal Tissues (Part 2) || in Hindi for Class 9

Показать описание
In this Science (Biology) video in Hindi for class 9th we explained the functions and working of epithelial tissue and its types. This is a topic of Chapter 6 of science from NCERT.
Animal tissues can broadly be categorized into four types, viz., epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue and nervous tissue.
𝑬𝒑𝒊𝒕𝒉𝒆𝒍𝒊𝒂𝒍 𝑻𝒊𝒔𝒔𝒖𝒆 − These are protective tissues covering most of the organs or form a barrier to keep different body system separate.
Internal organs and soft tissues of our body need protection from the external environment. So, we have protective tissues. e.g., skin, lining of mouth, inner lining of stomach, inner lining of intestine, respiratory tract. These are the examples of epithelial tissue.
→ It covers most organs and cavities within the body.
→ It forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate.
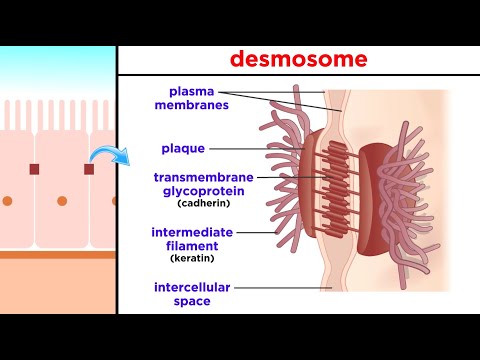
→ Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet.
→ These cells have almost no intercellular spaces and have a small amount of cementing material between them.
→ Anything entering or leaving the body must cross at least one layer of epithelium.
→ The permeability of the cells of various epithelia play an important role in regulating the exchange of materials between the body and the external environment and also between different parts of the body.
→ All glands are made up of epithelial cells.
→ All epithelium is usually separated from the underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane.
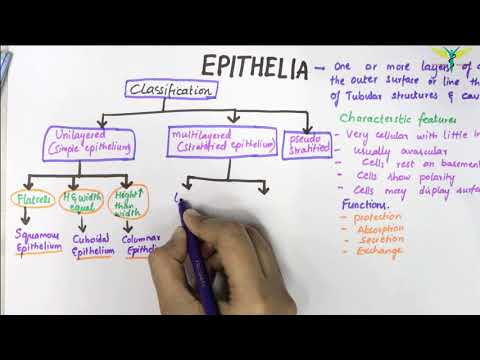
Epithelial tissue can be categorised, broadly, in three types, viz., squamous epithelium, columnar epithelium and cuboidal epithelium.
Squamous epithelium -
→ It has extremely thin and flat cells.
→ It is found in the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, lining of blood vessels, skin etc.
→ Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. This epithelium is called 𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑒𝑑 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑚𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝑒𝑝𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑢𝑚.
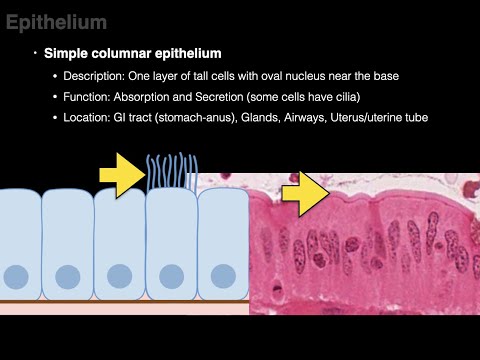
Columnar epithelium -
→ It has column like cells.
→ It is present where absorption and secretion occur.
→ It is found in the inner lining of the stomach, inner lining of the intestine, respiratory tract etc.
→ In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which can move, and their movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it. This type of epithelium is know as 𝑐𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑐𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑛𝑎𝑟 𝑒𝑝𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑢𝑚.
Cuboidal epithelium -
→ This epithelium has cube-shaped cells.
→ It performs secretion and absorption.
→ It also provides mechanical support.
→ It forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands
Sometimes a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular gland is formed. This is known as 𝑔𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑒𝑝𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑢𝑚.
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
🔴 Click here to watch the whole playlist on Chapter 6 : 'Tissues' for Class 9 :
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
Previous videos -
🔴 Tissues (Introduction)
🔴 Meristematic Tissue
🔴 Simple Permanent Tissue
🔴 Epidermis
🔴 Complex Permanent Tissue
🔴 Animal Tissues (Introduction)
**************************************
Animal tissues can broadly be categorized into four types, viz., epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue and nervous tissue.
𝑬𝒑𝒊𝒕𝒉𝒆𝒍𝒊𝒂𝒍 𝑻𝒊𝒔𝒔𝒖𝒆 − These are protective tissues covering most of the organs or form a barrier to keep different body system separate.
Internal organs and soft tissues of our body need protection from the external environment. So, we have protective tissues. e.g., skin, lining of mouth, inner lining of stomach, inner lining of intestine, respiratory tract. These are the examples of epithelial tissue.
→ It covers most organs and cavities within the body.
→ It forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate.
→ Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet.
→ These cells have almost no intercellular spaces and have a small amount of cementing material between them.
→ Anything entering or leaving the body must cross at least one layer of epithelium.
→ The permeability of the cells of various epithelia play an important role in regulating the exchange of materials between the body and the external environment and also between different parts of the body.
→ All glands are made up of epithelial cells.
→ All epithelium is usually separated from the underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane.
Epithelial tissue can be categorised, broadly, in three types, viz., squamous epithelium, columnar epithelium and cuboidal epithelium.
Squamous epithelium -
→ It has extremely thin and flat cells.
→ It is found in the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, lining of blood vessels, skin etc.
→ Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. This epithelium is called 𝑠𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑒𝑑 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑚𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝑒𝑝𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑢𝑚.
Columnar epithelium -
→ It has column like cells.
→ It is present where absorption and secretion occur.
→ It is found in the inner lining of the stomach, inner lining of the intestine, respiratory tract etc.
→ In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which can move, and their movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it. This type of epithelium is know as 𝑐𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑐𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑛𝑎𝑟 𝑒𝑝𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑢𝑚.
Cuboidal epithelium -
→ This epithelium has cube-shaped cells.
→ It performs secretion and absorption.
→ It also provides mechanical support.
→ It forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands
Sometimes a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular gland is formed. This is known as 𝑔𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑒𝑝𝑖𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑖𝑢𝑚.
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
🔴 Click here to watch the whole playlist on Chapter 6 : 'Tissues' for Class 9 :
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
Previous videos -
🔴 Tissues (Introduction)
🔴 Meristematic Tissue
🔴 Simple Permanent Tissue
🔴 Epidermis
🔴 Complex Permanent Tissue
🔴 Animal Tissues (Introduction)
**************************************
Комментарии
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:23:51
0:23:51
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:34:33
0:34:33
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 2:21:18
2:21:18
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:13:40
0:13:40
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:04:02
0:04:02
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:16:02
0:16:02
 0:16:00
0:16:00
 0:21:04
0:21:04
 0:10:43
0:10:43
 0:37:43
0:37:43
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:56:18
0:56:18
 0:06:35
0:06:35
 0:06:50
0:06:50