filmov
tv
EPITHELIUM | Classification | Basic Histology

Показать описание
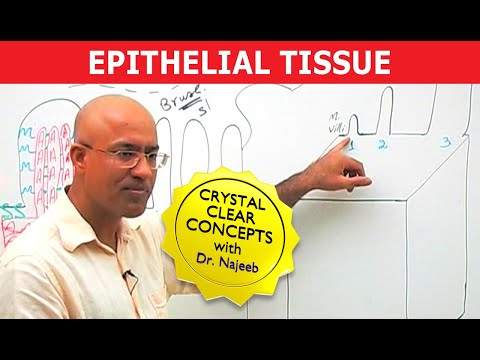
Epithelium (/ˌɛpɪˈθiːliəm/)[1] is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
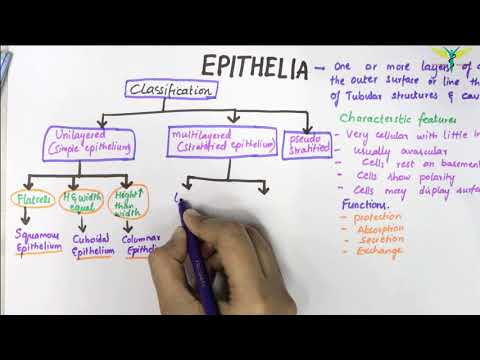
There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a single layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or compound, either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called a pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelial cells. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport, and sensing.
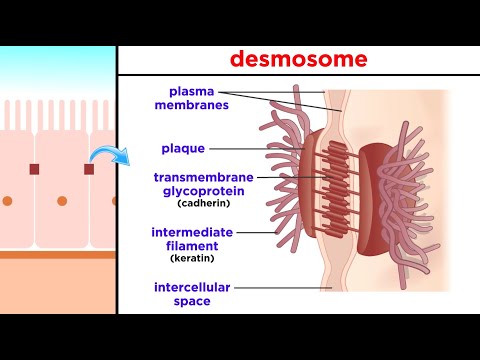
Epithelial layers contain no blood vessels, so they must receive nourishment via diffusion of substances from the underlying connective tissue, through the basement membrane.[2][3] Cell junctions are well employed in epithelial tissues.
Classification
Summary showing different epithelial cells/tissues and their characteristics.
In general, epithelial tissues are classified by the number of their layers and by the shape and function of the cells.[2][4][5]
The three principal shapes associated with epithelial cells are squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
Squamous epithelium has cells that are wider than their height (flat and scale-like). This is found as the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, and including blood vessels and in the alveoli of the lungs.
Cuboidal epithelium has cells whose height and width are approximately the same (cube shaped).
Columnar epithelium has cells taller than they are wide (column-shaped). Columnar epithelium can be further classified into ciliated columnar epithelium and glandular columnar epithelium.
By layer, epithelium is classed as either simple epithelium, only one cell thick (unilayered), or stratified epithelium having two or more cells in thickness, or multi-layered – as stratified squamous epithelium, stratified cuboidal epithelium, and stratified columnar epithelium,[6][7] and both types of layering can be made up of any of the cell shapes.[4] However, when taller simple columnar epithelial cells are viewed in cross section showing several nuclei appearing at different heights, they can be confused with stratified epithelia. This kind of epithelium is therefore described as pseudostratified columnar epithelium.[8]
Transitional epithelium has cells that can change from squamous to cuboidal, depending on the amount of tension on the epithelium.[9]
Simple epithelium
Simple epithelium is a single layer of cells with every cell in direct contact with the basement membrane that separates it from the underlying connective tissue. In general, it is found where absorption and filtration occur. The thinness of the epithelial barrier facilitates these processes.[4]
In general, simple epithelial tissues are classified by the shape of their cells. The four major classes of simple epithelium are (1) simple squamous, (2) simple cuboidal, (3) simple columnar, and (4) pseudostratified.[4]
(1) Simple squamous: Squamous epithelial cells appear scale-like, flattened, or rounded (e.g., walls of capillaries, linings of the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities, linings of the alveoli of the lungs).
(2) Simple cuboidal: These cells may have secretory, absorptive, or excretory functions. Examples include small collecting ducts of the kidney, pancreas, and salivary gland.
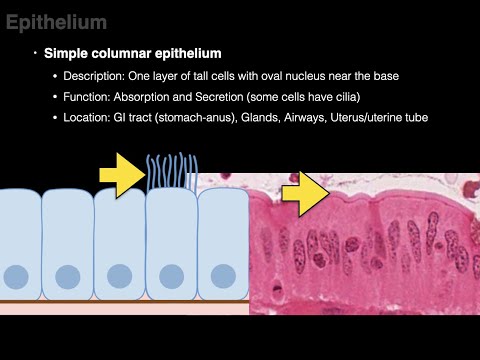
(3) Simple columnar: Cells can be secretory, absorptive, or excretory. Simple columnar epithelium can be ciliated or non-ciliated; ciliated columnar is found in the female reproductive tract and uterus. Non-ciliated epithelium can also possess microvilli. Some tissues contain goblet cells and are referred to as simple glandular columnar epithelium. These secrete mucus and are found in the stomach, colon, and rectum.
