filmov
tv
Hypertension - Definition, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment options

Показать описание
Hypertension - Definition, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment options
In this week's video, I will be going over hypertension (high blood pressure), I will be talking about how to define hypertension, how hypertension is diagnosed, the causes of hypertension, the symptoms of hypertension and what are the certain treatment options for hypertension.
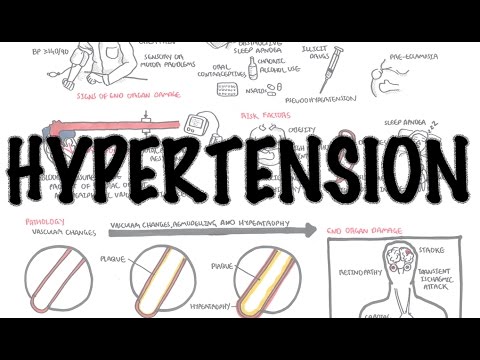
Hypertension (AKA High blood pressure) is quite literally what it says on the tin, it's having the pressure in your blood vessels be too high.
The normal range of blood pressure is 90-119 for systolic and 60-69 for diastolic.
Hypertension can be divided into two groups, the majority of people fall into the first category, which is known as primary hypertension, this type doesn't have a cure and is a result of age and lifestyle choices.
Most symptoms of hypertension do not manifest until, the pressure is very high, causing it to be known as the silent killer.
When assessing a patient with newly diagnosed hypertension, you need to check that there is no damage to the organs mentioned above, 3 investigations that need to be done are funduscopic to check for any retinopathy, Urine dipstick to check for renal disease, ECG to check for left ventricular hypertrophy and Ischemic heart disease. HbA1c to check for diabetes as that is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease and check lipids for similar reasons.
The first type of treatment of hypertension is lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, exercising, eating less salt, stopping smoking etc.
In terms of the medications the main classes I will speak about are diuretics, ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin 2 receptor antagonists, calcium channel blockers
Blood pressure is calculated as flow (that is the volume of fluid in your vessels) times resistance. So higher flow or higher resistance leads to a higher blood pressure, as a result, most blood pressure medications work to lower either flow or resistance and thus lower blood pressure.
DIruretics increase salt and water excretion, so lower the fluid volume in the body.
ACE inhibitors interfere with the renin-angiotensin, aldosterone system. they stop the formation of angiotensin 2 which is a vasoconstrictor. not only that but without angiotensin 2 there is less aldosterone which normally helps to retain sodium and water, so ACE inhibitors lower resistance and flow
Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers, these work in a similar fashion to ACE I but rather than stop the formation of angiotensin 2, they block the receptors for angiotensin 2.
Calcium channel blockers block channels in the smooth muscles of your blood vessels, calcium normally causes these vessels to contract, so if they are blocked, the vessels will relax and have lower resistance
Treatment:
Step 1
less than 55 give ACEi (or ARB if can tolerate ACE),
over 55 or if black give CCB (or Diuretic if can't tolerate)
Step 2
CCB + ACEi/ ARB (never use ACEi and ARB together )
Step 3
ACEi/ ARBS + CCB + diuretic
Sources:
Passmedicine
Oxford handbook of clinical medicine
FOLLOW ME
Twitter and Instagram: Medic_Ene
MedicEne provides a fun and different view of medical problems among other things, hope you enjoy it!
The information provided on this video is for informational purposes only and is not professional medical advice, diagnosis, treatment or care, nor is it intended to be a substitute therefor. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider properly licensed to practice medicine or general health care in your jurisdiction concerning any questions you may have regarding any information obtained from this video and any medical condition you believe may be relevant to you or to someone else. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have seen in this video. Always consult with your physician or other qualified health care provider before embarking on a new treatment, diet or fitness program. Information obtained in this video is not exhaustive and does not cover all diseases, ailments, physical conditions or their treatment.
In this week's video, I will be going over hypertension (high blood pressure), I will be talking about how to define hypertension, how hypertension is diagnosed, the causes of hypertension, the symptoms of hypertension and what are the certain treatment options for hypertension.
Hypertension (AKA High blood pressure) is quite literally what it says on the tin, it's having the pressure in your blood vessels be too high.
The normal range of blood pressure is 90-119 for systolic and 60-69 for diastolic.
Hypertension can be divided into two groups, the majority of people fall into the first category, which is known as primary hypertension, this type doesn't have a cure and is a result of age and lifestyle choices.
Most symptoms of hypertension do not manifest until, the pressure is very high, causing it to be known as the silent killer.
When assessing a patient with newly diagnosed hypertension, you need to check that there is no damage to the organs mentioned above, 3 investigations that need to be done are funduscopic to check for any retinopathy, Urine dipstick to check for renal disease, ECG to check for left ventricular hypertrophy and Ischemic heart disease. HbA1c to check for diabetes as that is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease and check lipids for similar reasons.
The first type of treatment of hypertension is lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, exercising, eating less salt, stopping smoking etc.
In terms of the medications the main classes I will speak about are diuretics, ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin 2 receptor antagonists, calcium channel blockers
Blood pressure is calculated as flow (that is the volume of fluid in your vessels) times resistance. So higher flow or higher resistance leads to a higher blood pressure, as a result, most blood pressure medications work to lower either flow or resistance and thus lower blood pressure.
DIruretics increase salt and water excretion, so lower the fluid volume in the body.
ACE inhibitors interfere with the renin-angiotensin, aldosterone system. they stop the formation of angiotensin 2 which is a vasoconstrictor. not only that but without angiotensin 2 there is less aldosterone which normally helps to retain sodium and water, so ACE inhibitors lower resistance and flow
Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers, these work in a similar fashion to ACE I but rather than stop the formation of angiotensin 2, they block the receptors for angiotensin 2.
Calcium channel blockers block channels in the smooth muscles of your blood vessels, calcium normally causes these vessels to contract, so if they are blocked, the vessels will relax and have lower resistance
Treatment:
Step 1
less than 55 give ACEi (or ARB if can tolerate ACE),
over 55 or if black give CCB (or Diuretic if can't tolerate)
Step 2
CCB + ACEi/ ARB (never use ACEi and ARB together )
Step 3
ACEi/ ARBS + CCB + diuretic
Sources:
Passmedicine
Oxford handbook of clinical medicine
FOLLOW ME
Twitter and Instagram: Medic_Ene
MedicEne provides a fun and different view of medical problems among other things, hope you enjoy it!
The information provided on this video is for informational purposes only and is not professional medical advice, diagnosis, treatment or care, nor is it intended to be a substitute therefor. Always seek the advice of a physician or other qualified health provider properly licensed to practice medicine or general health care in your jurisdiction concerning any questions you may have regarding any information obtained from this video and any medical condition you believe may be relevant to you or to someone else. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have seen in this video. Always consult with your physician or other qualified health care provider before embarking on a new treatment, diet or fitness program. Information obtained in this video is not exhaustive and does not cover all diseases, ailments, physical conditions or their treatment.
Комментарии
 0:06:17
0:06:17
 0:03:35
0:03:35
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:01:17
0:01:17
 0:04:48
0:04:48
 0:41:56
0:41:56
 0:19:02
0:19:02
 0:16:31
0:16:31
 0:11:25
0:11:25
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:01:50
0:01:50
 0:06:45
0:06:45
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:01:09
0:01:09
 0:01:46
0:01:46
 0:01:52
0:01:52
 0:28:31
0:28:31
 0:09:48
0:09:48
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:07:09
0:07:09
 0:03:53
0:03:53