filmov
tv
Demineralisation process (Deionization/Ion-exchange process) - Water Technology
Показать описание
This video explains the demineralisation process in detail. ion-exchange process. Water softening/water purification method. Removal of ions/minerals from hard water. It describes the cation exchange resins and anion exchange resins. It describes the process of removing the cations and anions present in the water. it also explains the regeneration of cation and anion resins. It lists the advantages and disadvantages of demineralisation process or ion exchange process.
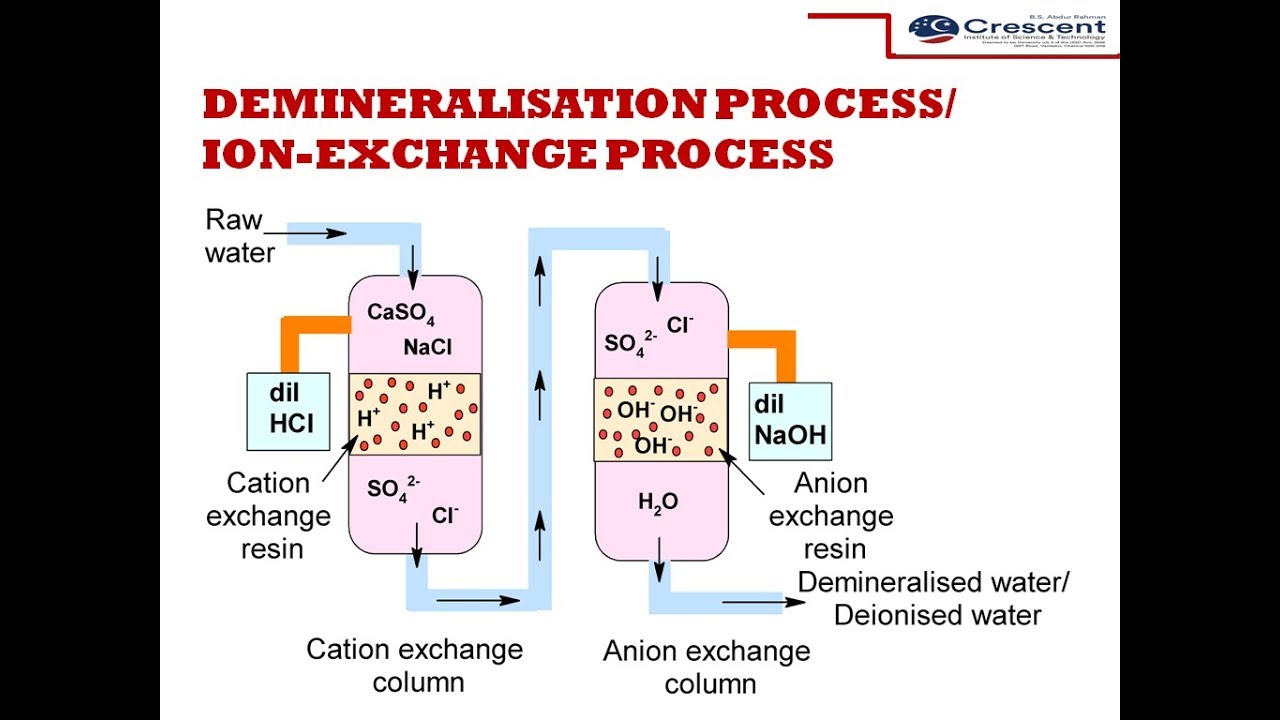
Demineralisation process/Ion-exchange process
You will be able to define ion-exchange resin.
You will be able to describe the demineralisation process/ion-exchange process with a neat diagram.
You will be able to mention the advantages and limitations of demineralisation process.
Ion-exchange resin
Ion-exchange resins are cross-linked, long chain organic polymers microporous in nature, carrying exchangeable ions.
Types of ion-exchange resin
Cation exchange resin carries acidic functional groups such as –COOH, –HSO3 which are capable of exchanging their H+ ions.
Anion exchange resin carries basic functional groups such as amines, quaternary ammonium, quaternary phosphonium which on treatment with dilute NaOH are capable of exchanging their OH - ions.
