filmov
tv
How Electrical Bushings Work (Power Engineering)

Показать описание
Want to continue learning about engineering with videos like this one? Then visit:
Want to teach/instruct with the 3D models shown in this video? Then visit:
******************************************************************
Learn how electrical bushings work! Learn all of a bushing’s components, design features, and how it works! Electrical bushing’s are present throughout the power generation, transmission, distribution, and electrical engineering industries, so why not learn about them!
Like this video? Then check out our other videos!
📚Want to learn more about engineering?
Then join saVRee to access over 45 hours of engineering video courses! New courses every month!
Hope to see you on a course soon! 👋
🏫Want to use the 3D model in this video to present, instruct, or teach? Simply join saVRee! We have over 400 engineering models that will make your life a lot easier!
📱Check out our socials!
▶️Introduction
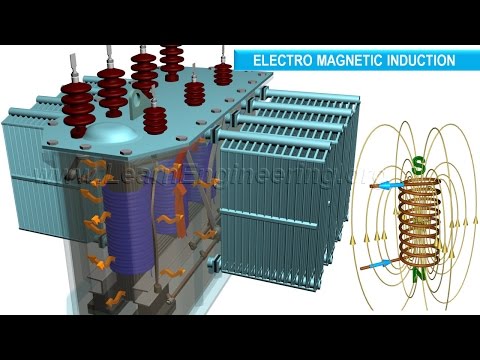
Electrical bushings allow live conductors to be passed through grounded partitions, walls, or tanks etc. without raising their electrical potential (voltage). They perform this task by insulating the central conductor.
The example used in this video shows a 3D animation of an oil insulated porcelain solid/bulk bushing; this bushing is often used with electrical transformers (hermetic and conservator type). Another common bushing design type is the condenser/capacitance graded bushing.
Bushings are commonly seen at substations, power stations and generally in the power engineering industry (generation, distribution and transmission of electricity). Bushings may be of various designs, but are roughly split into two main designs, the bulk/solid type, and the condenser (capacitor grade) type.
How Electrical Bushings Work
Electrical current flowing through a conductor will create a magnetic field and an electric field. The magnetic field is of little interest concerning bushings, but the electric field is. The electric field strength increases as the voltage potential increases. A higher voltage potential will always try to flow to a lower voltage potential e.g. ground. Bushings prevent this by insulating the conductor from the grounded component through which it passes.
Bushing Components
A bushing consists of a conductor, terminals and some form of insulator. The insulator chosen in this video is manufactured from porcelain.
Mineral oil is added to a void space surrounding the conductor and it also acts as an insulator.
To aid with keeping the bushing clean and to maintain resistance on the creepage path (leakage path), rain sheds are used.
The porcelain body is hot glazed as this puts the porcelain under compression stress, which makes it stronger mechanically. Porcelain is weak when tensile stress is applied. The glaze also helps keep the bushing clean.
**********
#saVRee_Nuggets, #saVRee
Want to teach/instruct with the 3D models shown in this video? Then visit:
******************************************************************
Learn how electrical bushings work! Learn all of a bushing’s components, design features, and how it works! Electrical bushing’s are present throughout the power generation, transmission, distribution, and electrical engineering industries, so why not learn about them!
Like this video? Then check out our other videos!
📚Want to learn more about engineering?
Then join saVRee to access over 45 hours of engineering video courses! New courses every month!
Hope to see you on a course soon! 👋
🏫Want to use the 3D model in this video to present, instruct, or teach? Simply join saVRee! We have over 400 engineering models that will make your life a lot easier!
📱Check out our socials!
▶️Introduction
Electrical bushings allow live conductors to be passed through grounded partitions, walls, or tanks etc. without raising their electrical potential (voltage). They perform this task by insulating the central conductor.
The example used in this video shows a 3D animation of an oil insulated porcelain solid/bulk bushing; this bushing is often used with electrical transformers (hermetic and conservator type). Another common bushing design type is the condenser/capacitance graded bushing.
Bushings are commonly seen at substations, power stations and generally in the power engineering industry (generation, distribution and transmission of electricity). Bushings may be of various designs, but are roughly split into two main designs, the bulk/solid type, and the condenser (capacitor grade) type.
How Electrical Bushings Work
Electrical current flowing through a conductor will create a magnetic field and an electric field. The magnetic field is of little interest concerning bushings, but the electric field is. The electric field strength increases as the voltage potential increases. A higher voltage potential will always try to flow to a lower voltage potential e.g. ground. Bushings prevent this by insulating the conductor from the grounded component through which it passes.
Bushing Components
A bushing consists of a conductor, terminals and some form of insulator. The insulator chosen in this video is manufactured from porcelain.
Mineral oil is added to a void space surrounding the conductor and it also acts as an insulator.
To aid with keeping the bushing clean and to maintain resistance on the creepage path (leakage path), rain sheds are used.
The porcelain body is hot glazed as this puts the porcelain under compression stress, which makes it stronger mechanically. Porcelain is weak when tensile stress is applied. The glaze also helps keep the bushing clean.
**********
#saVRee_Nuggets, #saVRee
Комментарии
 0:15:00
0:15:00
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:01:22
0:01:22
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:00:11
0:00:11
 0:40:30
0:40:30
 0:21:51
0:21:51
 0:03:15
0:03:15
 0:06:33
0:06:33
 0:05:48
0:05:48
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:11:09
0:11:09
 0:10:47
0:10:47
 0:00:12
0:00:12
 0:06:34
0:06:34
 0:02:53
0:02:53
 0:06:29
0:06:29
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:16:49
0:16:49
 0:02:54
0:02:54
 0:01:34
0:01:34