filmov
tv
Optical Aberration And Parabola

Показать описание
Light reflectors, search lights, solar cooker and these radio antennas have one thing in common. All are shaped like a paraboloid. This shape enables collection or projection of rays at a particular point. Why parabolic shape and not spherical ? Let us find out.
We will create a spherical and parabolic profile from this acrylic mirror strip and understand it better.
We will build a concave mirror profile with focal length of 5 cm. Let us draw an arc with the help of a ruler. Mirror is fixed in place with the help of pins.
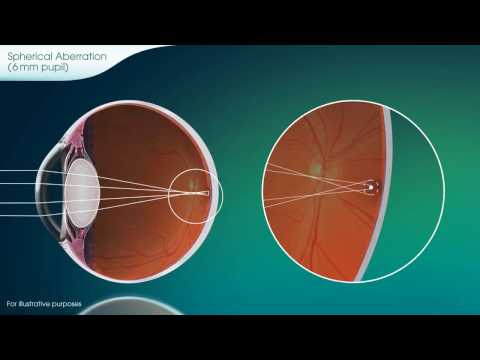
All Spherical mirrors have an aberration. Let us understand it first.
As per the law, when an incident ray parallel to the principal axis strikes the mirror, it should pass through the focal point after reflection. Rays that strike the outer edges of the mirror fail to focus in the same precise location as light rays that strike the inner portions of the mirror.
Spherical aberration is most commonly corrected by use of a mirror with a different shape. Usually, a parabolic mirror is substituted for a spherical mirror.
We will use the focus directrix method to draw a parabola. Mirror strip is fixed with the help of pins.
When incident rays parallel to the principal axis strike the mirror,all rays pass through the focal point after reflection.
If you don't have an acrylic mirror strip, you can perform this activity with the help of small mirrors as well. We will attach small mirrors to the eraser. Let us place these erasers at various points along the tangent and find out the ray path taken by reflected ray.
Similar behaviour is observed in case of spherical and parabolic profile as seen earlier.
You can also use graph paper to plot a parabola and repeat the same activity.
Try with concave profiles of different focal lengths. You can use incident light of different colors to understand the behaviour better.
Do convex mirrors also have this defect ? Do find out !
Thank You.
We will create a spherical and parabolic profile from this acrylic mirror strip and understand it better.
We will build a concave mirror profile with focal length of 5 cm. Let us draw an arc with the help of a ruler. Mirror is fixed in place with the help of pins.
All Spherical mirrors have an aberration. Let us understand it first.
As per the law, when an incident ray parallel to the principal axis strikes the mirror, it should pass through the focal point after reflection. Rays that strike the outer edges of the mirror fail to focus in the same precise location as light rays that strike the inner portions of the mirror.
Spherical aberration is most commonly corrected by use of a mirror with a different shape. Usually, a parabolic mirror is substituted for a spherical mirror.
We will use the focus directrix method to draw a parabola. Mirror strip is fixed with the help of pins.
When incident rays parallel to the principal axis strike the mirror,all rays pass through the focal point after reflection.
If you don't have an acrylic mirror strip, you can perform this activity with the help of small mirrors as well. We will attach small mirrors to the eraser. Let us place these erasers at various points along the tangent and find out the ray path taken by reflected ray.
Similar behaviour is observed in case of spherical and parabolic profile as seen earlier.
You can also use graph paper to plot a parabola and repeat the same activity.
Try with concave profiles of different focal lengths. You can use incident light of different colors to understand the behaviour better.
Do convex mirrors also have this defect ? Do find out !
Thank You.
Комментарии
 0:06:20
0:06:20
 0:05:31
0:05:31
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:03:05
0:03:05
 0:14:01
0:14:01
 0:23:08
0:23:08
 0:19:28
0:19:28
 0:01:57
0:01:57
 0:04:39
0:04:39
 0:44:38
0:44:38
 0:03:56
0:03:56
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:10:02
0:10:02
 0:18:44
0:18:44
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 0:00:50
0:00:50
 0:13:53
0:13:53
 0:04:19
0:04:19
 0:07:51
0:07:51
 0:18:26
0:18:26
 0:01:47
0:01:47
 1:13:22
1:13:22
 0:25:40
0:25:40
 0:06:04
0:06:04