filmov
tv
19.7 Electrolytic Cells | General Chemistry

Показать описание
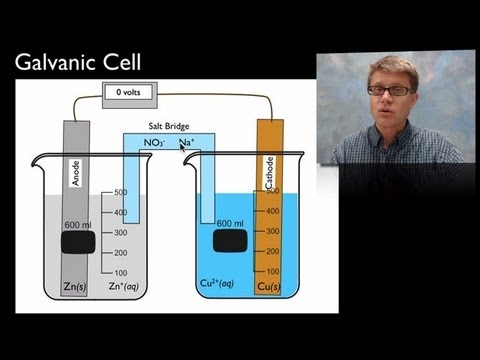
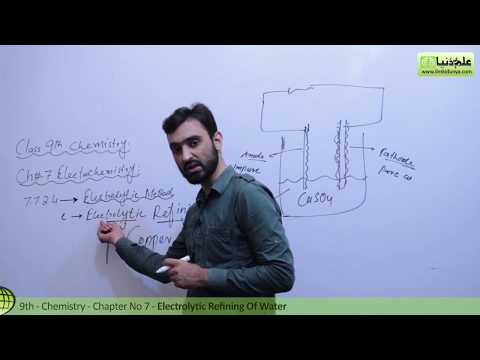
Chad provides a brief lesson on electrolytic cells highlighting the differences between molten and aqueous electrolysis. Molten electrolysis generally occurs at high temperatures, high enough to melt the salt of interest. But aqueous electrolysis can occur at room temperature as the salt is simply dissolved in water rather than melted. For molten electrolysis predicting the products is straightforward as the cation will be reduced at the cathode, and the anion will be oxidized at the anode both resulting in the production of an element in its elemental form. However, it is a little more challenging to predict the products with aqueous electrolysis as water can also get oxidized and reduced. This complicates the prediction as you generally are only going to have one reduction half reaction occurring at the cathode; either the cation is reduced or water is reduced, whichever is easier (whichever has a higher reduction potential). Generally only one oxidation half reaction will occur at the anode; either the anion is oxidized or water is oxidized, whichever is easier (whichever has a higher oxidation potential).
00:00 Lesson Introduction
00:23 Molten Electrolysis vs Aqueous Electrolysis
01:33 How to Predict the Products of Molten Electrolysis
04:14 How to Predict the Products of Aqueous Electrolysis
00:00 Lesson Introduction
00:23 Molten Electrolysis vs Aqueous Electrolysis
01:33 How to Predict the Products of Molten Electrolysis
04:14 How to Predict the Products of Aqueous Electrolysis
Комментарии
 0:05:11
0:05:11
 0:27:42
0:27:42
 0:07:39
0:07:39
 0:00:54
0:00:54
 0:12:26
0:12:26
 0:25:19
0:25:19
 0:28:40
0:28:40
 1:59:00
1:59:00
 0:28:04
0:28:04
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:19:33
0:19:33
 0:07:01
0:07:01
 0:09:12
0:09:12
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:01:28
0:01:28
 0:08:44
0:08:44
 0:06:37
0:06:37
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:16:28
0:16:28
 0:36:10
0:36:10
 0:01:00
0:01:00
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:56:44
0:56:44