filmov
tv
Signed vs Unsigned Data Types in SQL What's the Difference?

Показать описание
In this video titled "Signed vs Unsigned Data Types in SQL: What's the Difference?", we'll explore the concepts of signed and unsigned data types in SQL, highlighting their significance and applications.
Here’s a breakdown of the key areas discussed in the video:
00:00 Introduction
00:26 Signed vs Unsigned Data Types
01:15 Why Use Signed and Unsigned Data Types?
03:33 Converting Between Signed and Unsigned Data Types
05:14 Benefits of Using Unsigned Data Types
06:06 Conclusion
What are signed data types?
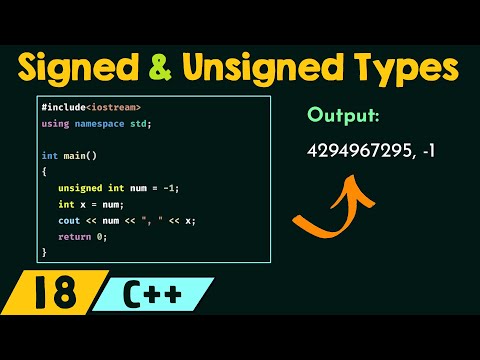
Signed data types can store both positive and negative values. For example, an INT data type in SQL can hold values ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. This is useful when the data being stored can naturally have negative values, such as in financial calculations or temperature readings.
What are unsigned data types?
Unsigned data types, on the other hand, can only store non-negative values, effectively doubling the upper limit of the data type's range. For instance, an UNSIGNED INT can hold values from 0 to 4,294,967,295. This is advantageous when you know that negative values will never be part of your data, such as in scenarios involving counts or ages.
When should you use signed vs. unsigned?
Choosing between signed and unsigned data types depends on the nature of the data you intend to store. If you need to accommodate negative values, opt for signed data types. If your data will always be positive, consider using unsigned data types to maximise the range of possible values.
🔑 Key Features:
✅ Diverse Training Options – Online, Instructor-led, Onsite
✅ Device Compatibility – Access your course on all devices
✅ Interactive Learning Tools - Observe the trainer's screen, utilise virtual whiteboard, and share documents
✅ Best Industry Prize – Obtain your certification at competitive rates
✅ High-Quality Resources - Access detailed resources such as eBooks, Blogs, and more
✅ Worldwide Professional Recognition – Our courses are accredited by globally recognised bodies
About The Knowledge Academy:
Global Reach: Join over 2 million successful delegates with The Knowledge Academy
High Success Rate: Accomplish your goals with our 98% pass rate
Industry Accredited: Learn with confidence, accredited by PeopleCert, PMI
Worldwide Centers: Access top-tier learning in 195 countries
Excellence Acknowledged: Recognised by The Times and PWC for our commitment
Wide Partnerships: Benefit from our extensive network of 3000+ organisations
Flexible Learning: Explore diverse training methods tailored to your needs
Join us for expert-led courses tailored to your needs, wherever you are. Let's unlock your potential together! 🎓🌍
🔵 For more information about The Knowledge Academy courses, visit:
#SignedVsUnsigned #DataTypesInSQL #SQLTutorial #TheKnowledgeAcademy #DatabaseManagement #SQLTraining #LearnSQL #DataTypeDifferences
Here’s a breakdown of the key areas discussed in the video:
00:00 Introduction
00:26 Signed vs Unsigned Data Types
01:15 Why Use Signed and Unsigned Data Types?
03:33 Converting Between Signed and Unsigned Data Types
05:14 Benefits of Using Unsigned Data Types
06:06 Conclusion
What are signed data types?
Signed data types can store both positive and negative values. For example, an INT data type in SQL can hold values ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. This is useful when the data being stored can naturally have negative values, such as in financial calculations or temperature readings.
What are unsigned data types?
Unsigned data types, on the other hand, can only store non-negative values, effectively doubling the upper limit of the data type's range. For instance, an UNSIGNED INT can hold values from 0 to 4,294,967,295. This is advantageous when you know that negative values will never be part of your data, such as in scenarios involving counts or ages.
When should you use signed vs. unsigned?
Choosing between signed and unsigned data types depends on the nature of the data you intend to store. If you need to accommodate negative values, opt for signed data types. If your data will always be positive, consider using unsigned data types to maximise the range of possible values.
🔑 Key Features:
✅ Diverse Training Options – Online, Instructor-led, Onsite
✅ Device Compatibility – Access your course on all devices
✅ Interactive Learning Tools - Observe the trainer's screen, utilise virtual whiteboard, and share documents
✅ Best Industry Prize – Obtain your certification at competitive rates
✅ High-Quality Resources - Access detailed resources such as eBooks, Blogs, and more
✅ Worldwide Professional Recognition – Our courses are accredited by globally recognised bodies
About The Knowledge Academy:
Global Reach: Join over 2 million successful delegates with The Knowledge Academy
High Success Rate: Accomplish your goals with our 98% pass rate
Industry Accredited: Learn with confidence, accredited by PeopleCert, PMI
Worldwide Centers: Access top-tier learning in 195 countries
Excellence Acknowledged: Recognised by The Times and PWC for our commitment
Wide Partnerships: Benefit from our extensive network of 3000+ organisations
Flexible Learning: Explore diverse training methods tailored to your needs
Join us for expert-led courses tailored to your needs, wherever you are. Let's unlock your potential together! 🎓🌍
🔵 For more information about The Knowledge Academy courses, visit:
#SignedVsUnsigned #DataTypesInSQL #SQLTutorial #TheKnowledgeAcademy #DatabaseManagement #SQLTraining #LearnSQL #DataTypeDifferences
 0:06:52
0:06:52
 0:14:46
0:14:46
 0:03:20
0:03:20
 0:11:37
0:11:37
 0:08:40
0:08:40
 0:07:12
0:07:12
 0:11:07
0:11:07
 0:06:51
0:06:51
 1:01:30
1:01:30
 0:11:07
0:11:07
 0:04:33
0:04:33
 0:02:26
0:02:26
 0:02:27
0:02:27
 0:00:23
0:00:23
 0:11:08
0:11:08
 0:06:05
0:06:05
 0:10:15
0:10:15
 0:10:11
0:10:11
 0:03:51
0:03:51
 0:21:48
0:21:48
 0:09:19
0:09:19
 0:08:25
0:08:25
 0:00:32
0:00:32
 0:07:07
0:07:07