filmov
tv
How to use ROM as Programmable Logic Device | ROM as PLD

Показать описание
In this video, how ROM (Read Only Memory) can be used as a Programmable Logic Device is explained through various examples.
Here is the list of topics covered in the video:
0:00 What is Programmable Logic Device
3:24 PROM as Programmable Logic Device
6:10 Example 1 (Full Adder and Subtractor)
9:12 Example 2 (Binary to Gray Code Converter)
12:36 Example 3
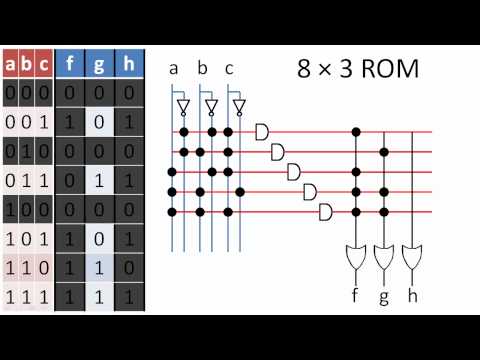
Read Only Memory is typically used for storing the permanent data and instructions in the various applications. But apart from that, it can also be used as a Programmable Logic Device (PLD).
In this video, through various examples the same has been in explained.
First how, Full-adder and Full-subtractor can be implemented using 8 x 4 PROM is shown. Then in the second example, how Binary to Gray Code Converter can be implemented in 8 x 4 PROM is explained. And then through a third example, how to implement a combinational circuit which generates a square of 3-bit binary number using PROM is explained.
The link of the other useful related videos:
1) Half-Adder and Full-Adder:
2) Half-Subtractor and Full-Subtractor:
3) Binary to Gray Code and Gray Code to Binary Conversion:
4) RAM (Random Access Memory) Explained:
5) ROM (Read Only Memory) Explained:
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding how the ROM can be used as Programmable Logic Device.
#allaboutelectronics
#digitalelectronics
#rom
#programmablelogicdevice
#pld
Support the channel through membership program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Follow my second channel:
Follow me on Facebook:
Follow me on Instagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Here is the list of topics covered in the video:
0:00 What is Programmable Logic Device
3:24 PROM as Programmable Logic Device
6:10 Example 1 (Full Adder and Subtractor)
9:12 Example 2 (Binary to Gray Code Converter)
12:36 Example 3
Read Only Memory is typically used for storing the permanent data and instructions in the various applications. But apart from that, it can also be used as a Programmable Logic Device (PLD).
In this video, through various examples the same has been in explained.
First how, Full-adder and Full-subtractor can be implemented using 8 x 4 PROM is shown. Then in the second example, how Binary to Gray Code Converter can be implemented in 8 x 4 PROM is explained. And then through a third example, how to implement a combinational circuit which generates a square of 3-bit binary number using PROM is explained.
The link of the other useful related videos:
1) Half-Adder and Full-Adder:
2) Half-Subtractor and Full-Subtractor:
3) Binary to Gray Code and Gray Code to Binary Conversion:
4) RAM (Random Access Memory) Explained:
5) ROM (Read Only Memory) Explained:
This video will be helpful to all the students of science and engineering in understanding how the ROM can be used as Programmable Logic Device.
#allaboutelectronics
#digitalelectronics
#rom
#programmablelogicdevice
#pld
Support the channel through membership program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Follow my second channel:
Follow me on Facebook:
Follow me on Instagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Комментарии
 0:16:16
0:16:16
 0:18:03
0:18:03
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:06:40
0:06:40
 0:07:00
0:07:00
 0:28:00
0:28:00
 0:03:31
0:03:31
 0:05:13
0:05:13
 0:17:32
0:17:32
 0:05:05
0:05:05
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:03:33
0:03:33
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:05:55
0:05:55
 0:11:18
0:11:18
 0:10:03
0:10:03
 0:14:52
0:14:52
 0:00:20
0:00:20
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:11:53
0:11:53
 0:04:21
0:04:21
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:01:08
0:01:08