filmov
tv
Ever Wondered What Causes Tooth Cavities? Unlock the Mystery

Показать описание
Dental cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are primarily caused by a combination of factors related to the bacteria in the mouth, the type of food consumed, and poor oral hygiene practices. Here are the main reasons for dental cavities:
#toothdecay
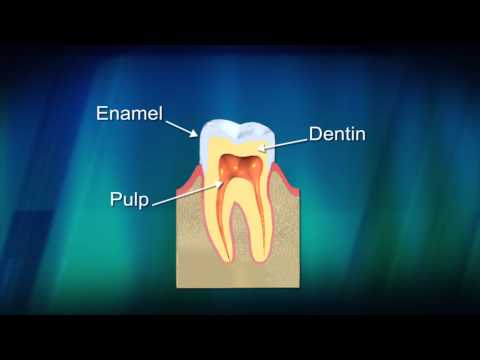
Bacteria: Our mouths are home to numerous types of bacteria, including Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. These bacteria form a sticky film called dental plaque, which adheres to the teeth and feeds on sugars from the foods we eat. As bacteria break down these sugars, they produce acids that attack the tooth enamel, leading to decay.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow dental plaque to build up on the teeth. When plaque is not regularly removed through proper oral hygiene practices, the bacteria can thrive, leading to an increased risk of cavities.
Sugar and Carbohydrate Consumption: Foods and beverages that are high in sugars and carbohydrates provide an ample food source for the bacteria in the mouth. Frequent consumption of sugary snacks, sodas, candies, and even starchy foods like bread and chips can contribute to the development of cavities.
Acidic Foods and Drinks: Acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, fruit juices, carbonated drinks, and vinegar-based dressings, can erode tooth enamel, making the teeth more susceptible to decay.
Dry Mouth: Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids and helping to remineralize teeth. When the mouth is dry (a condition known as xerostomia), there is reduced saliva flow, which can increase the risk of tooth decay.
Tooth Anatomy: Certain tooth structures, such as deep pits and fissures, can be more prone to plaque accumulation and are harder to clean effectively. These areas provide a conducive environment for cavities to develop.
Lack of Fluoride: Fluoride is a mineral that helps strengthen tooth enamel and makes it more resistant to acid attacks. Insufficient fluoride exposure, whether through drinking water, toothpaste, or professional treatments, can increase the likelihood of developing cavities.
It's important to note that individual factors, such as genetics, age, overall oral health, and lifestyle choices, can also influence cavity formation. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive sugary and acidic foods are essential for preventing dental cavities.
#toothdecay
Bacteria: Our mouths are home to numerous types of bacteria, including Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. These bacteria form a sticky film called dental plaque, which adheres to the teeth and feeds on sugars from the foods we eat. As bacteria break down these sugars, they produce acids that attack the tooth enamel, leading to decay.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow dental plaque to build up on the teeth. When plaque is not regularly removed through proper oral hygiene practices, the bacteria can thrive, leading to an increased risk of cavities.
Sugar and Carbohydrate Consumption: Foods and beverages that are high in sugars and carbohydrates provide an ample food source for the bacteria in the mouth. Frequent consumption of sugary snacks, sodas, candies, and even starchy foods like bread and chips can contribute to the development of cavities.
Acidic Foods and Drinks: Acidic foods and beverages, such as citrus fruits, fruit juices, carbonated drinks, and vinegar-based dressings, can erode tooth enamel, making the teeth more susceptible to decay.
Dry Mouth: Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids and helping to remineralize teeth. When the mouth is dry (a condition known as xerostomia), there is reduced saliva flow, which can increase the risk of tooth decay.
Tooth Anatomy: Certain tooth structures, such as deep pits and fissures, can be more prone to plaque accumulation and are harder to clean effectively. These areas provide a conducive environment for cavities to develop.
Lack of Fluoride: Fluoride is a mineral that helps strengthen tooth enamel and makes it more resistant to acid attacks. Insufficient fluoride exposure, whether through drinking water, toothpaste, or professional treatments, can increase the likelihood of developing cavities.
It's important to note that individual factors, such as genetics, age, overall oral health, and lifestyle choices, can also influence cavity formation. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive sugary and acidic foods are essential for preventing dental cavities.
Комментарии
 0:01:17
0:01:17
 0:01:01
0:01:01
 0:01:38
0:01:38
 0:02:41
0:02:41
 0:03:14
0:03:14
 0:26:47
0:26:47
 0:00:31
0:00:31
 0:05:33
0:05:33
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:08:00
0:08:00
 0:05:54
0:05:54
 0:03:30
0:03:30
 0:02:20
0:02:20
 0:03:02
0:03:02
 0:04:41
0:04:41
 0:01:04
0:01:04
 0:02:09
0:02:09
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:02:44
0:02:44
 0:07:16
0:07:16
 0:03:36
0:03:36
 0:01:10
0:01:10
 0:00:27
0:00:27
 0:11:01
0:11:01