filmov
tv
Pile Foundation in detail | Deep Foundation | Bridge Engineering | Pile foundation and its types

Показать описание
Dear Viewers,
In this video, I have explained in detail about Pile Foundation.
Foundation is the lowest part of the building or the civil structure, that is in direct contact with the soil which transfers loads from structure to the soil safely.
Generally, Foundation can be classified into
1. Shallow Foundation
2. Deep Foundation
When the depth of foundation is less than or equal to the width of foundation, it is called Shallow Foundation.
When the depth of foundation is greater than the width of foundation, it is called Deep Foundation.
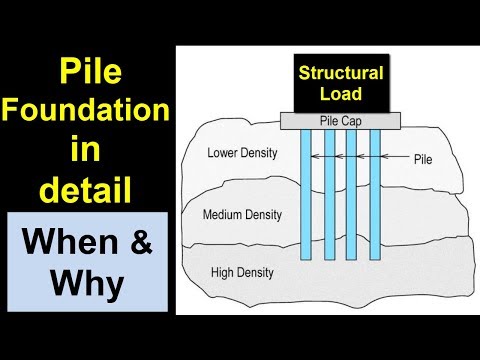
What Is Pile Foundation?
A Pile Foundation is one type of slender structural member made of steel, concrete, wood, or composite material. A Piles may be cast-in-situ excavating a hole and filling it with concrete or precast concrete member which is driven into the soil.
The most common forms of deep foundations are :
Pile foundations
Cassions or Aell foundations
Cofferdams
Why Pile Foundations are used?
The load of the superstructure is heavy and its distribution is uneven
The topsoil has poor bearing capacity.
The subsoil water is high so that .pumping of water from the open trenches for the shallow foundations is difficult and uneconomical.
There are large fluctuations in the subsoil water level.
Where timbering to the trenches is difficult and costly.
The structure is situated on the seashore or river bed, where there is a danger of scouring action of water.
Canal or deep drainage lines exit near the foundation.
The topsoil is of expansive nature.
Piles are used for the foundation of transmission towers, an off-shore platform that is subjected to uplift forces.
Piles are of following types based on its use:
1. End bearing piles
2. Friction piles
3. Compaction piles
4. Tension piles
5. Anchor piles
6. Fender piles
7. Batter piles
8. Sheet piles
End bearing piles
End bearing piles penetrate through the soft soil andtransfer its load to a hard and relatively incompressible stratum like rock or dense sand.
These piles virtually act as columns.
The soft soil surrounding the pile provides some lateral support.
These piles derive its bearing capacity from end bearing at the pile tip.
Friction pile:
The pile which does not rest on hard stratum but derives its load carrying capacity from the adhesion or friction/resistance between the pile surface and the neighbouring soil is known as Friction Pile.
Compaction Pile:
The compaction piles are used to compact loose granular soil, thereby increasing their bearing capacity.
Thesetypes of pilesdo not carry any load themselves.
Sand piles can be used as compaction piles
Tension Pile:
Tension piles are anchored down the structures subjected to uplift due to hydrostatic pressure or due to overturning.
It is also called uplift pile.
Anchor Pile:
Anchor piles provide anchorage against the horizontal force from sheet piling or other pulling forces.
Depending upon the function or usage, piles are classified as following:
1. Steel piles
2. Timber piles
3. Composite piles
4. Sand piles
5. Concrete piles
Load Bearing Piles
This type of pile foundation is mainly used to transfer the vertical loads from the structure to the soil. These foundations transmit loads through the soil with poor supporting property onto a layer which is capable of bearing the load. Depending on the mechanism of load transfer from pile to the soil, load-bearing piles can be further classified as flowed.
Classification of Piles Based on Materials and Construction Method
Primarily piles can be classified into two parts. Displacement piles and Non-displacement or Replacement piles. Piles which causes the soil to be displaced vertically and radially as they are driven to the ground is known as Displacement piles. In case of Replacement piles, the ground is bored and the soil is removed and then the resulting hole is either filled with concrete or a pre-cast concrete pile is inserted. On the basis of materials of pile construction and their installation process load-bearing piles can be classified as follows:
Timber Piles
Untreated
Treated with Preservative
Concrete Piles
Pre-cast Piles
Cast-in-place Piles
Steel Piles
I-Section Piles
Hollow Piles
Timber Piles
Timber piles are placed under the water level. They last for approximately about 30 years. They can be rectangular or circular in shape. Their diameter or size can vary from 12 to 16 inches. The length of the pile is usually 20 times of the top width.
They are usually designed for 15 to 20 tons. Additional strength can be obtained by bolting fish plates to the side of the piles.
Advantages of Timber Piles-
Timber piles of regular size are available.
Economical.
Easy to install.
Low possibility of damage.
Timber piles can be cut off at any desired length after they are installed.