Demineralisation Process/
ION-EXCHANGE PROCESS
Cation exchange process
The H+ ions present in the cation-exchange resin get exchanged with the cations present in the raw water such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ etc.
The water coming out of this column is free from cations.
Anion exchange process
OH - ions present in the anion-exchange resin get exchanged with the anions present in the raw water such as Cl - , CO32-, HCO3-, SO42- etc.
The water coming out of this column is free from both cations and anions.
The H+ ions released in the cation exchange column and OH- released in the anion exchange column combines to form water
Regeneration if ion-exchange resins
When all the exchangeable H+ ions and OH- ions of the cation and anion exchange resins get exchanged with the cations and anions present in the water, the ion-exchange resins are said to be exhausted. Then they are regenerated using dilute HCl and dilute NaOH solutions.
Advantages of Demineralisation/Advantages of ion-exchange process
Can obtain demineralised water with hardness less than 2ppm.
This method can be used for both acidic and alkaline water.
Both cations and anions can be removed.
Limitations/Disadvantages of Demineralisation/Disadvantages of ion-exchange process
This method is expensive, as the ion-exchange resins and the installation costs are high.
The efficiency of the process is reduced, if the water is turbid.
This method is not suitable, if heavy metals are present, since regeneration of resin is not possible.
Demineralisation process/Ion-exchange process
You will be able to define ion-exchange resin.
You will be able to describe the demineralisation process/ion-exchange process with a neat diagram.
You will be able to mention the advantages and limitations of demineralisation process.
Ion-exchange resin
Ion-exchange resins are cross-linked, long chain organic polymers microporous in nature, carrying exchangeable ions.
Types of ion-exchange resin
Cation exchange resin carries acidic functional groups such as –COOH, –HSO3 which are capable of exchanging their H+ ions.
Anion exchange resin carries basic functional groups such as amines, quaternary ammonium, quaternary phosphonium which on treatment with dilute NaOH are capable of exchanging their OH - ions.
Demineralisation Process/
ION-EXCHANGE PROCESS
Cation exchange process
The H+ ions present in the cation-exchange resin get exchanged with the cations present in the raw water such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ etc.
The water coming out of this column is free from cations.
Anion exchange process
OH - ions present in the anion-exchange resin get exchanged with the anions present in the raw water such as Cl - , CO32-, HCO3-, SO42- etc.
The water coming out of this column is free from both cations and anions.
The H+ ions released in the cation exchange column and OH- released in the anion exchange column combines to form water
Regeneration if ion-exchange resins
When all the exchangeable H+ ions and OH- ions of the cation and anion exchange resins get exchanged with the cations and anions present in the water, the ion-exchange resins are said to be exhausted. Then they are regenerated using dilute HCl and dilute NaOH solutions.
Advantages of Demineralisation/Advantages of ion-exchange process
Can obtain demineralised water with hardness less than 2ppm.
This method can be used for both acidic and alkaline water.
Both cations and anions can be removed.
Limitations/Disadvantages of Demineralisation/Disadvantages of ion-exchange process
This method is expensive, as the ion-exchange resins and the installation costs are high.
The efficiency of the process is reduced, if the water is turbid.
This method is not suitable, if heavy metals are present, since regeneration of resin is not possible.
Комментарии
 0:06:07
0:06:07
 0:12:08
0:12:08
 0:02:22
0:02:22
 0:02:34
0:02:34
 0:15:01
0:15:01
 0:15:02
0:15:02
 0:04:54
0:04:54
 0:13:17
0:13:17
 0:14:45
0:14:45
 0:02:05
0:02:05
 0:14:04
0:14:04
 0:23:09
0:23:09
 0:16:03
0:16:03
 0:27:55
0:27:55
 0:13:28
0:13:28
 0:43:59
0:43:59
 0:07:37
0:07:37
 0:01:41
0:01:41
 0:08:30
0:08:30
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:11:46
0:11:46
 0:09:03
0:09:03
 0:01:21
0:01:21
 0:10:22
0:10:22