filmov
tv
Intrusion Prevention System✔️

Показать описание
Intrusion sensors are systems that detect activity that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information resources, processing, or systems. Intrusions can come in many forms. The security analyst investigates various alerts from intrusion sensors and security appliances to determine if an alert is indicating malicious activity, a false positive, or to recommend where tuning of the intrusion sensor may be required.
To detect intrusions, various technologies have been developed. The first technology that was developed, IDS, had sensing capabilities but little capability to take action upon what it detected. An IPS builds upon previous IDS technology. An IPS has the ability to analyze traffic from the data link layer to the application layer. For example, an IPS can:
Analyze the traffic that controls Layer 2 to Layer 3 mappings, such as ARP and DHCP.
Verify that the rules of networking protocols such as IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP are followed.
Analyze the payload of application traffic to identify things such as network attacks, the presence of malware, and server misconfigurations.
IPS can identify, stop, and block attacks that would normally pass through a traditional firewall device. When traffic comes in through an interface on an IPS, if that traffic matches an IPS signature/rule, then that traffic can be dropped by the IPS. The essential difference between an IDS and an IPS is that an IPS can respond immediately, and prevent possible malicious traffic from passing. An IDS simply produces alerts when suspicious traffic is seen. An IDS is not responsible for mitigating the threat.
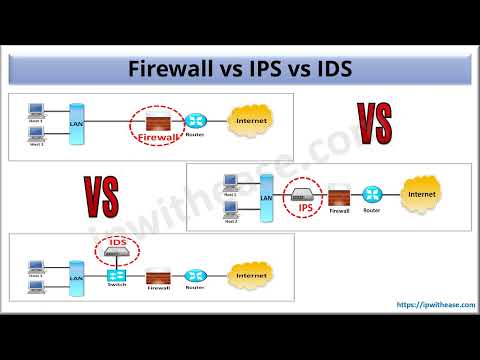
The figure above shows a common IPS deployment, in which the Cisco adaptive security appliance (Cisco ASA) controls access between the corporate network and the Internet, based on source and destination IP addresses and ports, while the IPS controls access based on packet payload. An IPS also has other valuable capabilities, such as providing deeper insight into what is actually happening on your network.
IPS technology is deployed in a sensor, which is variously described as one of the following:
An appliance that is specifically designed to provide dedicated IPS services
A module that is installed in another network device, such as an adaptive security appliance, a switch, or a router
Intrusion detection technology uses different strategies to detect and mitigate against attacks:
Anomaly detection: This type of technology generally learns patterns of normal network activity and, over time, produces a baseline profile for a given network. Sensors detect suspicious activity by evaluating patterns of activity that deviate from this baseline.
Rule-based detection: Attackers use various techniques to invade and compromise systems. Many techniques are directed at known weaknesses in operating systems, applications, or protocols. Various remote surveillance techniques are also frequently used. Some surveillance and attack methods have known patterns by which the method can be identified. Malicious activity detectors typically analyze live network traffic using a database of IPS rules (or also called IPS signatures) to determine whether suspicious activity is occurring.
Reputation-based: IPS security appliances can also make informed decisions on whether to permit or block the traffic based on reputations. Reputation-based filtering allows the IPS to block all traffic from known bad sources before any significant inspection is done.
#genesis #lab #blockchain #crypto #ai #machine #learning #genesislab #genesit #defi #nft #dapps #wallets #explorer #mainnet #zero #knowledge #zkrollups
To detect intrusions, various technologies have been developed. The first technology that was developed, IDS, had sensing capabilities but little capability to take action upon what it detected. An IPS builds upon previous IDS technology. An IPS has the ability to analyze traffic from the data link layer to the application layer. For example, an IPS can:
Analyze the traffic that controls Layer 2 to Layer 3 mappings, such as ARP and DHCP.
Verify that the rules of networking protocols such as IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP are followed.
Analyze the payload of application traffic to identify things such as network attacks, the presence of malware, and server misconfigurations.
IPS can identify, stop, and block attacks that would normally pass through a traditional firewall device. When traffic comes in through an interface on an IPS, if that traffic matches an IPS signature/rule, then that traffic can be dropped by the IPS. The essential difference between an IDS and an IPS is that an IPS can respond immediately, and prevent possible malicious traffic from passing. An IDS simply produces alerts when suspicious traffic is seen. An IDS is not responsible for mitigating the threat.
The figure above shows a common IPS deployment, in which the Cisco adaptive security appliance (Cisco ASA) controls access between the corporate network and the Internet, based on source and destination IP addresses and ports, while the IPS controls access based on packet payload. An IPS also has other valuable capabilities, such as providing deeper insight into what is actually happening on your network.
IPS technology is deployed in a sensor, which is variously described as one of the following:
An appliance that is specifically designed to provide dedicated IPS services
A module that is installed in another network device, such as an adaptive security appliance, a switch, or a router
Intrusion detection technology uses different strategies to detect and mitigate against attacks:
Anomaly detection: This type of technology generally learns patterns of normal network activity and, over time, produces a baseline profile for a given network. Sensors detect suspicious activity by evaluating patterns of activity that deviate from this baseline.
Rule-based detection: Attackers use various techniques to invade and compromise systems. Many techniques are directed at known weaknesses in operating systems, applications, or protocols. Various remote surveillance techniques are also frequently used. Some surveillance and attack methods have known patterns by which the method can be identified. Malicious activity detectors typically analyze live network traffic using a database of IPS rules (or also called IPS signatures) to determine whether suspicious activity is occurring.
Reputation-based: IPS security appliances can also make informed decisions on whether to permit or block the traffic based on reputations. Reputation-based filtering allows the IPS to block all traffic from known bad sources before any significant inspection is done.
#genesis #lab #blockchain #crypto #ai #machine #learning #genesislab #genesit #defi #nft #dapps #wallets #explorer #mainnet #zero #knowledge #zkrollups
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:06:31
0:06:31
 0:05:39
0:05:39
 0:06:02
0:06:02
 0:05:14
0:05:14
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:10:50
0:10:50
 0:10:27
0:10:27
 0:00:59
0:00:59
 0:07:58
0:07:58
 0:06:16
0:06:16
 0:09:13
0:09:13
 0:18:20
0:18:20
 0:03:19
0:03:19
 0:08:57
0:08:57
 0:11:23
0:11:23
 0:04:23
0:04:23
 0:14:08
0:14:08
 0:19:52
0:19:52
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:58:10
0:58:10
 0:17:53
0:17:53
 1:11:20
1:11:20
 0:02:51
0:02:51