filmov
tv
Find AE | Intersecting Secant Theorem | Double Angle Identities

Показать описание
In the figure below, BC is the diameter of a semicircle centered at O, which intersects AB and
AC at D and E respectively. Suppose that AD = 9, DB = 4, and ∠ACD = ∠DOB. Find the
length of AE.
In the problem, we are going to use the following theorems/math concepts
Exterior Angle Theorem
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles.
Thales Theorem,
In geometry, Thales's theorem states that if A, B, and C are distinct points on a circle where the line AC is a diameter, the angle ABC is a right angle. Thales's theorem is a special case of the inscribed angle theorem and is mentioned and proved as part of the 31st proposition in the third book of Euclid's Elements.[1] It is generally attributed to Thales of Miletus, but it is sometimes attributed to Pythagoras.
Double Angle Identities for Tangent
The trigonometric double angle formulas give a relationship between the basic trigonometric functions applied to twice an angle in terms of trigonometric functions of the angle itself.
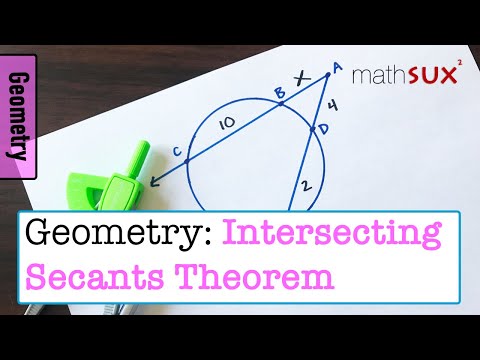
Intersecting Secants Theorem a.k.a Secant Secant Theorem
The intersecting secants theorem or just secant theorem describes the relation of line segments created by two intersecting secants and the associated circle.
For two lines AD and BC that intersect each other in P and some circle in A and D and B and C, respectively, the following equation holds:
(PA)(PD)=(PB)(PC).
Please watch the video until the end so you can learn more on how to solve problems like this.
Learn math with me.
Cheers!!
AC at D and E respectively. Suppose that AD = 9, DB = 4, and ∠ACD = ∠DOB. Find the
length of AE.
In the problem, we are going to use the following theorems/math concepts
Exterior Angle Theorem
The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles.
Thales Theorem,
In geometry, Thales's theorem states that if A, B, and C are distinct points on a circle where the line AC is a diameter, the angle ABC is a right angle. Thales's theorem is a special case of the inscribed angle theorem and is mentioned and proved as part of the 31st proposition in the third book of Euclid's Elements.[1] It is generally attributed to Thales of Miletus, but it is sometimes attributed to Pythagoras.
Double Angle Identities for Tangent
The trigonometric double angle formulas give a relationship between the basic trigonometric functions applied to twice an angle in terms of trigonometric functions of the angle itself.
Intersecting Secants Theorem a.k.a Secant Secant Theorem
The intersecting secants theorem or just secant theorem describes the relation of line segments created by two intersecting secants and the associated circle.
For two lines AD and BC that intersect each other in P and some circle in A and D and B and C, respectively, the following equation holds:
(PA)(PD)=(PB)(PC).
Please watch the video until the end so you can learn more on how to solve problems like this.
Learn math with me.
Cheers!!
Комментарии
 0:10:52
0:10:52
 0:04:29
0:04:29
 0:23:01
0:23:01
 0:03:54
0:03:54
 0:03:43
0:03:43
 0:04:47
0:04:47
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:32:31
0:32:31
 0:13:49
0:13:49
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:18:44
0:18:44
 0:04:27
0:04:27
 0:12:18
0:12:18
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:06:03
0:06:03
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:05:56
0:05:56
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:14:22
0:14:22
 0:30:40
0:30:40
 0:19:16
0:19:16
 0:04:31
0:04:31
 0:08:33
0:08:33
 0:27:54
0:27:54