filmov
tv
10a - Voltage Division Rule
Показать описание
Voltage Divider Circuit Explained with Solved Examples
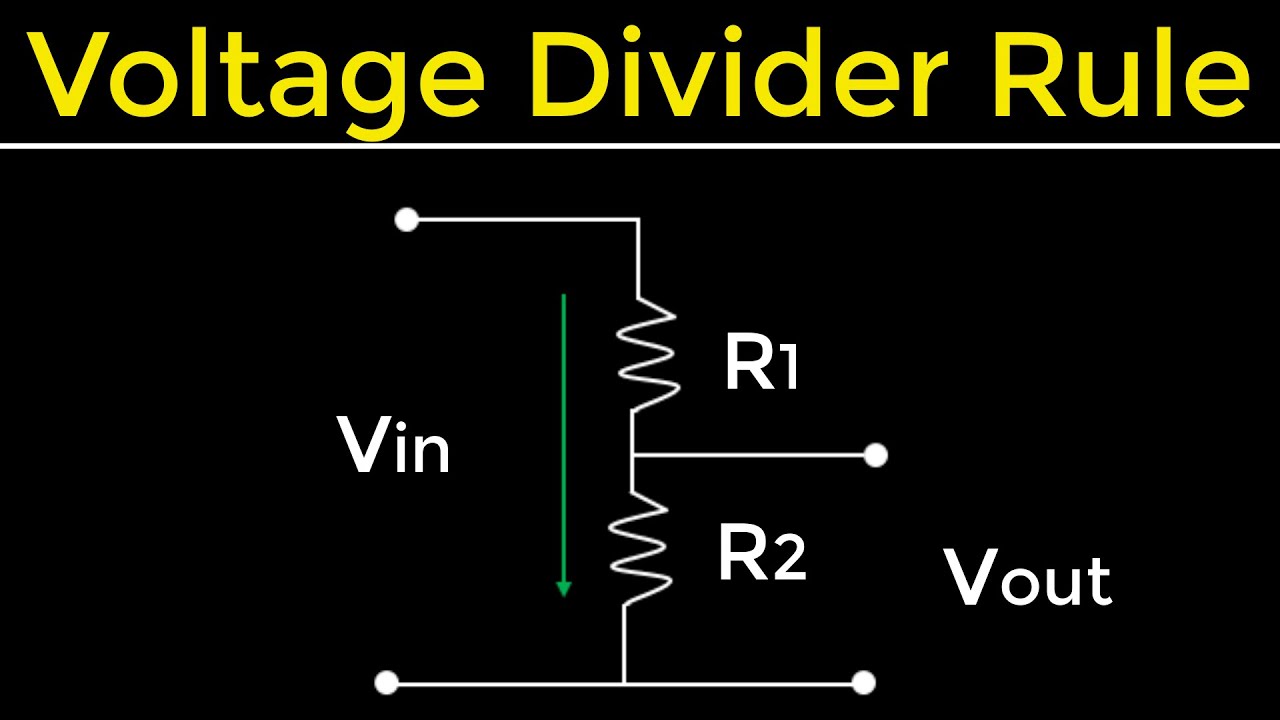
This video explains the concept of voltage division with solved examples. The voltage divider rule is applied to divide voltages between series resistors in direct proportion to their resistance.
Given two series resistors; R1 and R2 respectively, the voltage across R1; V1 = [R1/R1+R2]*V
And the voltage V2 across R2; V2 = [R2/R1+R2]*V;
For three resistors connected in series, the voltage drop across the respective resistors are
V1 = [R1/R1+R2+R3]*V
V2 = [R2/R1+R2+R3]*V
V3 = [R3/R1+R2+R3]*V
In this video, three examples were addressed.
This video explains the concept of voltage division with solved examples. The voltage divider rule is applied to divide voltages between series resistors in direct proportion to their resistance.
Given two series resistors; R1 and R2 respectively, the voltage across R1; V1 = [R1/R1+R2]*V
And the voltage V2 across R2; V2 = [R2/R1+R2]*V;
For three resistors connected in series, the voltage drop across the respective resistors are
V1 = [R1/R1+R2+R3]*V
V2 = [R2/R1+R2+R3]*V
V3 = [R3/R1+R2+R3]*V
In this video, three examples were addressed.
10a - Voltage Division Rule
VOLTAGE DIVISION RULE and CURRENT DIVISION RULE in JUST 7 Min
Voltage Dividers - Basic Electronics 10A
Voltage Divider Problems
☑️10 - Parallel Resistors and Current Division
Voltage Divider Rule (English)
Voltage Divider - A super useful and extremely simple circuit
Diodes (10a)
Intro to Circuits 22: Voltage Divider
Real Sources vs. Ideal | Voltage ⇄ Current Practical Source Transformation | Maximum Power Transfer...
10b - Total Resistance and Voltage Drop Principles
HP 6433B 0-36V 10A mains frequency switch mode supply 1966 test teardown
Ammeter circuit :Ayrton shunt
Series Circuit calculation- Electricity
Current Divider Rule in Sinhala
24v to 12v converter use a resiator|dc to dc 12v converter|24v to 12v easy converter|12v zener diode
elettrotecnica parte 23
Norton's Theorem Example | Electric Circuits | Network Analysis | Network Theory
Transformers Physics Problems - Voltage, Current & Power Calculations - Electromagnetic Inductio...
12 - Current Division 2 - More Examples on How to divide current in a parallel circuit
Parallel Resistive Circuits - Lecture 11B
Practice Problem 4.12 Fundamental of Electric Circuits (Sadiku) 5th Ed Norton + Independent Source
How to use a multimeter like a pro! The Ultimate guide
Power Supply
Комментарии
 0:09:21
0:09:21
 0:06:59
0:06:59
 0:17:59
0:17:59
 0:20:23
0:20:23
 0:25:12
0:25:12
 0:10:46
0:10:46
 0:02:47
0:02:47
 0:12:37
0:12:37
 0:06:54
0:06:54
 1:28:06
1:28:06
 0:18:01
0:18:01
 0:22:57
0:22:57
 0:05:24
0:05:24
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:17:23
0:17:23
 0:02:24
0:02:24
 0:14:41
0:14:41
 0:07:03
0:07:03
 0:17:11
0:17:11
 0:07:10
0:07:10
 0:11:19
0:11:19
 0:17:00
0:17:00
 0:28:43
0:28:43
 0:22:26
0:22:26