filmov
tv
Enzymatic Regulation: Covalent (Post translational )modifications
Показать описание
Regulation
Enzymes can be either activated or inhibited by other molecules. For example, the end product(s) of a metabolic pathway are often inhibitors for one of the first enzymes of the pathway (usually the first irreversible step, called committed step), thus regulating the amount of end product made by the pathways. Such a regulatory mechanism is called a negative feedback mechanism, because the amount of the end product produced is regulated by its own concentration.[85]:141–48 Negative feedback mechanism can effectively adjust the rate of synthesis of intermediate metabolites according to the demands of the cells. This helps with effective allocations of materials and energy economy, and it prevents the excess manufacture of end products. Like other homeostatic devices, the control of enzymatic action helps to maintain a stable internal environment in living organisms.[85]:141
Post-translational modification
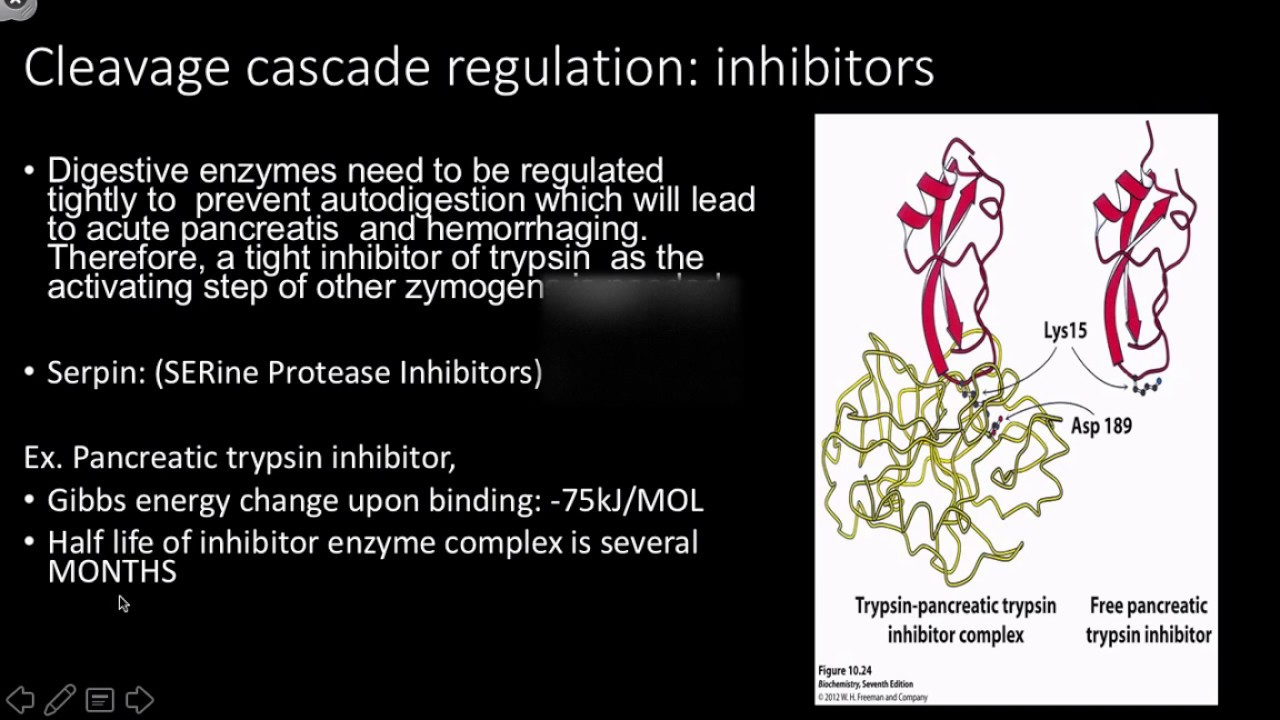
Examples of post-translational modification include phosphorylation, myristoylation and glycosylation.[85]:149–69 For example, in the response to insulin, the phosphorylation of multiple enzymes, including glycogen synthase, helps control the synthesis or degradation of glycogen and allows the cell to respond to changes in blood sugar.[86] Another example of post-translational modification is the cleavage of the polypeptide chain. Chymotrypsin, a digestive protease, is produced in inactive form as chymotrypsinogen in the pancreas and transported in this form to the stomach where it is activated. This stops the enzyme from digesting the pancreas or other tissues before it enters the gut. This type of inactive precursor to an enzyme is known as a zymogen[85]:149–53 or proenzyme.
Quantity
Enzyme production (transcription and translation of enzyme genes) can be enhanced or diminished by a cell in response to changes in the cell's environment. This form of gene regulation is called enzyme induction. For example, bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics such as penicillin because enzymes called beta-lactamases are induced that hydrolyse the crucial beta-lactam ring within the penicillin molecule.[87] Another example comes from enzymes in the liver called cytochrome P450 oxidases, which are important in drug metabolism. Induction or inhibition of these enzymes can cause drug interactions.[88] Enzyme levels can also be regulated by changing the rate of enzyme degradation.[1]:30.1.1 The opposite of enzyme induction is enzyme repression.
