filmov
tv
Soil Sampling Techniques Using QGIS. 2 Convenience Sampling. Contaminated Soils.

Показать описание
To learn more about Geo RGB, visit us at:
Contact us at:
Soil Sampling Techniques Using QGIS. 2 Convenience Sampling. Contaminated Soils.
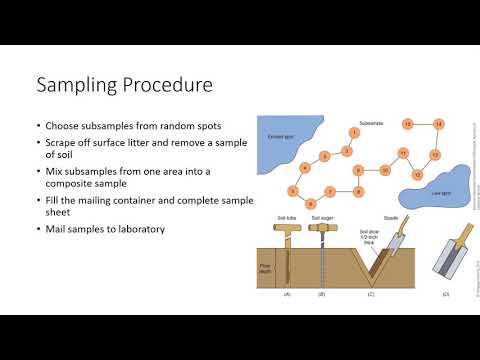
In this tutorial we are going to learn how we can use QGIS to create a sampling campaign for contaminated soils. We are going to see some of the algorithms that QGIS can offer us to simplify the mathematical part of the probabilistic sample techniques.
Probability samples: Probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a population using a method based on the theory of probability. In this case, each member of the population has equal chance of being selected. Examples, Random sampling, Systematic sampling, stratified sampling and cluster sampling.
Non-Probability Samples: non-probability sampling is defined as a technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a population using a method based on the subjective judgement. Members of the population are selected in non random way. Examples, convenience sampling, judgement sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling.
Contact us at:
Soil Sampling Techniques Using QGIS. 2 Convenience Sampling. Contaminated Soils.
In this tutorial we are going to learn how we can use QGIS to create a sampling campaign for contaminated soils. We are going to see some of the algorithms that QGIS can offer us to simplify the mathematical part of the probabilistic sample techniques.
Probability samples: Probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a population using a method based on the theory of probability. In this case, each member of the population has equal chance of being selected. Examples, Random sampling, Systematic sampling, stratified sampling and cluster sampling.
Non-Probability Samples: non-probability sampling is defined as a technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a population using a method based on the subjective judgement. Members of the population are selected in non random way. Examples, convenience sampling, judgement sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling.
 0:26:18
0:26:18
 1:03:19
1:03:19
 0:40:13
0:40:13
 0:07:13
0:07:13
 0:06:21
0:06:21
 0:15:37
0:15:37
 0:00:17
0:00:17
 0:02:04
0:02:04
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:09:40
0:09:40
 0:08:06
0:08:06
 0:09:28
0:09:28
 0:05:46
0:05:46
 0:09:40
0:09:40
 0:07:02
0:07:02
 0:16:21
0:16:21
 0:01:43
0:01:43
 0:00:29
0:00:29
 0:02:11
0:02:11
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:07:53
0:07:53
 0:10:24
0:10:24
 0:02:40
0:02:40