(4) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: These can be ciliated or non-ciliated. The ciliated type is also called respiratory epithelium since it is almost exclusively confined to the larger respiratory airways of the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi.
Stratified epithelium
Stratified epithelium differs from simple epithelium in that it is multilayered. It is therefore found where body linings have to withstand mechanical or chemical insult such that layers can be abraded and lost without exposing subepithelial layers. Cells flatten as the layers become more apical, though in their most basal layers, the cells can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar.[10]
Stratified epithelia (of columnar, cuboidal, or squamous type) can have the following specializations
There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a single layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or compound, either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called a pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelial cells. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective absorption, protection, transcellular transport, and sensing.
Epithelial layers contain no blood vessels, so they must receive nourishment via diffusion of substances from the underlying connective tissue, through the basement membrane.[2][3] Cell junctions are well employed in epithelial tissues.
Classification
Summary showing different epithelial cells/tissues and their characteristics.
In general, epithelial tissues are classified by the number of their layers and by the shape and function of the cells.[2][4][5]
The three principal shapes associated with epithelial cells are squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
Squamous epithelium has cells that are wider than their height (flat and scale-like). This is found as the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, and including blood vessels and in the alveoli of the lungs.
Cuboidal epithelium has cells whose height and width are approximately the same (cube shaped).
Columnar epithelium has cells taller than they are wide (column-shaped). Columnar epithelium can be further classified into ciliated columnar epithelium and glandular columnar epithelium.
By layer, epithelium is classed as either simple epithelium, only one cell thick (unilayered), or stratified epithelium having two or more cells in thickness, or multi-layered – as stratified squamous epithelium, stratified cuboidal epithelium, and stratified columnar epithelium,[6][7] and both types of layering can be made up of any of the cell shapes.[4] However, when taller simple columnar epithelial cells are viewed in cross section showing several nuclei appearing at different heights, they can be confused with stratified epithelia. This kind of epithelium is therefore described as pseudostratified columnar epithelium.[8]
Transitional epithelium has cells that can change from squamous to cuboidal, depending on the amount of tension on the epithelium.[9]
Simple epithelium
Simple epithelium is a single layer of cells with every cell in direct contact with the basement membrane that separates it from the underlying connective tissue. In general, it is found where absorption and filtration occur. The thinness of the epithelial barrier facilitates these processes.[4]
In general, simple epithelial tissues are classified by the shape of their cells. The four major classes of simple epithelium are (1) simple squamous, (2) simple cuboidal, (3) simple columnar, and (4) pseudostratified.[4]
(1) Simple squamous: Squamous epithelial cells appear scale-like, flattened, or rounded (e.g., walls of capillaries, linings of the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities, linings of the alveoli of the lungs).
(2) Simple cuboidal: These cells may have secretory, absorptive, or excretory functions. Examples include small collecting ducts of the kidney, pancreas, and salivary gland.
(3) Simple columnar: Cells can be secretory, absorptive, or excretory. Simple columnar epithelium can be ciliated or non-ciliated; ciliated columnar is found in the female reproductive tract and uterus. Non-ciliated epithelium can also possess microvilli. Some tissues contain goblet cells and are referred to as simple glandular columnar epithelium. These secrete mucus and are found in the stomach, colon, and rectum.
(4) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium: These can be ciliated or non-ciliated. The ciliated type is also called respiratory epithelium since it is almost exclusively confined to the larger respiratory airways of the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi.
Stratified epithelium
Stratified epithelium differs from simple epithelium in that it is multilayered. It is therefore found where body linings have to withstand mechanical or chemical insult such that layers can be abraded and lost without exposing subepithelial layers. Cells flatten as the layers become more apical, though in their most basal layers, the cells can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar.[10]
Stratified epithelia (of columnar, cuboidal, or squamous type) can have the following specializations
Комментарии
 0:06:50
0:06:50
 0:23:51
0:23:51
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:09:42
0:09:42
 0:08:28
0:08:28
 0:16:02
0:16:02
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:34:33
0:34:33
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:07:11
0:07:11
 0:31:30
0:31:30
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:13:40
0:13:40
 0:08:21
0:08:21
 0:09:27
0:09:27
 0:00:06
0:00:06
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:10:46
0:10:46
 0:20:16
0:20:16
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:03:18
0:03:18
 0:04:54
0:04:54