Subcellular distribution
Enzymes can be compartmentalized, with different metabolic pathways occurring in different cellular compartments. For example, fatty acids are synthesized by one set of enzymes in the cytosol, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi and used by a different set of enzymes as a source of energy in the mitochondrion, through β-oxidation.[89] In addition, trafficking of the enzyme to different compartments may change the degree of protonation (e.g., the neutral cytoplasm and the acidic lysosome) or oxidative state (e.g., oxidizing periplasm or reducing cytoplasm) which in turn affects enzyme activity.[90] In contrast to partitioning into membrane bound organelles, enzyme subcellular localisation may also be altered through polymerisation of enzymes into macromolecular cytoplasmic filaments.[91][92]
Organ specialization
In multicellular eukaryotes, cells in different organs and tissues have different patterns of gene expression and therefore have different sets of enzymes (known as isozymes) available for metabolic reactions. This provides a mechanism for regulating the overall metabolism of the organism. For example, hexokinase, the first enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, has a specialized form called glucokinase expressed in the liver and pancreas that has a lower affinity for glucose yet is more sensitive to glucose concentration.[93] This enzyme is involved in sensing blood sugar and regulating insulin production.[94]
Enzymes can be either activated or inhibited by other molecules. For example, the end product(s) of a metabolic pathway are often inhibitors for one of the first enzymes of the pathway (usually the first irreversible step, called committed step), thus regulating the amount of end product made by the pathways. Such a regulatory mechanism is called a negative feedback mechanism, because the amount of the end product produced is regulated by its own concentration.[85]:141–48 Negative feedback mechanism can effectively adjust the rate of synthesis of intermediate metabolites according to the demands of the cells. This helps with effective allocations of materials and energy economy, and it prevents the excess manufacture of end products. Like other homeostatic devices, the control of enzymatic action helps to maintain a stable internal environment in living organisms.[85]:141
Post-translational modification
Examples of post-translational modification include phosphorylation, myristoylation and glycosylation.[85]:149–69 For example, in the response to insulin, the phosphorylation of multiple enzymes, including glycogen synthase, helps control the synthesis or degradation of glycogen and allows the cell to respond to changes in blood sugar.[86] Another example of post-translational modification is the cleavage of the polypeptide chain. Chymotrypsin, a digestive protease, is produced in inactive form as chymotrypsinogen in the pancreas and transported in this form to the stomach where it is activated. This stops the enzyme from digesting the pancreas or other tissues before it enters the gut. This type of inactive precursor to an enzyme is known as a zymogen[85]:149–53 or proenzyme.
Quantity
Enzyme production (transcription and translation of enzyme genes) can be enhanced or diminished by a cell in response to changes in the cell's environment. This form of gene regulation is called enzyme induction. For example, bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics such as penicillin because enzymes called beta-lactamases are induced that hydrolyse the crucial beta-lactam ring within the penicillin molecule.[87] Another example comes from enzymes in the liver called cytochrome P450 oxidases, which are important in drug metabolism. Induction or inhibition of these enzymes can cause drug interactions.[88] Enzyme levels can also be regulated by changing the rate of enzyme degradation.[1]:30.1.1 The opposite of enzyme induction is enzyme repression.
Subcellular distribution
Enzymes can be compartmentalized, with different metabolic pathways occurring in different cellular compartments. For example, fatty acids are synthesized by one set of enzymes in the cytosol, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi and used by a different set of enzymes as a source of energy in the mitochondrion, through β-oxidation.[89] In addition, trafficking of the enzyme to different compartments may change the degree of protonation (e.g., the neutral cytoplasm and the acidic lysosome) or oxidative state (e.g., oxidizing periplasm or reducing cytoplasm) which in turn affects enzyme activity.[90] In contrast to partitioning into membrane bound organelles, enzyme subcellular localisation may also be altered through polymerisation of enzymes into macromolecular cytoplasmic filaments.[91][92]
Organ specialization
In multicellular eukaryotes, cells in different organs and tissues have different patterns of gene expression and therefore have different sets of enzymes (known as isozymes) available for metabolic reactions. This provides a mechanism for regulating the overall metabolism of the organism. For example, hexokinase, the first enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, has a specialized form called glucokinase expressed in the liver and pancreas that has a lower affinity for glucose yet is more sensitive to glucose concentration.[93] This enzyme is involved in sensing blood sugar and regulating insulin production.[94]
 0:06:25
0:06:25
 0:04:38
0:04:38
 0:02:43
0:02:43
 0:07:48
0:07:48
 0:11:44
0:11:44
 0:13:24
0:13:24
 0:14:21
0:14:21
 0:12:04
0:12:04
 0:18:19
0:18:19
 0:16:05
0:16:05
 0:07:18
0:07:18
 0:03:42
0:03:42
 0:05:23
0:05:23
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:04:56
0:04:56
 0:35:46
0:35:46
 0:00:43
0:00:43
 0:27:18
0:27:18
 0:32:43
0:32:43
 0:09:04
0:09:04
 0:23:23
0:23:23
 0:28:04
0:28:04
 0:09:05
0:09:05
 0:18:06
0:18:06