filmov
tv
What is Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning Tutorial [Updated 2024]-igmGuru

Показать описание
The terms Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings, especially in the context of data science:
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Definition: AI refers to the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way that we would consider “smart”. It's a general field that encompasses everything from good old-fashioned AI (GOFAI) all the way to futuristic technologies such as deep learning. AI aims to create machines that can solve problems and achieve goals like humans do.
Application in Data Science: In data science, AI might involve automated decision-making, natural language processing, robotics, and more. The goal is to enable computers to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, understanding language, or making predictions.
Machine Learning (ML):
Definition: Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on a narrow range of activities. It's essentially about teaching a machine how to learn and make decisions based on data. ML algorithms use statistical techniques to enable computers to 'learn' from and make predictions or decisions based on data.
Application in Data Science: ML is at the heart of many data science activities. It's used for predictive modeling, data mining, and complex data analysis. For instance, it can be used for customer segmentation, forecasting stock market trends, or identifying patterns in customer behavior.
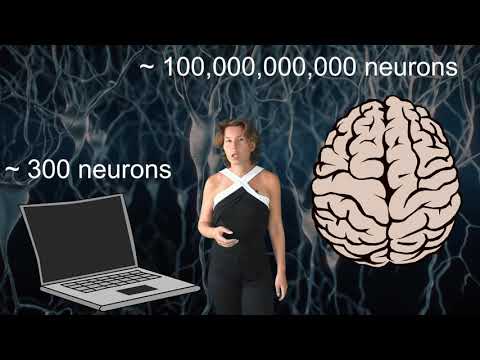
Deep Learning (DL):
Definition: Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, which in turn is a subset of AI. Deep Learning involves neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”). These neural networks attempt to simulate human decision-making processes using data and neural networks to train models.
Application in Data Science: Deep Learning is particularly powerful for data science tasks that involve large amounts of unstructured data. It's used in image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing (NLP). For example, DL techniques are behind the advancements in voice-activated assistants and self-driving cars.
To summarize:
AI is the broadest concept, aimed at creating smart machines.
ML is a practical application of AI that involves teaching machines to learn from data.
Deep Learning is a specific ML technique that uses sophisticated neural networks to handle especially complex tasks.
In data science, these technologies are used to analyze and interpret complex data, automate analytical model building, and enable machines to learn from experiences without being explicitly programmed for each task.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Definition: AI refers to the broader concept of machines being able to carry out tasks in a way that we would consider “smart”. It's a general field that encompasses everything from good old-fashioned AI (GOFAI) all the way to futuristic technologies such as deep learning. AI aims to create machines that can solve problems and achieve goals like humans do.
Application in Data Science: In data science, AI might involve automated decision-making, natural language processing, robotics, and more. The goal is to enable computers to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, understanding language, or making predictions.
Machine Learning (ML):
Definition: Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on a narrow range of activities. It's essentially about teaching a machine how to learn and make decisions based on data. ML algorithms use statistical techniques to enable computers to 'learn' from and make predictions or decisions based on data.
Application in Data Science: ML is at the heart of many data science activities. It's used for predictive modeling, data mining, and complex data analysis. For instance, it can be used for customer segmentation, forecasting stock market trends, or identifying patterns in customer behavior.
Deep Learning (DL):
Definition: Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, which in turn is a subset of AI. Deep Learning involves neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”). These neural networks attempt to simulate human decision-making processes using data and neural networks to train models.
Application in Data Science: Deep Learning is particularly powerful for data science tasks that involve large amounts of unstructured data. It's used in image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing (NLP). For example, DL techniques are behind the advancements in voice-activated assistants and self-driving cars.
To summarize:
AI is the broadest concept, aimed at creating smart machines.
ML is a practical application of AI that involves teaching machines to learn from data.
Deep Learning is a specific ML technique that uses sophisticated neural networks to handle especially complex tasks.
In data science, these technologies are used to analyze and interpret complex data, automate analytical model building, and enable machines to learn from experiences without being explicitly programmed for each task.
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:04:07
0:04:07
 0:05:52
0:05:52
 0:06:47
0:06:47
 0:05:42
0:05:42
 0:05:59
0:05:59
 0:06:15
0:06:15
 0:04:37
0:04:37
 0:19:34
0:19:34
 0:04:45
0:04:45
 0:00:19
0:00:19
 0:00:14
0:00:14
 0:03:45
0:03:45
 0:05:35
0:05:35
 0:05:28
0:05:28
 0:08:04
0:08:04
 0:04:55
0:04:55
 0:11:27
0:11:27
 0:07:50
0:07:50
 0:08:05
0:08:05
 0:12:47
0:12:47
 0:07:01
0:07:01
 0:12:06
0:12:06
 0:42:26
0:42:26