filmov
tv
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram of B2 and C2 Molecule

Показать описание
The molecular orbital theory (MO theory) explains chemical bonding and accounts for the oxygen molecule's paramagnetism. It also explains the bonding in a variety of other molecules, such as octet rule violations and more intricate bonding molecules (which are outside the scope of this work) that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures. Additionally, it provides a model for describing the energies of electrons in a molecule and the probable location of these electrons. Unlike valence bond theory, which uses hybrid orbitals that are assigned to one specific atom, MO theory uses the combination of atomic orbitals to yield molecular orbitals that are delocalized over the entire molecule rather than being localised on its constituent. MO theory also helps us understand why some substances are electrical conductors, others are semiconductors, and still others are insulators. The main points of the two complementary bonding theories. Both theories provide different, useful ways of describing molecular structure.
 0:21:36
0:21:36
 0:11:05
0:11:05
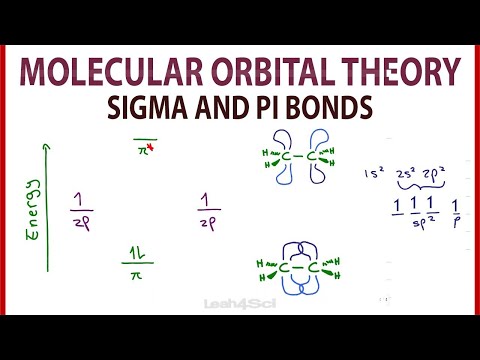 0:13:19
0:13:19
 0:07:54
0:07:54
 0:04:01
0:04:01
 0:04:11
0:04:11
 0:02:03
0:02:03
 0:04:10
0:04:10
 0:04:40
0:04:40
 0:04:15
0:04:15
 0:45:53
0:45:53
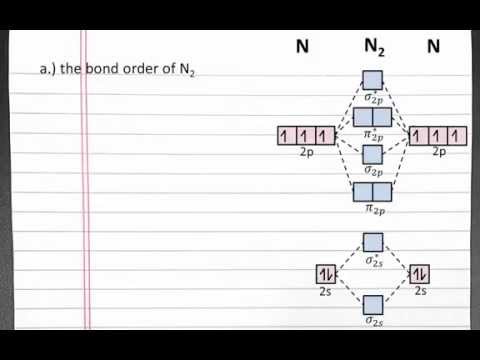 0:05:51
0:05:51
 0:04:17
0:04:17
 0:00:26
0:00:26
 0:07:28
0:07:28
 0:04:30
0:04:30
 0:00:15
0:00:15
 0:00:56
0:00:56
 0:05:03
0:05:03
 0:12:11
0:12:11
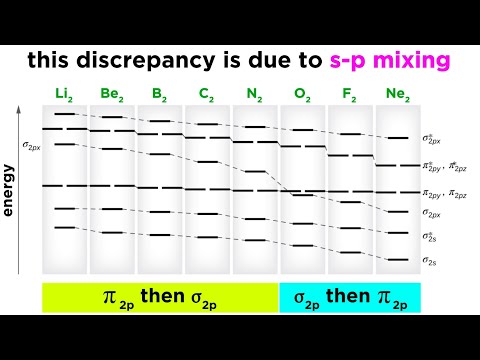 0:09:49
0:09:49
 1:05:37
1:05:37
 0:00:53
0:00:53
 0:00:59
0:00:59