filmov
tv
Resolver theory of operation. Advantages vs Encoders, good shielding, and arc seconds of resolution.

Показать описание
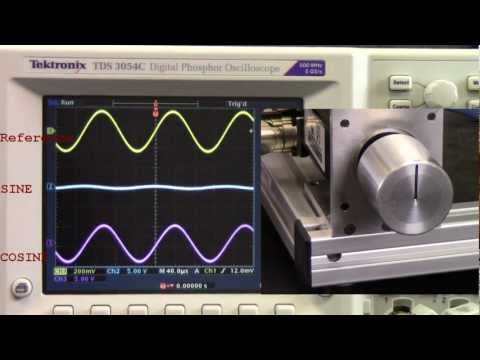
Basic theory of operation with pointers to finding the mathematics of demodulating the SIN an COS signals developed through property of mutual inductance when rotor turns excitation coil 360 Deg. with respect to stator coils for SIN COS modulated excitation. How to confirm resolver can take 4Vrms, what is +/- a decibel of flat gain or transformer for kHz excitation, and how to stay above +/-250mVp-p with 2:1 or 1:2 turns ratio using AGC (Automatic Gain Control).
The resolver is one of the most rugged feedback devices possible. It is popular in the aerospace and defense industry as it is made of passive components, can operate above 155 Deg C, has over 100 years of MTBF, and high resolution +/- few arc seconds sufficient for many applications.
Advantages include absolute position for one resolver cycle (typically one cycle/motor rev but more with multi speed), no Halls required for commutation, and easily over 100 yards of cable distance is possible without count drift. Motor companies know how to wind so making a resolver is cheap or they buy a low cost high resolution Tamagawa and mount it. The Copley Xenus Plus, Accelnt Plus, and Argus have -R resolver option and can do 2^16 bits of resolution with fair ENOB (effective number of bits). Copley also offers a CRS (Copley Serial Resolver) chip that converts resolver to digital clock and data. More to come on this in the Copley CSR video but for now know that even with a -R drive CME can still select most all feedback types: Incremental with Halls, Absolute Biss-C, etc. and even the new CSR with FW 4.60 or greater.
Good resolver cabling, grounding, and shielding is investigated to improve signal to noise ratio for highest possible count resolution. How to troubleshoot a feedback fault with resolver with an ohms meter, monitoring voltage stator SIN and COS from excitation by rotating the rotor, and how not to blow up my drive.
The resolver is one of the most rugged feedback devices possible. It is popular in the aerospace and defense industry as it is made of passive components, can operate above 155 Deg C, has over 100 years of MTBF, and high resolution +/- few arc seconds sufficient for many applications.
Advantages include absolute position for one resolver cycle (typically one cycle/motor rev but more with multi speed), no Halls required for commutation, and easily over 100 yards of cable distance is possible without count drift. Motor companies know how to wind so making a resolver is cheap or they buy a low cost high resolution Tamagawa and mount it. The Copley Xenus Plus, Accelnt Plus, and Argus have -R resolver option and can do 2^16 bits of resolution with fair ENOB (effective number of bits). Copley also offers a CRS (Copley Serial Resolver) chip that converts resolver to digital clock and data. More to come on this in the Copley CSR video but for now know that even with a -R drive CME can still select most all feedback types: Incremental with Halls, Absolute Biss-C, etc. and even the new CSR with FW 4.60 or greater.
Good resolver cabling, grounding, and shielding is investigated to improve signal to noise ratio for highest possible count resolution. How to troubleshoot a feedback fault with resolver with an ohms meter, monitoring voltage stator SIN and COS from excitation by rotating the rotor, and how not to blow up my drive.
Комментарии
 0:12:03
0:12:03
 0:04:28
0:04:28
 0:04:43
0:04:43
 0:02:06
0:02:06
 0:02:56
0:02:56
 0:00:36
0:00:36
 0:01:16
0:01:16
 0:06:26
0:06:26
 0:53:52
0:53:52
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:10:16
0:10:16
 0:00:10
0:00:10
 0:02:45
0:02:45
 0:13:04
0:13:04
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:02:30
0:02:30
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:09:58
0:09:58
 0:01:27
0:01:27
 0:18:36
0:18:36
 0:05:47
0:05:47
 0:10:08
0:10:08