If necessary, timber piles can be easily pulled out.
#pilefoundation
#deepfoundation
#foundation
In this video, I have explained in detail about Pile Foundation.
Foundation is the lowest part of the building or the civil structure, that is in direct contact with the soil which transfers loads from structure to the soil safely.
Generally, Foundation can be classified into
1. Shallow Foundation
2. Deep Foundation
When the depth of foundation is less than or equal to the width of foundation, it is called Shallow Foundation.
When the depth of foundation is greater than the width of foundation, it is called Deep Foundation.
What Is Pile Foundation?
A Pile Foundation is one type of slender structural member made of steel, concrete, wood, or composite material. A Piles may be cast-in-situ excavating a hole and filling it with concrete or precast concrete member which is driven into the soil.
The most common forms of deep foundations are :
Pile foundations
Cassions or Aell foundations
Cofferdams
Why Pile Foundations are used?
The load of the superstructure is heavy and its distribution is uneven
The topsoil has poor bearing capacity.
The subsoil water is high so that .pumping of water from the open trenches for the shallow foundations is difficult and uneconomical.
There are large fluctuations in the subsoil water level.
Where timbering to the trenches is difficult and costly.
The structure is situated on the seashore or river bed, where there is a danger of scouring action of water.
Canal or deep drainage lines exit near the foundation.
The topsoil is of expansive nature.
Piles are used for the foundation of transmission towers, an off-shore platform that is subjected to uplift forces.
Piles are of following types based on its use:
1. End bearing piles
2. Friction piles
3. Compaction piles
4. Tension piles
5. Anchor piles
6. Fender piles
7. Batter piles
8. Sheet piles
End bearing piles
End bearing piles penetrate through the soft soil andtransfer its load to a hard and relatively incompressible stratum like rock or dense sand.
These piles virtually act as columns.
The soft soil surrounding the pile provides some lateral support.
These piles derive its bearing capacity from end bearing at the pile tip.
Friction pile:
The pile which does not rest on hard stratum but derives its load carrying capacity from the adhesion or friction/resistance between the pile surface and the neighbouring soil is known as Friction Pile.
Compaction Pile:
The compaction piles are used to compact loose granular soil, thereby increasing their bearing capacity.
Thesetypes of pilesdo not carry any load themselves.
Sand piles can be used as compaction piles
Tension Pile:
Tension piles are anchored down the structures subjected to uplift due to hydrostatic pressure or due to overturning.
It is also called uplift pile.
Anchor Pile:
Anchor piles provide anchorage against the horizontal force from sheet piling or other pulling forces.
Depending upon the function or usage, piles are classified as following:
1. Steel piles
2. Timber piles
3. Composite piles
4. Sand piles
5. Concrete piles
Load Bearing Piles
This type of pile foundation is mainly used to transfer the vertical loads from the structure to the soil. These foundations transmit loads through the soil with poor supporting property onto a layer which is capable of bearing the load. Depending on the mechanism of load transfer from pile to the soil, load-bearing piles can be further classified as flowed.
Classification of Piles Based on Materials and Construction Method
Primarily piles can be classified into two parts. Displacement piles and Non-displacement or Replacement piles. Piles which causes the soil to be displaced vertically and radially as they are driven to the ground is known as Displacement piles. In case of Replacement piles, the ground is bored and the soil is removed and then the resulting hole is either filled with concrete or a pre-cast concrete pile is inserted. On the basis of materials of pile construction and their installation process load-bearing piles can be classified as follows:
Timber Piles
Untreated
Treated with Preservative
Concrete Piles
Pre-cast Piles
Cast-in-place Piles
Steel Piles
I-Section Piles
Hollow Piles
Timber Piles
Timber piles are placed under the water level. They last for approximately about 30 years. They can be rectangular or circular in shape. Their diameter or size can vary from 12 to 16 inches. The length of the pile is usually 20 times of the top width.
They are usually designed for 15 to 20 tons. Additional strength can be obtained by bolting fish plates to the side of the piles.
Advantages of Timber Piles-
Timber piles of regular size are available.
Economical.
Easy to install.
Low possibility of damage.
Timber piles can be cut off at any desired length after they are installed.
If necessary, timber piles can be easily pulled out.
#pilefoundation
#deepfoundation
#foundation
Комментарии
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 0:20:52
0:20:52
 0:09:36
0:09:36
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:13:12
0:13:12
 0:16:42
0:16:42
 0:12:58
0:12:58
 0:03:41
0:03:41
 0:04:51
0:04:51
 0:00:22
0:00:22
 0:00:13
0:00:13
 0:00:30
0:00:30
 0:00:16
0:00:16
 0:00:05
0:00:05
 0:13:00
0:13:00
 0:13:23
0:13:23
 0:05:40
0:05:40
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:00:18
0:00:18
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:00:25
0:00:25
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:10
0:00:10